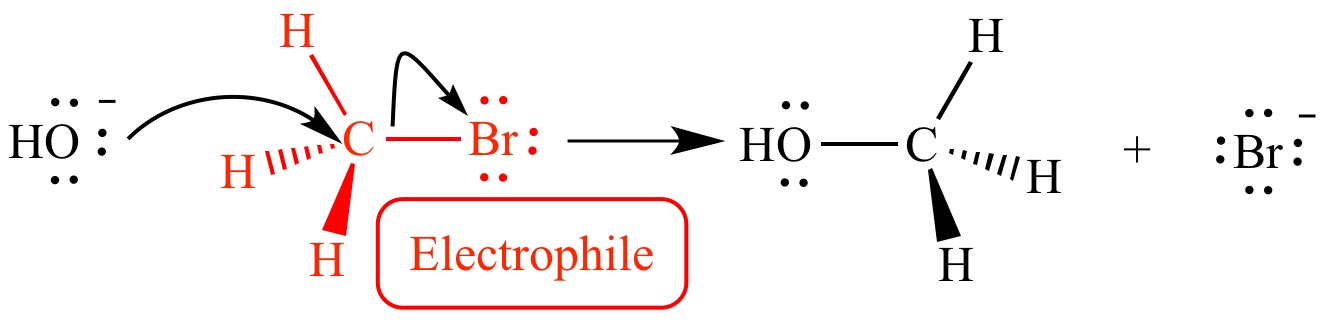
Imagine a world without chemistry. It’s hard to fathom, as this scientific discipline is a cornerstone of our everyday lives. One fascinating aspect of chemistry is its exploration of various chemical reactions and mechanisms. One such mechanism involves electrophiles, which play a crucial role in many organic reactions.
Electrophiles are chemical species that possess a positive or partially positive charge, making them attractive to electron-rich molecules or regions. They have the ability to accept a pair of electrons and form new bonds with nucleophiles. Understanding electrophiles and their reactivity is essential in fields such as drug discovery, material science, and environmental studies.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of electrophiles and explore 14 fascinating facts about these electron-seeking entities. From their distinct properties to their involvement in novel chemical reactions, we will uncover the essential role of electrophiles in the realm of chemistry.
Key Takeaways:
- Electrophiles are molecules with a strong affinity for electrons, playing a crucial role in organic chemistry reactions, including substitution, addition, and polymerization.
- Understanding electrophiles and their interactions with nucleophiles allows chemists to design and carry out a wide range of chemical reactions, enabling the synthesis of complex molecules with practical applications.
What is an Electrophile?
Before we dive into the world of electrophiles, let’s first understand what they are. An electrophile is a molecule or ion with a strong affinity for electrons. It is attracted towards regions of high electron density, where it can accept a pair of electrons to form a new chemical bond.
Electrophiles and Nucleophiles
Electrophiles are often paired with nucleophiles, which are molecules or ions that donate a pair of electrons to form a new bond. This combination of electrophiles and nucleophiles is crucial in many chemical reactions, including addition, elimination, and substitution reactions.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
One of the most important reactions involving electrophiles is electrophilic aromatic substitution. This reaction allows an electrophile to substitute a hydrogen atom in an aromatic compound, resulting in the formation of a new substituted molecule.
Common Electrophiles
There are several common electrophiles in organic chemistry, including carbocations, acyl chlorides, alkyl halides, and carbonyl compounds. Each of these electrophiles possesses specific properties that make them suitable for different types of reactions.
Electrophilic Addition Reactions
Electrophiles are involved in many addition reactions, where they add to unsaturated compounds such as alkenes and alkynes. The electrophile attacks the pi bond of the unsaturated compound, resulting in the formation of a new sigma bond.
Electrophiles in Oxidation Reactions
Electrophiles also play a significant role in oxidation reactions. They can accept a pair of electrons from a nucleophile, resulting in the transfer of electrons from the nucleophile to the electrophile. This process often leads to the formation of a new bond.
Lewis Acids as Electrophiles
Lewis acids, such as aluminum chloride and boron trifluoride, are commonly used as electrophiles in many organic reactions. They can accept a pair of electrons from a nucleophile, facilitating the formation of new bonds.
