Complexometric titration is a fascinating technique used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of metal ions in a solution. This method involves the use of complexing agents, which form stable complexes with metal ions, leading to a visible color change or other indicators. The process relies on the principle of chelation, where the complexing agent forms multiple coordinate bonds with the metal ion, resulting in the formation of a highly stable complex.
In this article, we will explore 17 intriguing facts about complexometric titration that highlight its importance and applications in various fields. From its historical roots to its modern-day advancements, complexometric titration offers a precise and reliable means of analyzing metal ions in complex mixtures. So, let’s dive in and unravel the fascinating world of complexometric titration!
Key Takeaways:
- Complexometric titration is a cool chemistry technique that measures metal ions in solutions using chelating agents and indicators. It’s used in industries like pharmaceuticals and environmental monitoring.
- pH, chelating agents, and metallochromic dyes are key players in complexometric titration, helping scientists analyze metal ions in solutions for various applications like water hardness and drug quality control.
What is Complexometric Titration?
Complexometric titration is a technique used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of metal ions in a solution. It involves the formation of a complex between the metal ion and a chelating agent, which can be measured using indicators or instruments.
Versatility of Complexometric Titration
Complexometric titration can be used to analyze a wide range of metal ions, including transition metals, alkaline earth metals, and heavy metals. It is particularly useful in industries such as pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and food analysis.
Chelating Agents in Complexometric Titration
The success of complexometric titration relies on the use of chelating agents, which are compounds capable of forming stable complexes with metal ions. Common chelating agents include ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and its derivatives.
Indicators in Complexometric Titration
Indicators, such as metallochromic dyes, are used to detect the endpoint of complexometric titration. These indicators undergo a color change when they bind to the metal ion, signaling that all the metal ions have been complexed.
EDTA Complexometric Titration
EDTA is one of the most widely used chelating agents in complexometric titration. It forms stable complexes with metal ions, and the formation constants of these complexes are well-known, making it suitable for quantitative analysis.
Complexometric Titration vs. Acid-Base Titration
Unlike acid-base titration, which involves the neutralization of an acid or base, complexometric titration is based on the formation and stability of complexes. It offers a different perspective on analyzing metal ions in solution.
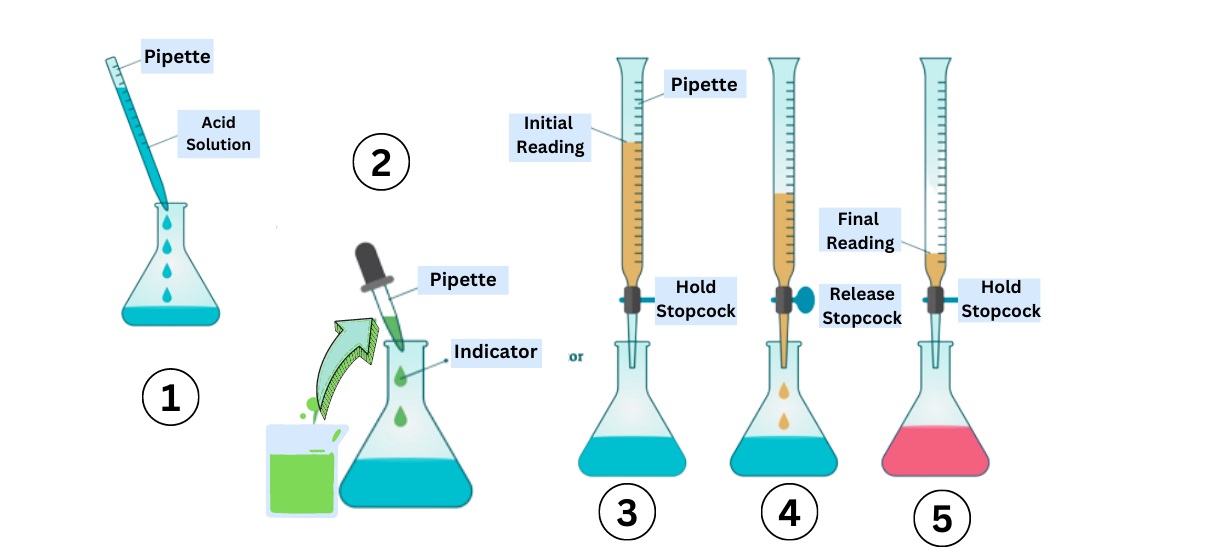
Complexometric Titration Steps
Complexometric titration typically involves adding a known concentration of chelating agent to the solution containing the metal ions. The solution is then titrated until the endpoint is reached, indicating the completion of the complex formation.
