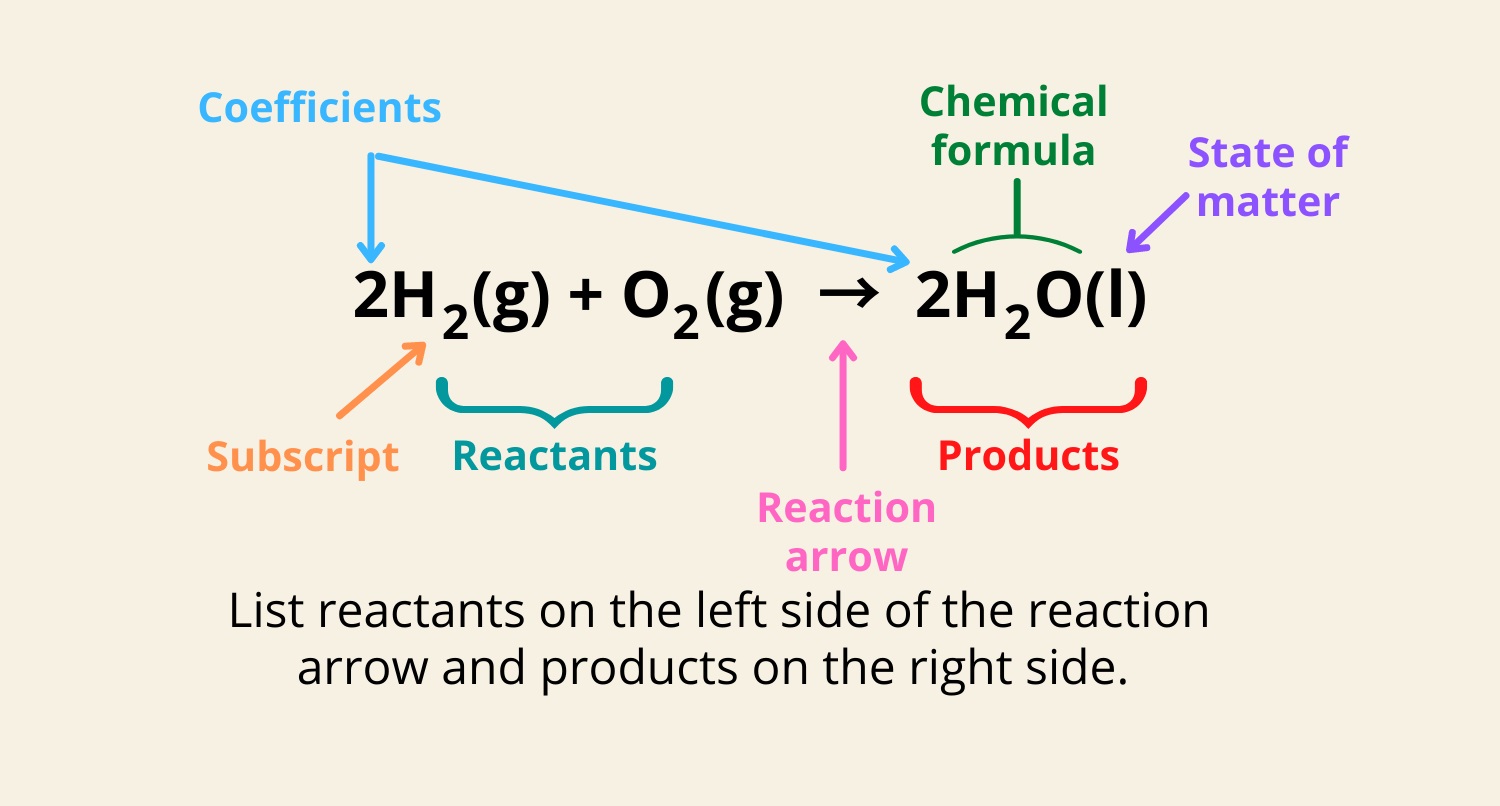
Chemical equations are an integral part of understanding the world of chemistry. They provide a symbolic representation of reactions that occur between different substances, giving us a deeper insight into the fundamental principles of matter and how it interacts. While chemical equations may seem complex and intimidating at first glance, they hold a wealth of fascinating information that highlights the intricacies of the chemical world.
In this article, we will explore thirteen extraordinary facts about chemical equations. From their historical significance to their role in everyday life, these facts will shed light on the importance of chemical equations in our understanding of the natural world. So, let’s dive in and uncover the fascinating world of chemical equations!
Key Takeaways:
- Chemical equations are like recipes for reactions, showing what goes in and what comes out. They must be balanced, just like a balanced diet, to follow the law of conservation of mass.
- By using chemical equations, scientists can predict, communicate, and calculate important aspects of reactions, like the products formed, reaction yields, and even the heat flow. It’s like a secret code for understanding chemical transformations!
Chemical equations represent chemical reactions
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction. It uses chemical formulas and symbols to show the reactants and products involved in the reaction.
Chemical equations must be balanced
In a chemical equation, the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. This is known as balancing the equation and is essential to maintain the law of conservation of mass.
Chemical equations follow specific rules
Chemical equations follow certain rules, such as using the correct symbols for elements and compounds, indicating the state of matter (solid, liquid, gas, or aqueous), and including coefficients to balance the equation.
