Chemical reactions are an integral part of the world we live in. They are responsible for the formation of compounds, the release of energy, and the transformation of matter. When studying chemical reactions, scientists use various tools and concepts to understand how they proceed and reach equilibrium. One such concept is the reaction quotient, commonly known as Q.
In this article, we will explore 13 enigmatic facts about reaction quotient (Q) and its significance in understanding chemical reactions. From its definition and calculation to its relationship with equilibrium constants and the conditions for a reaction to be at equilibrium, we will delve into the depths of this essential concept. So, get ready to unlock the mysteries surrounding reaction quotient and embark on a journey into the fascinating world of chemical equilibrium.
Key Takeaways:
- Q helps predict if a reaction will go forward or backward. When Q equals K, the reaction is at equilibrium. If Q is greater than K, it shifts towards the reactants; if less, towards the products.
- Changes in pressure and temperature can affect Q and the direction of a reaction. Catalysts don’t change Q, but they speed up reactions. When Q equals K, it’s dynamic equilibrium.
What is Reaction Quotient (Q)?
The reaction quotient (Q) is a mathematical expression that determines the relative concentrations of reactants and products within a chemical reaction at any given moment. It provides insights into whether a reaction is at equilibrium or if it will proceed forward or backward to reach equilibrium.
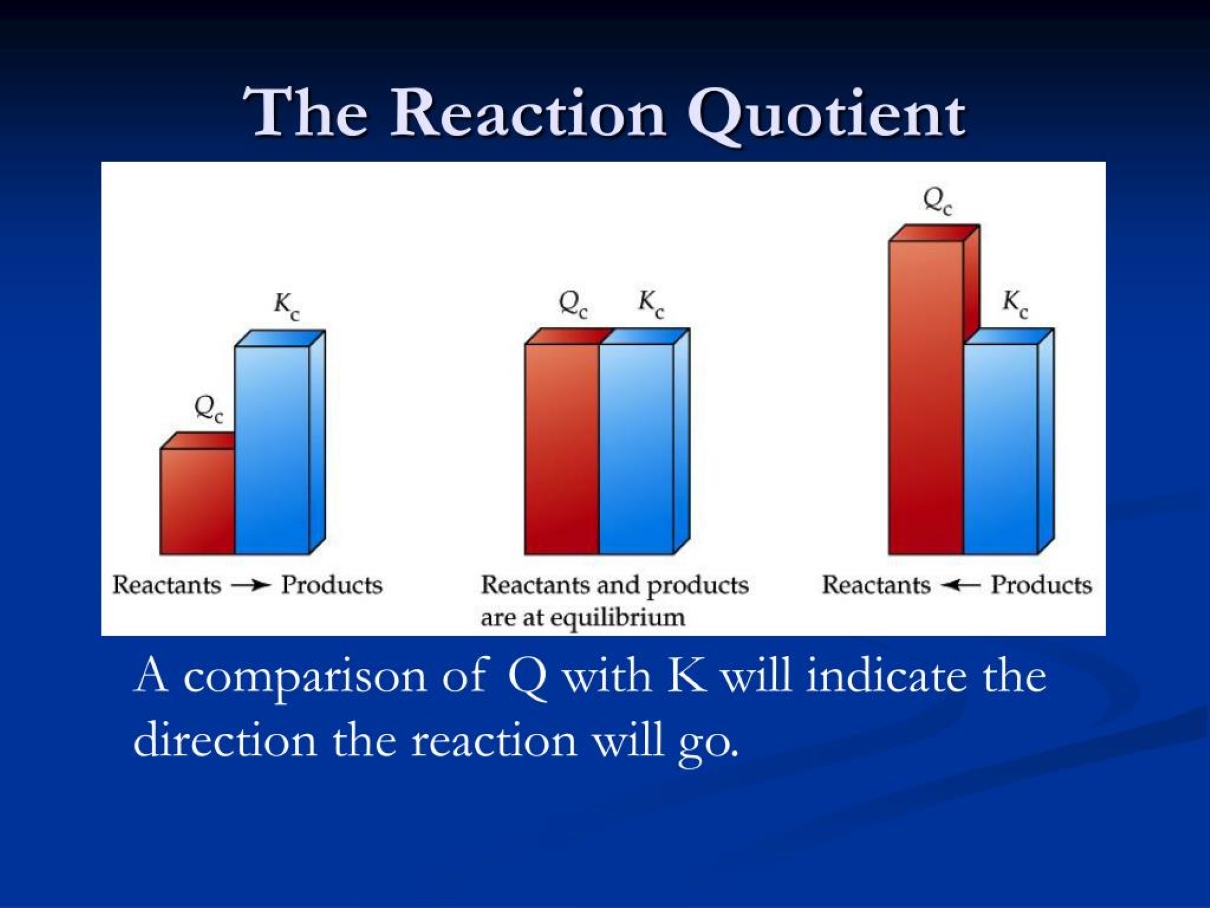
Q vs. K – Understanding the Difference
Q and K are both expressions involving concentrations of reactants and products. However, while K (equilibrium constant) describes the concentrations at equilibrium, Q describes the concentrations at any point during the reaction. When Q is equal to K, the reaction is at equilibrium.
