The Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is an essential concept in the field of chemistry that revolutionized our understanding of acid-base reactions. Developed by Danish chemist Johannes Nicolaus Bronsted and English chemist Thomas Martin Lowry in the early 20th century, this theory introduced a new perspective on how acids and bases interact.
In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory and explore 18 fascinating facts that will deepen your appreciation for this fundamental concept. From understanding the role of protons to exploring conjugate acid-base pairs, we will uncover the intricacies of this groundbreaking theory and its implications in various chemical reactions.
So, prepare to be intrigued and captivated as we unravel the mysteries of the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory, shedding light on its significance in the realm of chemistry.
Key Takeaways:
- The Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors, revolutionizing our understanding of chemical reactions beyond just water solutions.
- Understanding this theory helps explain everyday phenomena like the sourness of citrus fruits and the soothing effects of antacids, making chemistry more relatable and fascinating.
Acids and bases according to the Bronsted-Lowry Theory
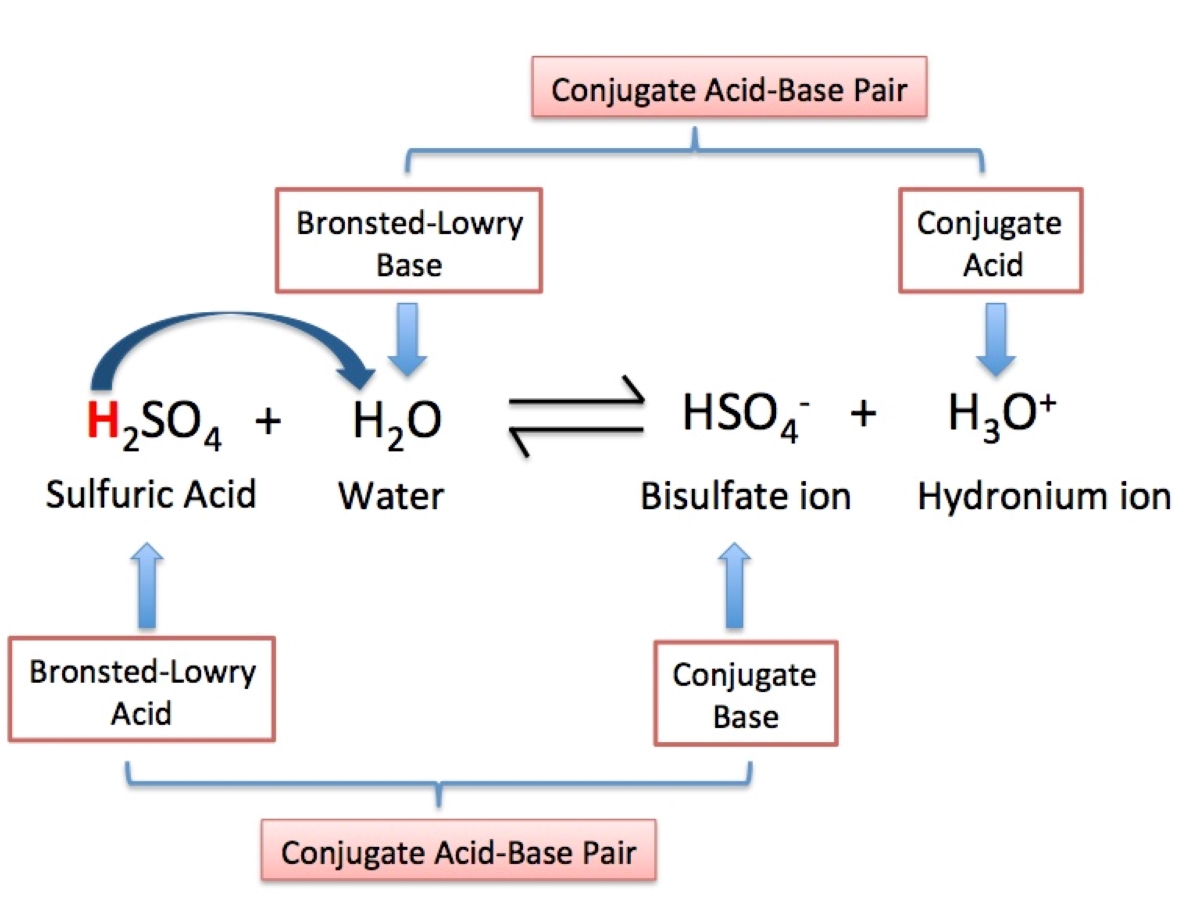
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory defines acids as substances that donate protons (H+) and bases as substances that accept protons.
Proton transfer as the central concept
The theory emphasizes the transfer of protons as the key process in acid-base reactions, highlighting the role of proton donors and acceptors.
Acid-base equilibrium
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory explains acid-base equilibrium as the interplay between the forward and reverse reactions of proton transfer.
