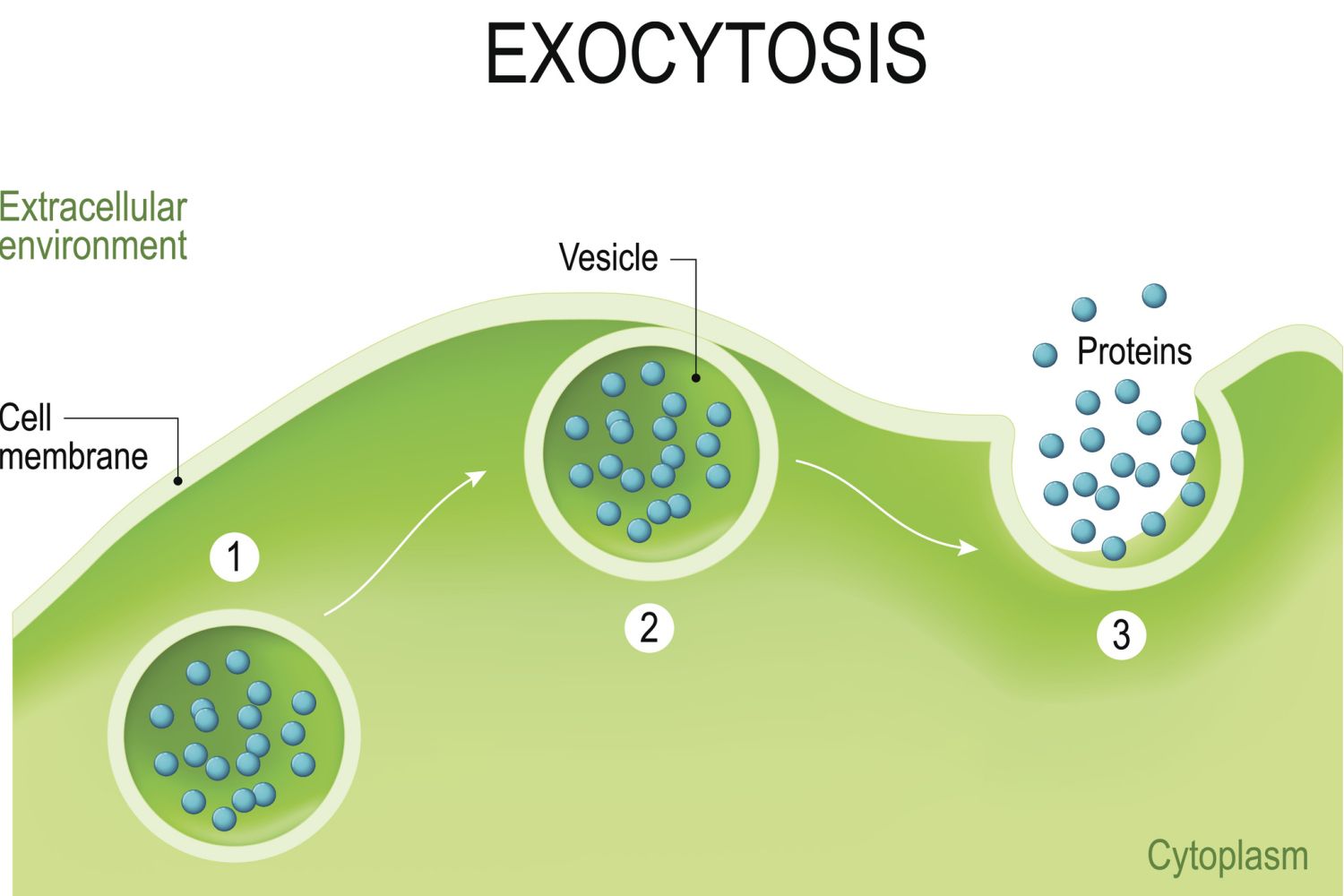
Exocytosis is a fascinating biological process that plays a crucial role in the functioning of cells. It involves the release of molecules, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and enzymes, from the interior of a cell to its external environment. This complex mechanism allows cells to communicate with each other, regulate bodily functions, and perform essential processes like digestion and immune responses.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of exocytosis and explore 16 astounding facts that will deepen your understanding of this biological phenomenon. From the discovery of exocytosis to its involvement in various diseases, we will unravel the mysteries and wonders of this vital cellular process. So, buckle up as we embark on a journey to uncover the fascinating secrets of exocytosis.
Key Takeaways:
- Exocytosis is like a cellular delivery service, releasing important substances like neurotransmitters, hormones, and digestive enzymes. It’s crucial for cell communication, growth, and maintaining a healthy balance in the body.
- Exocytosis is like a superhero power for cells, helping them fight off invaders, share information, and adapt to changes. It’s like a carefully choreographed dance that keeps cells and the body in harmony.
Exocytosis is a vital cellular process.
Exocytosis is a fundamental process that plays a crucial role in various cellular functions. It allows cells to release substances and communicate with their surroundings.
Exocytosis is a form of active transport.
Exocytosis requires energy to transport molecules from inside the cell to the outside. It is an active process that relies on the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane.
Neurotransmitters are released through exocytosis.
