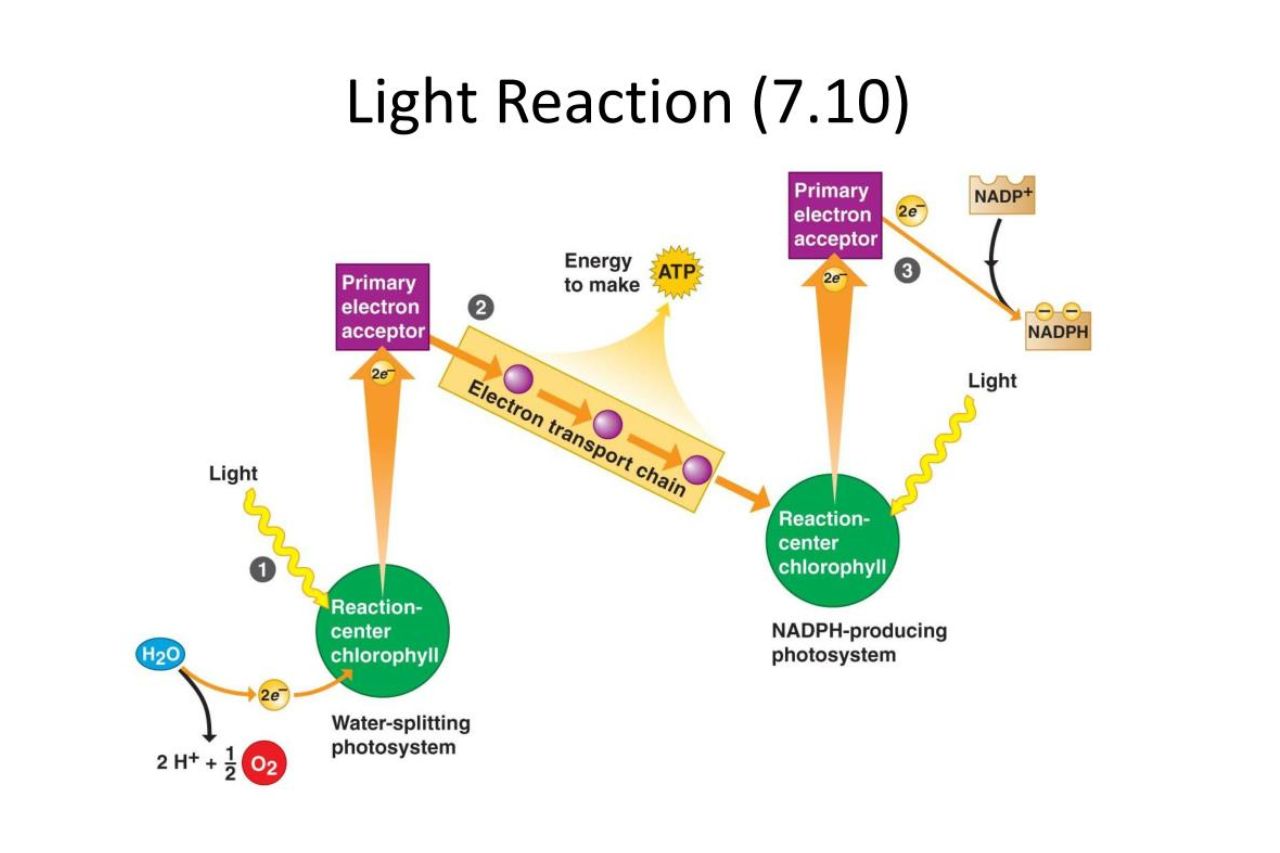
Light reactions are a crucial process that takes place in photosynthesis, the fundamental process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy. These reactions occur in specialized structures within plant cells called chloroplasts, specifically in the thylakoid membranes. Light reactions capture and convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the subsequent reactions of photosynthesis.
While light reactions may seem like a simple and straightforward process at first glance, there are numerous astonishing facts that highlight the complexity and importance of this biological phenomenon. In this article, we will explore 14 fascinating facts about light reactions, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms behind this vital process. From the role of pigments to the involvement of electron transport chains, get ready to dive into the world of light reactions and discover the wonders that occur when light meets photosynthesis.
