The Kinetic Molecular Theory is a fundamental concept in the field of Chemistry that helps us understand the behavior of gases at the molecular level. It provides us with a framework to explain various properties of gases such as pressure, temperature, and volume. While many are familiar with the basic principles of the theory, there are some extraordinary facts that are often overlooked. In this article, we will delve into 14 extraordinary facts about the Kinetic Molecular Theory that will not only intrigue your curiosity but also deepen your understanding of the molecular world. From the motion of gas molecules to the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy, get ready to be amazed by the intricacies of the Kinetic Molecular Theory.
Key Takeaways:
- Gases are made up of tiny particles that are always moving and colliding with each other and their container walls, explaining their behavior and properties.
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory helps us understand how gas molecules behave, why gases have certain properties, and how temperature affects their motion.
Kinetic Molecular Theory explains the behavior of gases.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides insights into the behavior of gases.
It states that gases are composed of small particles called molecules.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, gases consist of tiny particles called molecules.
These molecules are constantly in motion.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gas molecules are always moving, colliding with each other and the walls of their container.
The motion of gas molecules is random and chaotic.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, the movement of gas molecules is completely random and follows no particular pattern or direction.
Gases have no definite shape or volume.
One of the key aspects of the Kinetic Molecular Theory is that gases do not have a fixed shape or volume. They take the shape and volume of their container.
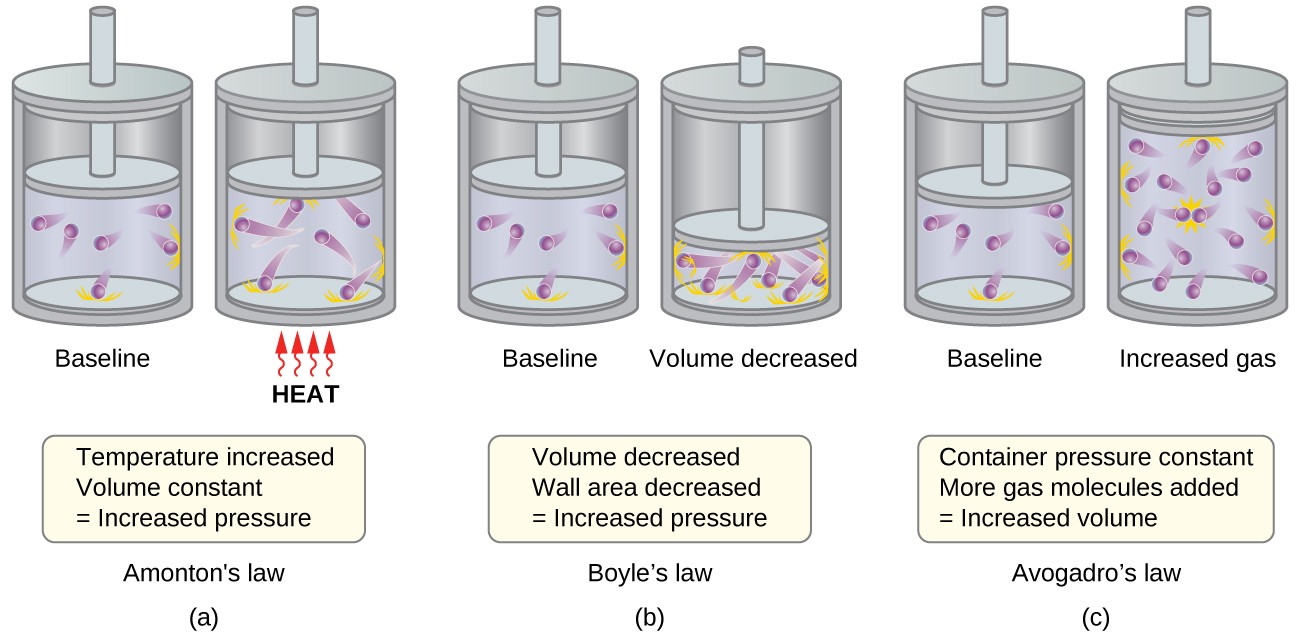
The pressure of a gas is a result of molecular collisions with the container walls.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, the pressure exerted by a gas is caused by the constant collisions of its molecules with the walls of the container.
The average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to temperature.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory states that the average kinetic energy of gas molecules increases with temperature. In other words, as temperature increases, molecular motion and speed also increase.
The volume of gas molecules is negligible compared to the volume of the gas.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, the volume occupied by gas molecules is tiny compared to the overall volume of the gas. Hence, it can be assumed that gases are mostly empty space.
Gas molecules exhibit elastic collisions.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, gas molecules undergo elastic collisions with each other and with the walls of their container. This means that no energy is lost during collisions.
The average speed of gas molecules is inversely proportional to the square root of their molar mass.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory predicts that at the same temperature, lighter gas molecules have higher average speeds compared to heavier gas molecules.
The temperature of a gas is a measure of its average kinetic energy.
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, the temperature of a gas is a direct measure of the average kinetic energy of its molecules.
Gases can be compressed due to the large spaces between gas molecules.
Due to the relatively large spaces between gas molecules, gases can be easily compressed. This property is explained by the Kinetic Molecular Theory.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory only applies to ideal gases.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory is most accurate for ideal gases, which follow the assumptions of the theory closely.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory has provided a solid foundation for understanding gas behavior.
Since its inception, the Kinetic Molecular Theory has played a vital role in explaining the behavior of gases and has laid the groundwork for various other concepts in the field of chemistry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Kinetic Molecular Theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the behavior of gases at the molecular level. Through the theory, we learn that the properties of gases can be explained by the motion and collisions of individual particles. This theory lays the foundation for our understanding of temperature, pressure, and volume relationships in gases.
Furthermore, we have discovered various extraordinary facts about the Kinetic Molecular Theory throughout this article. From the constant motion of gas particles to the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy, these facts shed light on the fascinating world of chemistry and the intricate nature of gases.
Having a profound knowledge of the Kinetic Molecular Theory allows us to make predictions and understand the behavior of gases in both everyday life and scientific research. It is a cornerstone in the study of chemistry and a valuable tool for scientists across various disciplines.
FAQs
Q: What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory?
A: The Kinetic Molecular Theory is a scientific model that explains the microscopic behavior of gases, based on the concept that gases are composed of particles (atoms or molecules) in constant motion.
Q: What are the main principles of the Kinetic Molecular Theory?
A: The main principles of the Kinetic Molecular Theory include the assumptions that gas particles are in constant motion, have negligible volume compared to the container they occupy, and that their collisions are elastic.
Q: How does the Kinetic Molecular Theory explain gas pressure?
A: According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, gas pressure arises from the collisions of gas particles with the walls of the container. The more frequent and energetic the collisions, the higher the pressure.
Q: How does temperature affect the motion of gas particles?
A: Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of gas particles. As temperature increases, the particles gain more energy and move faster, increasing the pressure and volume of the gas.
Q: How does the Kinetic Molecular Theory explain the properties of gases?
A: The Kinetic Molecular Theory explains gas properties by considering the average behavior of a large number of gas particles. It explains concepts such as gas expansion, diffusion, and the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
