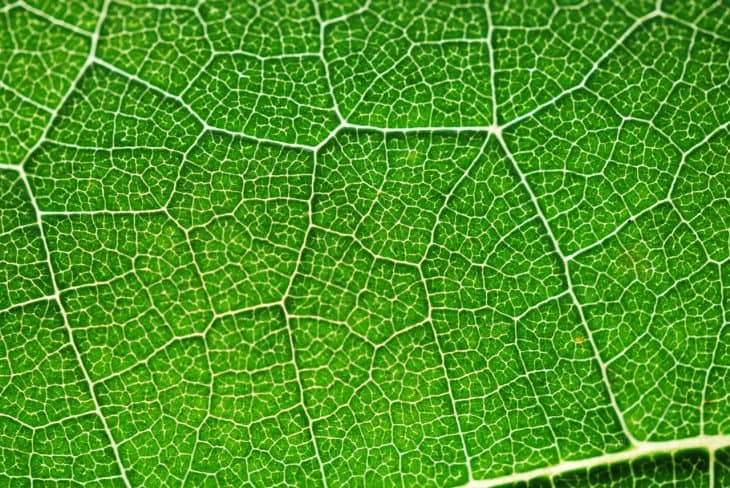

We all learned about photosynthesis in school, but there’s more to it than what’s been taught. Find out more about the process that lets us breathe with these photosynthesis facts.
- Photosynthesis collects an estimated 130 terawatts of energy from the sun.
- Photosynthetic life forms turn 100-115 million tons of carbon into biomass every year.
- Plants can only turn 0.1%-8% of the sunlight they receive into energy.
- Photosynthetic phytoplankton in the seas produces 70% of the world’s oxygen.
- Land-based photosynthetic life produces only 30% of the world’s oxygen.
- The first photosynthetic life forms were bacteria that lived around 3.4 billion years ago.
- Green algae evolved in the Proterozoic Eon between 2.5 billion to 543 million years ago.
- The ancestors of modern phytoplankton evolved in the Mesozoic, between 251 to 66 million years ago.
- Scientists first began looking into photosynthesis in the mid-18th century.
- Jean Senebier first discovered plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen in 1796.
- Various scientists outlined the photosynthetic process in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
- Charles Barnes first introduced the term photosynthesis in 1893.
- Robert Hill’s experiments in 1937 to 1939 proved chloroplasts’ key role in the photosynthetic process.
- Chemists in California detailed the photosynthetic processing of carbon in the late 1940s.
- From 1958 to 1963, experiments at Cornell University, New York showed the different photosynthetic rates of plant species.
- Photosynthesis comes from the Greek words for light and puts together, referring to the process using sunlight to produce sugar and proteins.
- Photosynthetic life forms are the foundation of the food chain, thanks to their ability to produce their own food.
- Photosynthesis is one of the most important chemical reactions on the planet.
- Without sunlight like at night, photosynthetic life forms breathe in oxygen like other life forms.
- Photosynthesis needs more than carbon dioxide and sunlight to work, such as water, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
Before photosynthesis, life depended on chemosynthesis for survival.