In neurons, exocytosis is responsible for the release of neurotransmitters, which transmit signals between nerve cells. This process is essential for proper brain function and communication.
Hormones are also released through exocytosis.
In endocrine cells, exocytosis is responsible for the release of hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate various bodily functions and ensure proper physiological balance.
Exocytosis is involved in cell growth and repair.
During cell growth and repair, exocytosis plays a vital role in incorporating new membrane components and delivering them to the cell surface.
Exocytosis is essential for the immune response.
During an immune response, immune cells release signaling molecules through exocytosis to communicate with other cells and coordinate the immune system’s defense mechanisms.
Exocytosis is involved in the release of digestive enzymes.
In the digestive system, exocytosis allows the release of digestive enzymes produced by cells in the stomach and intestines, facilitating the breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Exocytosis is critical for the release of milk in lactating mammals.
During lactation, exocytosis enables mammary gland cells to release milk, providing essential nourishment for newborn mammals.
Exocytosis regulates membrane surface area.
Exocytosis helps maintain the cell’s membrane surface area by adding new membrane material and compensating for any membrane loss during endocytosis.
Exocytosis is involved in synaptic transmission.
In synapses, exocytosis mediates the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic cell into the synaptic cleft, facilitating communication between nerve cells.
Exocytosis can be regulated by calcium ions.
Calcium ions play a crucial role in triggering exocytosis. They bind to specific proteins, enabling the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane and the release of their contents.
Exocytosis can be regulated by hormones and signaling molecules.
Hormones and signaling molecules can modulate exocytosis, regulating the timing and extent of substance release and ensuring proper cellular responses.
Exocytosis is a highly regulated process.
Exocytosis is precisely controlled to ensure the release of substances at the correct time and location in the cell. Dysregulation of exocytosis can have detrimental effects on cellular function.
Exocytosis is essential for neurotransmitter recycling.
After neurotransmitters have fulfilled their signaling role, exocytosis allows for their reuptake, recycling, and repackaging into vesicles for future use.
Exocytosis is involved in the formation of the cell plate during cell division.
In plant cells, exocytosis plays a crucial role in the formation of the cell plate during cytokinesis, leading to the separation of daughter cells.
Exocytosis can be regulated by cellular signals and external stimuli.
Cellular signals and external stimuli can trigger or inhibit exocytosis, allowing cells to respond and adapt to changing environments and physiological demands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exocytosis is a fascinating and essential process that plays a crucial role in various biological functions. From neurotransmission to cell growth and development, exocytosis is responsible for the release of molecules and maintaining cellular homeostasis. Understanding the intricacies of exocytosis can provide valuable insights into the functioning of cells and the human body as a whole.Through this article, we have explored 16 astounding facts about exocytosis. We have delved into the process itself, its significance, and the various mechanisms involved. From the discovery of exocytosis to its implications in disease and medical research, we now have a deeper understanding of this vital biological process.As research in the field of biology continues to advance, it is imperative to keep exploring and unraveling the mysteries of exocytosis. With further studies, we may uncover even more astounding facts and expand our knowledge of this intricate cellular process.In summary, exocytosis stands as a remarkable phenomenon that plays a pivotal role in cellular communication, maintenance, and overall organismal function. By continuing to study and appreciate the intricate details of exocytosis, we pave the way for future discoveries and advancements in medicine and biology.
FAQs
1. What is exocytosis?
Exocytosis is a cellular process where molecules or particles are released from a cell by fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane.
2. What is the role of exocytosis in the body?
Exocytosis is involved in various functions such as neurotransmission, hormone secretion, immune response, and cell growth and development.
3. How does exocytosis differ from endocytosis?
Exocytosis involves the release of molecules from the cell, whereas endocytosis is the process of bringing molecules into the cell.
4. What are the types of exocytosis?
The two main types of exocytosis are constitutive exocytosis, which occurs continuously, and regulated exocytosis, which is triggered by specific signals.
5. Can exocytosis be disrupted?
Yes, disruption of exocytosis can lead to various diseases, including neurological disorders and immune system dysfunction.
6. How was exocytosis discovered?
Exocytosis was first observed and described by Swedish cell biologist Björn Ekwall in the 1950s.
7. What are the key molecules involved in exocytosis?
Key molecules involved in exocytosis include vesicles, membrane proteins, and neurotransmitters or other cargo molecules.
8. How does exocytosis contribute to neurotransmission?
In neurotransmission, exocytosis allows for the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft, facilitating nerve signal transmission.
9. Can exocytosis be targeted for therapeutic purposes?
Yes, targeting exocytosis pathways can offer potential therapeutic interventions for diseases ranging from diabetes to cancer.
10. How does exocytosis impact cell secretion?
Exocytosis enables cells to secrete substances such as hormones, enzymes, and antibodies into the extracellular space.
Exocytosis plays a crucial role in cellular communication, growth, and secretion. But there's more to explore in the fascinating world of cell biology! Dive into the intricacies of protein trafficking, where molecules are expertly guided to their destinations within cells. Uncover the mysteries of neurotransmission, the language of neurons that enables our thoughts and actions. And prepare to be amazed by the boundless potential of embryonic stem cells, nature's master builders capable of becoming any cell type in the body. Keep learning and discover the wonders that lie within our cells!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