Key Takeaways:
- Light reactions are like a power station for plants, converting sunlight into energy-rich molecules that fuel their growth and survival. Without these reactions, plants wouldn’t be able to make their food!
- Just like a superhero team, different pigments and complexes work together during light reactions to capture light energy and produce the essential molecules ATP and NADPH. It’s like a colorful and powerful light show inside plant cells!
Light reactions are essential for photosynthesis
One of the most crucial functions of light reactions is their role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
They take place in thylakoid membranes
Light reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, which are specialized organelles found in plant cells.
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment involved
Chlorophyll, the green pigment present in plants, absorbs light energy during light reactions and initiates the process of photosynthesis.
Photosystem II comes before Photosystem I
During light reactions, Photosystem II functions before Photosystem I, as it is responsible for capturing light energy and transferring electrons.
Water molecules are split
One of the astonishing aspects of light reactions is that water molecules are split, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. This process is known as photolysis.
ATP and NADPH are produced
Light reactions generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are energy-rich molecules necessary for the Calvin cycle, the next stage of photosynthesis.
Light reactions are dependent on sunlight
Without sunlight, light reactions cannot occur. This highlights the importance of solar energy in the process of photosynthesis.
The electron transport chain is involved
Electron transport chains play a critical role in light reactions, facilitating the movement of electrons and the creation of a proton gradient for ATP synthesis.
Cytochrome b6f complex plays a role in electron transfer
The cytochrome b6f complex is an essential component of the electron transport chain during light reactions, enabling efficient electron transfer between Photosystem II and Photosystem I.
Light reactions produce chemical energy
The primary purpose of light reactions is to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which can be used for the synthesis of glucose and other organic molecules.
They are influenced by temperature and light intensity
Temperature and light intensity significantly affect the rate of light reactions. Optimal conditions are required for efficient photosynthesis to take place.
Photophosphorylation occurs during light reactions
Photophosphorylation is the process by which ATP is generated using the energy from light. This reaction is an essential component of light reactions.
Light reactions are the initial step of photosynthesis
Before the Calvin cycle can occur, light reactions act as the starting point of photosynthesis, capturing and converting light energy into chemical energy.
They involve multiple pigments
Aside from chlorophyll, other pigments such as carotenoids and phycobilins are also involved in light reactions, expanding the range of light wavelengths that can be absorbed.
These 14 astonishing facts about light reactions demonstrate the intricate and captivating nature of this essential process in plants. From the conversion of light energy to the production of ATP and NADPH, light reactions play a crucial role in the sustenance of life on Earth.
Conclusion
Light reactions are a fascinating and essential part of photosynthesis. Through a series of complex processes, light energy is converted into chemical energy, which is then used to power the synthesis of glucose and other organic molecules. Understanding the intricate mechanisms and astonishing facts about light reactions allows us to appreciate the remarkable efficiency of nature’s energy conversion systems.
From the importance of chlorophyll to the role of water splitting, the discoveries and advancements in the field of light reactions continue to deepen our understanding of plant biology and have the potential to impact various industries, from renewable energy to medicine.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of light reactions, we can look forward to not only expanding our knowledge but also applying this knowledge to develop sustainable solutions for a greener and healthier planet.
FAQs
Q: What are light reactions?
A: Light reactions are the initial stage of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy in plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
Q: What is the role of chlorophyll in light reactions?
A: Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells that absorbs light energy and initiates the process of photosynthesis.
Q: How does water splitting occur during light reactions?
A: Water splitting, also known as the photolysis of water, is a process in which water molecules are split into hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen atoms using light energy. This reaction provides the electrons needed for the production of ATP and NADPH.
Q: What is the significance of light reactions?
A: Light reactions are crucial for the production of ATP and NADPH, which are used in the subsequent dark reactions of photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
Q: Can light reactions occur without light?
A: No, light reactions require light energy to proceed. Without light, the process cannot be initiated.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