Chemical equations can be written in different formats
Chemical equations can be written in two main formats: word equations, which use words to describe the reaction, and symbolic equations, which use chemical formulas and symbols. Symbolic equations are more commonly used in scientific contexts.
Chemical equations can be used to predict reaction outcomes
By studying the chemical equation of a reaction, chemists can predict the type of reaction, the products formed, and the amount of each substance involved. This information is crucial for understanding and controlling chemical processes.
Chemical equations can be balanced using stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the calculation of the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It can be used to balance chemical equations by adjusting the coefficients of the reactants and products.
Chemical equations can represent both physical and chemical changes
Chemical equations are not limited to representing only chemical reactions. They can also represent physical changes, such as phase transitions or dissolving of substances. The same principles of balancing and symbolism apply in these cases.
Chemical equations are used to communicate and document reactions
Chemical equations serve as a universal language for chemists to communicate and document reactions. They provide a concise and standardized way of representing complex chemical processes and facilitate collaboration and understanding in the scientific community.
Chemical equations can be used to calculate reaction yields
Using stoichiometry and the balanced chemical equation, chemists can determine the theoretical yield of a reaction, which is the maximum amount of product that can be obtained. This information is crucial for assessing reaction efficiency and designing industrial processes.
Chemical equations are subject to the law of conservation of atoms
The law of conservation of atoms states that atoms cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Therefore, the total number of each type of atom must be the same on both sides of a balanced chemical equation.
Chemical equations can be used to calculate reaction enthalpy
By knowing the balanced chemical equation and the enthalpy change associated with each reaction step, chemists can calculate the overall enthalpy change of a reaction. This provides valuable information about the heat flow in chemical processes.
Chemical equations can be used for stoichiometric calculations
Stoichiometry calculations involve determining the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Chemical equations provide the necessary information to perform these calculations, allowing chemists to optimize reaction conditions and assess reaction efficiency.
Chemical equations can be represented graphically
In addition to symbolic representation, chemical equations can also be depicted graphically using diagrams or flowcharts. These visual representations provide a clear and intuitive way of understanding and interpreting chemical reactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chemical equations are fascinating tools that allow us to represent and understand the interactions between different substances. They play a crucial role in chemistry, helping scientists and students alike to visualize and comprehend chemical reactions. Understanding chemical equations is essential for various fields, including industrial processes, environmental studies, pharmaceutical development, and more.
The 13 extraordinary facts about chemical equations mentioned in this article highlight the complexity and beauty of these representations. From stoichiometry to balancing equations, these facts shed light on the fundamental principles behind chemical reactions.
By delving into the world of chemical equations, we expand our understanding of how matter transforms and interacts. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or just curious about the world around you, exploring the realm of chemical equations is sure to ignite your curiosity and deepen your appreciation for the wonders of chemistry.
FAQs
Q: What is a chemical equation?
A: A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction. It consists of reactants, which are the substances that enter the reaction, and products, which are the substances formed as a result of the reaction.
Q: Why are chemical equations important?
A: Chemical equations are crucial for understanding and predicting the outcome of chemical reactions. They provide a concise and systematic way of representing complex chemical transformations.
Q: How do you balance a chemical equation?
A: Balancing a chemical equation involves adjusting the coefficients in front of the reactants and products to ensure that the same number and type of atoms are present on both sides of the equation.
Q: What is stoichiometry?
A: Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships and calculations involving reactants and products in chemical reactions.
Q: Can you have a chemical equation without coefficients?
A: No, coefficients are necessary in a balanced chemical equation to represent the relative amounts of each substance involved in the reaction.
Q: Are chemical equations only used in laboratories?
A: No, chemical equations are used in a wide range of fields, including industrial processes, environmental studies, pharmaceutical development, and even everyday life.
Q: What is the purpose of arrows in a chemical equation?
A: The arrows in a chemical equation indicate the direction in which the reaction is proceeding, with the reactants on the left side and the products on the right side.
Q: Can a chemical equation have more than one arrow?
A: No, a chemical equation typically has only one arrow to indicate the direction of the reaction. However, reversible reactions can be represented using a double arrow.
Q: Are reactants and products always in a gaseous state?
A: No, reactants and products can exist in various states of matter, including solid, liquid, and gas, depending on the specific reaction.
Q: Can chemical equations be written for non-chemical reactions?
A: Yes, chemical equations can be written for various non-chemical reactions, such as nuclear reactions and biological processes.
Q: Can chemical equations change over time?
A: Chemical equations are static representations of specific reactions. However, they can be modified or adjusted as new information or experimental data become available.
Q: Can chemical equations predict the outcome of a reaction?
A: While chemical equations provide information about the reactants and products involved in a reaction, they do not always predict the precise outcome. Factors such as reaction conditions and side reactions can affect the actual result.
Q: How can I learn more about chemical equations?
A: To learn more about chemical equations, consider studying chemistry textbooks, taking online courses, or consulting with a chemistry tutor or instructor. Hands-on laboratory experiments can also enhance your understanding of chemical reactions.
Chemical equations offer a fascinating glimpse into the world of chemistry, but there's still more to explore! If you're curious about the underlying principles governing chemical reactions, Hess's Law provides enigmatic insights into the conservation of energy. For those interested in acid-base chemistry, the Bronsted-Lowry Theory offers an extraordinary perspective on proton transfer and the behavior of acids and bases. Delving deeper into these topics will enhance your understanding of chemical equations and the fundamental concepts that shape our universe.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