Electrophiles in Friedel-Crafts Reactions
The Friedel-Crafts reactions, including the alkylation and acylation reactions, are important transformations where electrophiles play a central role. These reactions allow the introduction of new alkyl or acyl groups into aromatic compounds.
Electrophiles in Polymerization
In polymerization reactions, electrophiles are used to initiate the reaction by interacting with monomers and activating them for further polymerization. This enables the creation of complex and useful polymers with diverse applications.
Acidic Nature of Electrophiles
Many electrophiles exhibit acidic characteristics due to the presence of polarized bonds or the ability to donate a proton. This acidity plays a role in various reactions, including protonation and formation of new bonds.
Electrophiles in Biochemical Reactions
Electrophiles are not only important in organic chemistry but also have an impact in biochemical reactions. For example, electrophiles are involved in DNA damage and can contribute to various disease processes.
Electrophilic Substitution in Aromatic Compounds
Electrophilic substitution reactions are a class of reactions where an electrophile replaces a substituent group in an aromatic compound. These reactions are widely encountered in synthesis and are crucial for the introduction of various functional groups into organic molecules.
Electrophilic Reagents in Oxidative Cleavage
Electrophilic reagents are often employed in oxidative cleavage reactions, where a compound is cleaved into two separate products. This type of reaction is valuable for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.
Electrophiles and Reactive Intermediates
Electrophiles are frequently involved in the formation of reactive intermediates, such as carbocations, which are highly reactive species with a positive charge. These intermediates play a crucial role in many organic reactions and are often stabilized through interactions with other molecules.
These 14 intriguing facts about electrophile provide a glimpse into the diverse and essential role they play in organic chemistry. Understanding the nature of electrophiles and their interactions with nucleophiles allows chemists to design and carry out a wide range of chemical reactions, enabling the synthesis of complex molecules with practical applications in various fields.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrophiles are fascinating chemical entities that play a crucial role in various chemical reactions. From their reactivity to their involvement in organic synthesis and drug development, electrophiles have captivated the interest of chemists worldwide. Understanding the nature and behavior of electrophiles can lead to breakthroughs in the field of chemistry and pave the way for innovative discoveries.Whether it’s their ability to attract electrons, their role in nucleophilic substitution, or their significance in electrophilic aromatic substitution, electrophiles are essential components in chemical reactions. Their reactivity and selectivity make them valuable tools for chemists to manipulate molecules and create new compounds.It is important to continue studying electrophiles and their diverse properties to uncover further applications and insights into chemical reactions. By expanding our knowledge of electrophiles, we can unlock even more possibilities in the field of chemistry and contribute to advancements in various areas, from drug development to materials science.So next time you encounter the term “electrophile,” remember the intriguing facts discussed in this article and appreciate the crucial role these compounds play in the world of chemistry.
FAQs
Q: What is an electrophile?
A: An electrophile is a chemical species that is electron-deficient and seeks to attract or accept electrons from other compounds to form a new bond.
Q: What are some examples of electrophiles?
A: Some examples of electrophiles include carbocations, nitrosonium ions, acyl halides, and electrophilic atoms such as hydrogen or chlorine in organic compounds.
Q: How are electrophiles involved in organic synthesis?
A: Electrophiles play a crucial role in organic synthesis by participating in reactions like nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic aromatic substitution, and addition reactions.
Q: Can electrophiles be used in drug development?
A: Yes, electrophiles can be used in drug development. They can target specific molecules or enzymes in the body, leading to the development of new drugs with desirable therapeutic effects.
Q: Are all electrophiles reactive?
A: Yes, electrophiles are generally reactive due to their electron-deficient nature. They are attracted to electron-rich species and tend to undergo reactions to acquire electrons and form stable compounds.
Electrophiles play crucial roles in chemical reactions, but their fascinating properties don't end there. Dive deeper into electrophilic substitution reactions and explore how these powerful compounds shape the world of organic chemistry. Nucleophilic addition reactions also hold intriguing secrets waiting to be uncovered. Continue your journey through the captivating realm of chemical reactivity and discover even more extraordinary facts about these essential building blocks of matter.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