Q and Direction of Reaction
Comparing Q to K helps determine the direction in which a reaction will proceed. If Q is greater than K, the reaction will shift towards the reactants. Conversely, if Q is less than K, the reaction will shift towards the products.
Calculating Q
To calculate Q, we use the same formula as the equilibrium constant. However, instead of using equilibrium concentrations, we use the concentrations of reactants and products at any given moment during the reaction.
Relationship between Q and Initial Concentrations
Q can be calculated using initial concentrations of reactants and products. This allows us to predict the direction a reaction will proceed based on the initial conditions.
Q and Solids/Liquids
When calculating Q, the concentrations of solids and liquids are not included in the expression since their concentrations remain constant and do not significantly affect the equilibrium.
Q and Gases
For reactions involving gases, Q can be calculated using either partial pressures or concentrations, depending on the given data and the information needed.
Q and Pure Solids/Liquids
When pure solids or liquids are involved in a reaction, their concentrations are considered to be constant and are not included in the calculation of Q.
Using Q to Predict Reaction Shifts
By comparing Q to K, we can predict the direction a reaction will shift to reach equilibrium. If Q is greater than K, the reaction will shift to the left (towards the reactants). If Q is less than K, the reaction will shift to the right (towards the products).
Q and Pressure Changes
Changes in pressure can affect Q and the direction of the reaction. Increasing the pressure generally favors the side with fewer moles of gas, while decreasing the pressure favors the side with more moles of gas.
Q and Temperature Changes
Changes in temperature can also impact Q and the direction of the reaction. The reaction is exothermic if it releases heat, and increasing the temperature will favor the reactants. On the other hand, if the reaction is endothermic and absorbs heat, increasing the temperature will favor the products.
Q and Catalysts
Catalysts do not affect the value of Q. They increase the rate of the reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
Q and Dynamic Equilibrium
When Q is equal to K, the system is at dynamic equilibrium, where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time.
These 13 enigmatic facts about reaction quotient (Q) shed light on its significance in determining the direction and extent of chemical reactions. Understanding Q is crucial to comprehend the intricacies of chemical equilibrium and the factors influencing reaction dynamics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the reaction quotient (Q) is a powerful tool in understanding the direction and progress of chemical reactions. It helps us determine whether a reaction is at equilibrium or if it will proceed towards the formation of more reactants or products. By comparing the Q value to the equilibrium constant (K), we can predict the behavior of a reaction under different conditions.Throughout this article, we have uncovered several enigmatic facts about the reaction quotient (Q). We have learned how to calculate it, interpret its value, and its significance in determining the feasibility of a reaction. We have also explored the relationship between Q and K, and the factors that can affect the value of Q.Understanding the concept of reaction quotient (Q) is essential for a deeper comprehension of chemical equilibrium and reaction kinetics. It allows chemists to manipulate reaction conditions to achieve desired outcomes. By harnessing the power of Q, we can control and optimize chemical reactions in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental chemistry.So, next time you come across a chemical reaction, remember the enigmatic nature of the reaction quotient (Q) and its role in unlocking the secrets of chemical systems.
FAQs
Q: What is the reaction quotient (Q)?
A: The reaction quotient (Q) is a numerical value that indicates the relative amounts of products and reactants present in a chemical reaction at a given point in time.
Q: How is the reaction quotient (Q) calculated?
A: The reaction quotient (Q) is calculated by substituting the concentrations (or partial pressures) of the reactants and products into the equilibrium expression, just like the equilibrium constant (K).
Q: How is the direction of a reaction determined using the reaction quotient (Q)?
A: If the reaction quotient (Q) is less than the equilibrium constant (K), the reaction proceeds in the forward direction to form more products. If Q is greater than K, the reaction proceeds in the reverse direction to form more reactants. When Q is equal to K, the reaction is at equilibrium.
Q: Can the reaction quotient (Q) change?
A: Yes, the reaction quotient (Q) can change as the concentrations of reactants and products change with time. It can be recalculated whenever the system reaches a new set of concentrations.
Q: What are the factors that can affect the value of the reaction quotient (Q)?
A: Changes in temperature, pressure, and concentrations of reactants and products can all influence the value of the reaction quotient (Q).
Reaction quotients provide valuable insights into chemical equilibrium, a fascinating concept explored in our article "10 Captivating Facts About Chemical Equilibrium." Dive deeper into the world of chemistry by discovering how Le Chatelier's principle influences reaction systems, as detailed in "14 Astonishing Facts About Le Chatelier's Principle." For a comprehensive understanding of the subject, don't miss "17 Enigmatic Facts About Physical Chemistry," which unveils the mysteries of this intriguing branch of science.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
