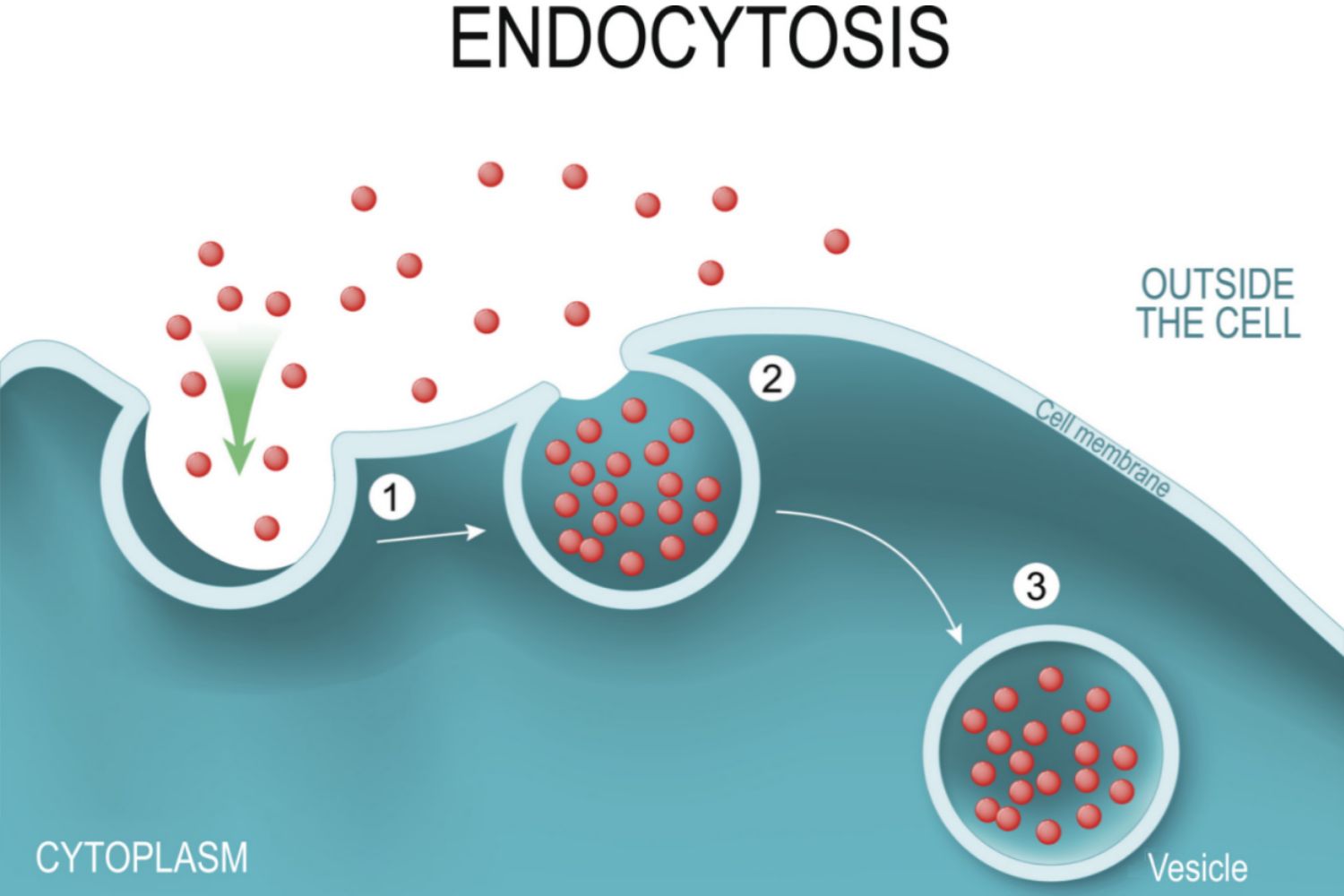
Endocytosis is a fascinating cellular process that plays a crucial role in various biological functions. In simple terms, it is the mechanism by which cells internalize materials from their surrounding environment. This highly regulated process allows cells to take in nutrients, eliminate waste, and even communicate with neighboring cells.
While endocytosis may sound like a complex scientific concept, it is a fundamental process that occurs in all living organisms. In this article, we will explore 13 surprising facts about endocytosis that will not only deepen your understanding of this cellular process but also reinforce its importance in maintaining the overall health and functioning of organisms.
Key Takeaways:
- Endocytosis is like a cellular delivery service, bringing in nutrients and removing waste. It’s crucial for keeping cells healthy and functioning properly.
- Different types of endocytosis, like “cellular eating” and “cellular drinking,” help cells stay nourished and protected from harmful substances. Understanding this process can lead to new ways to treat diseases.
Endocytosis is a fundamental cellular process
Endocytosis is a crucial mechanism that occurs in all eukaryotic cells. It involves the uptake of materials from the extracellular environment into the cell by forming vesicles from the plasma membrane.
There are three main types of endocytosis
The three major types of endocytosis are phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Each type involves a different mechanism and serves distinct functions within the cell.
Phagocytosis is like “cellular eating”
Phagocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which large particles, such as bacteria or cell debris, are engulfed by specialized cells called phagocytes. This process is essential for immune defense and the removal of potentially harmful substances.