Broader definition of acids and bases
Unlike the earlier Arrhenius Theory, which limited acids to substances that release H+ ions in water, the Bronsted-Lowry Theory expands the scope to include reactions in non-aqueous solvents.
Amphoteric substances
According to the Bronsted-Lowry Theory, amphoteric substances can act as both acids and bases, depending on the context.
Conjugate acid-base pairs
The theory introduces the concept of conjugate acid-base pairs, where an acid and its corresponding base differ by the presence or absence of a proton.
Acid and base strength
In the Bronsted-Lowry Theory, acid strength is determined by the tendency to donate protons, while base strength is defined by the ability to accept protons.
Acid dissociation constant (Ka)
Ka measures the extent of acid dissociation in a solution and is a quantitative representation of acid strength in the Bronsted-Lowry Theory.
pH scale
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory provides the foundation for the pH scale, which quantifies the acidity or basicity of a solution based on the concentration of H+ ions.
Lewis Acid-Base Theory connection
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory forms the basis for the Lewis Acid-Base Theory, which includes electron-pair acceptance and donation as a broader definition of acids and bases.
Acid-base titrations
Titrations, a common laboratory technique, rely on the principles of the Bronsted-Lowry Theory to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base solution.
Common acid-base indicators
Many common indicators, such as litmus paper and phenolphthalein, are used to visually detect acid-base reactions based on the color changes predicted by the Bronsted-Lowry Theory.
Acidic and basic buffers
The concept of acid-base buffers is essential in maintaining a stable pH. According to the Bronsted-Lowry Theory, buffers consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
Acid rain formation
Understanding the Bronsted-Lowry Theory helps explain the formation of acid rain, which occurs when pollutants, such as sulfur and nitrogen compounds, react with water to produce acidic solutions.
Biological applications
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory is crucial in understanding many biological processes, such as enzyme catalysis, DNA replication, and protein folding, which heavily rely on acid-base reactions.
Acid-base reactions in daily life
The Bronsted-Lowry Theory helps elucidate various everyday phenomena, including the sourness of citrus fruits (acidic properties) and the soothing effects of antacids (basic properties).
Acid-base reactions in industries
Multiple industries, such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and chemical manufacturing, utilize the principles of the Bronsted-Lowry Theory for various applications, such as drug design, soil pH regulation, and synthesis of organic compounds.
Further advancements in acid-base theories
Although the Bronsted-Lowry Theory is a significant milestone, subsequent theories, such as the solvent system theory and the hard-soft acid-base theory, have further expanded our understanding of acid-base interactions.
The Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory remains a cornerstone in the field of chemistry, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding how acids and bases behave and interact. Its implications can be seen in a wide range of applications, from predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions to explaining biological processes. By grasping the fundamental concepts of this theory, chemists can unlock the mysteries of acid-base chemistry and pave the way for further advancements in the field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that has revolutionized our understanding of acids and bases. It provides a comprehensive framework for explaining the behavior of these substances in chemical reactions. From the concept of proton transfer to the definition of conjugate acid-base pairs, the Bronsted-Lowry theory offers a deeper insight into the underlying principles of acid-base chemistry.By recognizing that acids donate protons and bases accept protons, this theory allows chemists to accurately predict the behavior of various substances in solution. Understanding the Bronsted-Lowry theory opens up a whole new world of possibilities in chemical synthesis, environmental science, drug development, and many other fields.By exploring the enigmatic facts about the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory, we have gained a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of acid-base chemistry. From the role of water as a solvent to the link between pH and pKa values, these facts highlight the wide-ranging implications of this theory in our daily lives.In summary, the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is a cornerstone of chemistry that continues to shape our understanding of the world around us. Its impact extends far beyond the confines of the laboratory, making it a crucial concept for students and professionals alike.
FAQs
Q: What is the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory?
A: The Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is a concept in chemistry that defines acids as substances that donate protons and bases as substances that accept protons.
Q: How is the Bronsted-Lowry theory different from the Arrhenius theory?
A: Unlike the Arrhenius theory, which defines acids as substances that produce H+ ions in aqueous solutions, the Bronsted-Lowry theory is more general as it can explain acid-base reactions in non-aqueous solvents.
Q: What is a conjugate acid-base pair?
A: A conjugate acid-base pair consists of two substances that are related to each other by the transfer of a proton. The acid donates a proton, becoming a conjugate base, while the base accepts the proton, becoming a conjugate acid.
Q: What is the significance of the pH scale in the Bronsted-Lowry theory?
A: The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is directly related to the concentration of H+ ions in the solution and can be used to determine the strength of an acid or a base.
Q: How is the Bronsted-Lowry theory relevant in everyday life?
A: The concepts of acids and bases, as defined by the Bronsted-Lowry theory, are applicable in various aspects of daily life, such as understanding the properties of household cleaning products, managing pH levels in swimming pools, and the functioning of the digestive system.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