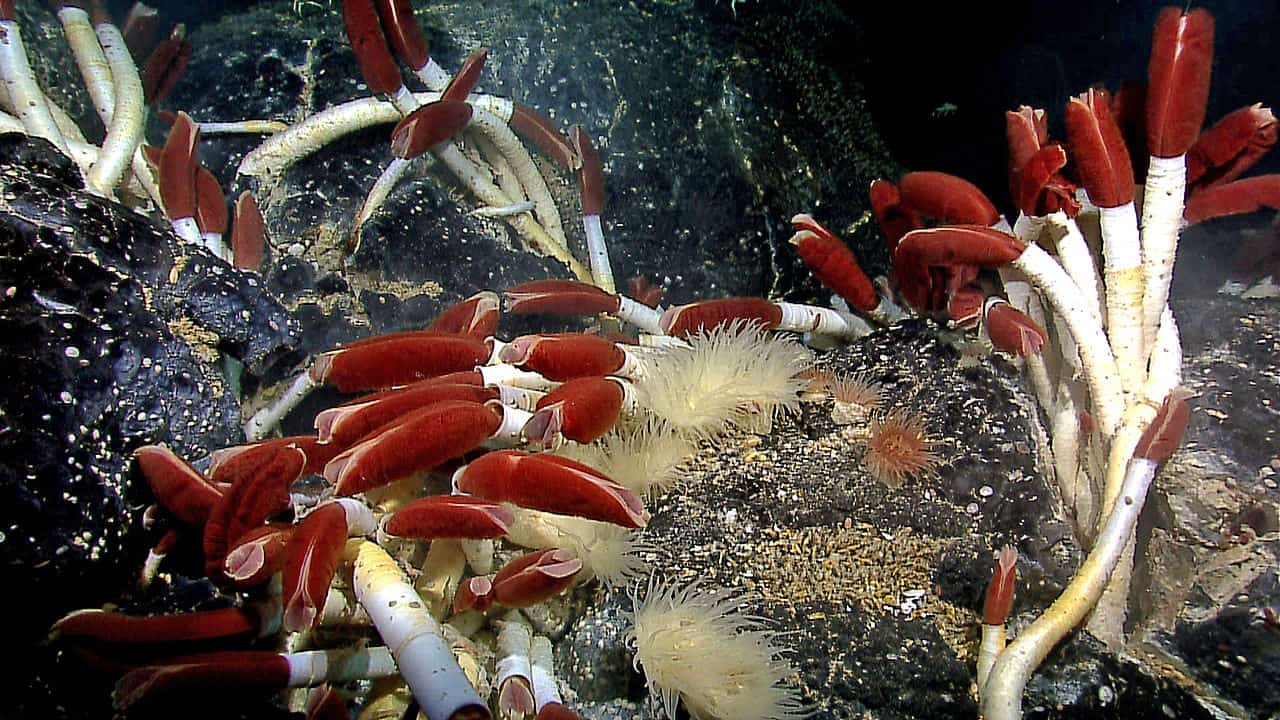

Chemosynthesis is a process where chemical reactions do not need sunlight to function. The most common chemical used by these early life forms was hydrogen sulfide, which reacted with carbon dioxide and oxygen to produce the carbohydrates needed for life. Today, chemosynthetic lifeforms are rare but thrive in places without sunlight. This includes underground caves and under the oceans, feeding off hydrogen sulfides to survive.
The evolution of photosynthesis caused the Oxygen Catastrophe.
Most life forms depend on oxygen to survive. But this leads to the fact that most people forget that oxygen is a very reactive element. In fact, the term oxidation roots from oxygen. When the first photosynthetic life forms evolved, oxygen was practically nonexistent in the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans.
However, as they supplied more oxygen to Earth’s environment, the life forms at the time succumbed to oxygen’s reactive property. Lasting between 2.4 to 2 billion years ago, this caused the near-extinction of all life on Earth. Talk about a shocking start for photosynthesis facts.
The evolution of photosynthesis also opened the door for multicellular life to evolve.
In order for life to survive an oxygen-rich environment, it had to develop complex cellular repair mechanisms to handle oxygen’s reactive property. Eventually, this allowed the first multicellular life forms to evolve. Now that’s one for photosynthesis facts to remember.
Plants use two kinds of photosynthetic processes.
The C3 and C4 processes share the same process and outcome, but differ in the chemicals used to react with carbon dioxide. The C3 process uses RuBP carboxylase, while the C4 process uses PEP carboxylase.
The C3 process is more commonly used by plants and allows them to make the most of their photosynthetic abilities. However, while the C4 process is less efficient, it is less water-dependent compared to the C3 process. Thus, the C4 process is favored by plants in arid climates such as deserts.
Plants use chloroplasts to perform photosynthesis.
Aside from plant respiration, chlorophyll also give plants their distinctive green color. Chlorophyll is found inside a plant’s chloroplasts. It’s also chlorophyll that absorbs the sunlight needed for photosynthesis. Despite what some people think, chloroplasts are not cells. Instead, they are parts of a cell.
The average plant cell contains between 10-100 chloroplasts. Considering the number of cells in an average multicellular life form, a plant could have between 450,000 to 800,000 chloroplasts for every square milliliter. Definitely one of the photosynthesis facts that proves how big things can come in small packages.