Pinocytosis is “cellular drinking”
Pinocytosis refers to the non-selective uptake of fluid and dissolved solutes into the cell. It allows cells to sample their surroundings and obtain necessary nutrients. This process is particularly important in cells that line the digestive tract and absorb nutrients from food.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is highly specific
In receptor-mediated endocytosis, specific molecules bind to receptor proteins on the cell surface, triggering the formation of coated pits and internalization of the receptors along with their bound ligands. This process allows cells to selectively internalize specific molecules, including hormones, enzymes, and cholesterol.
Endocytosis plays a crucial role in nutrient uptake
Endocytosis allows cells to take up essential nutrients, such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids, from the extracellular environment. These nutrients are transported into the cell through specific transporters present on the plasma membrane.
Endocytosis is involved in membrane recycling
Endocytosis is not just about bringing materials into the cell; it also plays a key role in membrane recycling. After internalization, the vesicles formed during endocytosis can fuse with other cellular compartments or the plasma membrane to release their contents or recycle membrane components.
Some viruses hijack the endocytic pathway
Certain viruses exploit the endocytic machinery to gain entry into host cells. They bind to specific receptors on the cell surface, triggering receptor-mediated endocytosis and allowing the viral particles to enter the cell.
Dysregulation of endocytosis is associated with diseases
Defects in endocytic processes have been implicated in various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. Understanding the mechanisms of endocytosis can provide valuable insights into these pathological conditions.
Endocytosis can be regulated by signaling pathways
Endocytosis is tightly regulated by various signaling pathways that respond to extracellular signals. These pathways can modulate the number and activity of receptors on the cell surface, thereby fine-tuning the ability of the cell to internalize specific molecules.
Clathrin is a key player in endocytosis
Clathrin is a protein that forms a lattice-like structure called a clathrin coat, which helps invaginate the plasma membrane during endocytosis. This coat protein plays a critical role in receptor-mediated endocytosis and the transport of cargo molecules into the cell.
Endocytosis is a dynamic process
Endocytosis is not a static process but rather a dynamic and finely regulated mechanism. It is influenced by multiple factors, including the cell type, the nature of the cargo, and the signaling cascades activated within the cell.
Endocytosis is essential for cell signaling
Endocytosis plays a crucial role in cell signaling by regulating the spatial distribution and availability of cell surface receptors. Internalization of receptors can terminate signaling cascades, prevent receptor desensitization, and regulate the responsiveness of cells to different stimuli.
Endocytosis is a fascinating and intricate process that underlies numerous cellular functions. From nutrient uptake to membrane recycling and disease implications, its significance cannot be overstated. By unraveling the complexities of endocytosis, researchers can shed light on various biological processes and potentially develop new therapeutic approaches.
Conclusion
Endocytosis is a fascinating biological process that plays a crucial role in various cellular activities. From its discovery to its numerous types, endocytosis continues to surprise us with its complexities and abilities. Understanding the mechanisms behind endocytosis is not only essential for advancing our knowledge in cell biology but also has significant implications for various fields including medicine and drug delivery.
Through this article, we have uncovered 13 surprising facts about endocytosis. We have explored how it helps in nutrient uptake, cell signaling, and the removal of damaged cellular components. We have delved into the different forms of endocytosis such as phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Endocytosis is a highly dynamic and regulated process that involves intricate molecular machinery. It is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and controlling the communication between cells and their environment. Further research in this field will undoubtedly unveil new and exciting insights into the remarkable world of endocytosis.
FAQs
1. What is endocytosis?
Endocytosis is a cellular process that involves the engulfment of substances or particles from the extracellular environment into the cell, using specialized membrane-bound structures called vesicles.
2. What are the different types of endocytosis?
There are three main types of endocytosis: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Each type serves different purposes and involves specific signaling and machinery.
3. How does endocytosis benefit cells?
Endocytosis is crucial for various cellular functions, including nutrient uptake, cell signaling, receptor recycling, and the removal of damaged cellular components. It helps maintain cellular homeostasis and regulates the communication between cells and their environment.
4. What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?
Endocytosis is the process of bringing substances into the cell, while exocytosis is the process of releasing substances from the cell. They are two opposite processes involved in maintaining cellular balance and regulating the transport of molecules.
5. How is endocytosis related to human health?
Endocytosis plays a critical role in various physiological processes, including immune response, neurotransmitter regulation, and the entry of therapeutic drugs into cells. Dysregulation of endocytosis can lead to various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases.
6. Can endocytosis be targeted for therapeutic purposes?
Yes, targeting endocytosis has enormous potential for therapeutic purposes. By understanding the mechanisms involved in endocytosis, scientists can develop strategies to selectively deliver drugs into cells, enhance immune response, and treat diseases associated with defective endocytic processes.
Endocytosis is a captivating cellular process that plays a vital role in our bodies. From nutrient uptake to cell signaling, this dynamic process keeps our cells functioning smoothly. If you're curious to learn more about the specific mechanisms involved, such as how receptor-mediated endocytosis works, check out our other informative articles. You'll be amazed by the intricacies of these cellular pathways and how they contribute to our overall health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