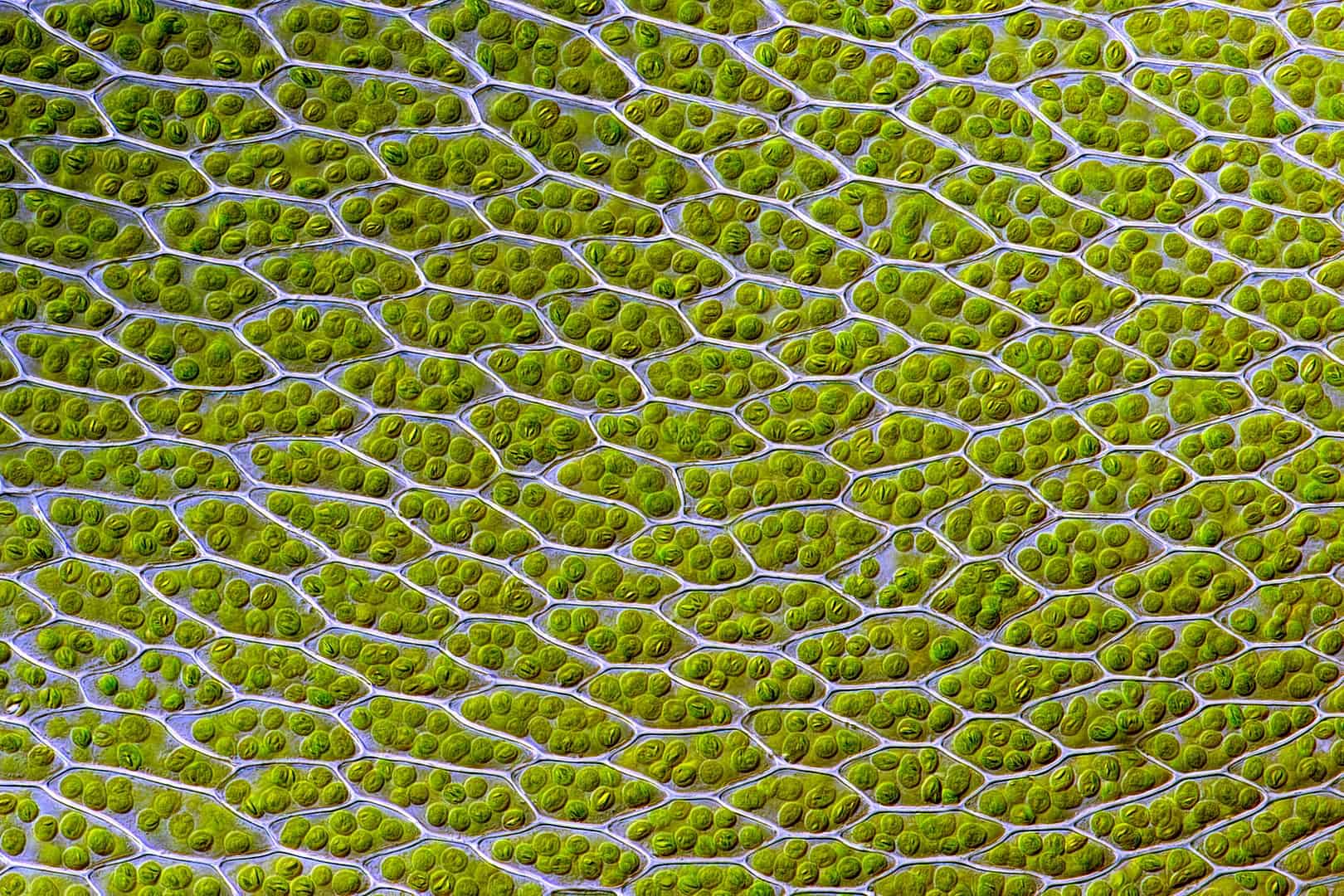

Photosynthesis is not limited to using chlorophyll.
For one, red algae use phycoerythrin in their chloroplasts to absorb sunlight. This is also what gives them their red color. Brown algae and phytoplankton use fucoxanthin, which is also what gives the former their brown color. Talk about a diverse example of photosynthesis facts.
Color matters when it comes to photosynthesis.
Humans perceive color depending on wavelengths that show how much energy light has. Color results when the light of a certain wavelength gets reflected, which is then caught by our eyes. Chlorophyll is green because it reflects green wavelengths, and allows plants to absorb low-power red and high-power wavelengths.
All chloroplasts share a common ancestor.
That common ancestor is cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae. They’re among the oldest life forms on Earth, dating back to 2.7 billion years ago. Scientists also believe that in prehistoric times, an unknown cell consumed a cyanobacterium, and somehow gained its ability to photosynthesize. All chloroplasts today descended from that single cyanobacterium.
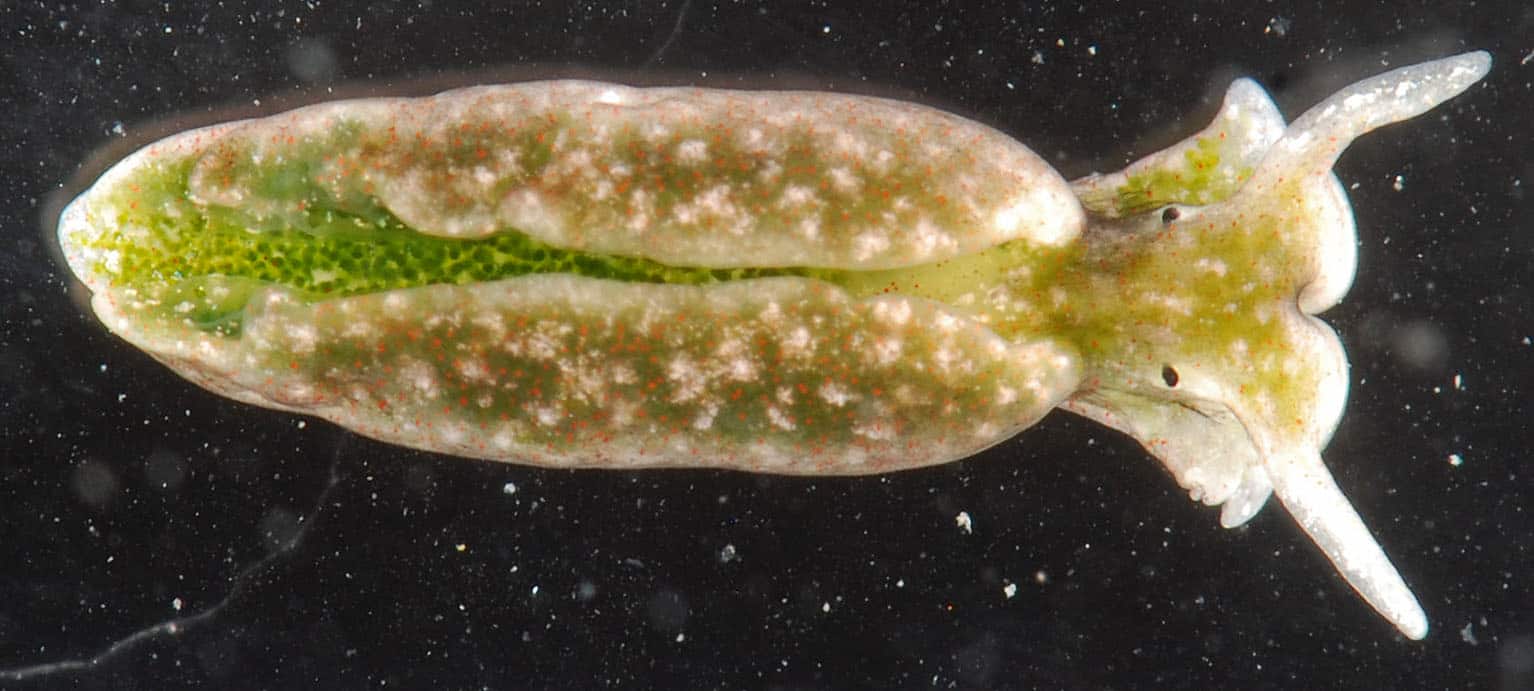
Some animals undergo photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis might seem like a plant’s business, but it’s not strictly the case. One example is the sea slug or Elysia chlorotica. It feeds on algae, from which it extracts chloroplasts and introduces them into its own cells. There, they photosynthesize and prove the sea slug with additional nutrition. How it’s able to do this is still not fully understood by scientists today.

Photosynthesis is a speedy process.
In fact, photosynthesis takes less than two seconds. The slowest part of the process where carbon gets turned into carbohydrates and oxygen gets released lasts barely a second. The other stages of photosynthesis – such as converting sunlight into energy and fueling chemical processes – takes only a millisecond to finish.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