Role of pH in Complexometric Titration
pH plays a crucial role in complexometric titration as it determines the stability of the metal ion complexes. The pH is carefully controlled to ensure optimal complex formation and accurate results.
Complexometric Titration Applications
Complexometric titration finds applications in various fields, including the determination of water hardness, metal content in pharmaceuticals, analysis of metal pollutants in environmental samples, and quality control in food and beverage industries.
Automation in Complexometric Titration
Modern complexometric titration techniques have been automated using sophisticated instruments known as complexometric titrators. These instruments offer increased accuracy, precision, and efficiency in the analysis process.
Limitations of Complexometric Titration
One of the limitations of complexometric titration is the interference from other metal ions present in the solution. Selectivity and masking agents are often employed to minimize these interferences and ensure accurate results.
Alternative Complexometric Methods
Aside from traditional titrimetric methods, complexometric titration can also be performed using spectrophotometry, which measures the absorbance of the metal-ion complex, or voltammetry, which measures the current generated by the complex.
Complexometric Titration in Environmental Analysis
Complexometric titration is widely used in environmental analysis to determine the concentration of metal pollutants in water, soil, and air samples. It helps in assessing the environmental impact and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Complexometric Titration and Water Hardness
Complexometric titration is commonly employed to determine water hardness, which is caused by the presence of calcium and magnesium ions. The total hardness can be calculated based on the amount of chelating agent consumed in the titration process.
Complexometric Titration in Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical companies utilize complexometric titration to analyze the metal content in drug formulations. This ensures the quality, purity, and stability of the drugs, as well as compliance with regulatory standards.
Complexometric Titration and Food Analysis
Complexometric titration is applied in the food and beverage industry to determine the presence of metal contaminants or additives. It helps in maintaining the safety and quality of food products for consumer consumption.
Research and Advancements in Complexometric Titration
Ongoing research focuses on improving complexometric titration techniques, exploring new chelating agents, developing selective sensors for specific metal ions, and enhancing the automation and miniaturization of complexometric titration methods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, complexometric titration is a fascinating analytical technique widely used in the field of chemistry. It provides valuable information about the concentration and composition of metal ions in solutions. Through the use of complexing agents and indicators, complexometric titration offers a precise and reliable method for determining metal ion concentrations.
The process involves the formation of stable complexes between metal ions and complexing agents, which can be measured using various techniques like colorimetry or potentiometry. Complexometric titration has a wide range of applications, including environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical analysis, and quality control in industrial processes.
Understanding the principles and techniques involved in complexometric titration can greatly enhance a chemist’s ability to accurately analyze solutions and determine the presence of metal ions. With its versatility and accuracy, complexometric titration continues to be an indispensable tool in the field of chemistry.
FAQs
1. What is complexometric titration?
Complexometric titration is an analytical technique used to determine the concentration of metal ions in solutions. It involves the formation of stable complexes between metal ions and complexing agents.
2. How does complexometric titration work?
Complexometric titration works by adding a solution of a known complexing agent to the sample solution containing the metal ions. The complexing agent binds with the metal ions to form a stable complex, which can be detected using various methods like colorimetry or potentiometry.
3. What are some common complexing agents used in complexometric titration?
Some common complexing agents used in complexometric titration include ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), diethylentriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA), and Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA).
4. What are the applications of complexometric titration?
Complexometric titration has wide applications in various industries such as environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical analysis, and quality control in industrial processes. It is used to determine the concentration of metal ions in water samples, identify impurities in drugs, and monitor the quality of plating baths.
5. What are the advantages of complexometric titration?
Complexometric titration offers several advantages, including high accuracy, wide applicability to different types of metal ions, and the ability to determine the concentration of metal ions even in complex mixtures.
6. Can complexometric titration be automated?
Yes, complexometric titration can be automated using instruments like titrators, which accurately measure the volume of the titrant added and calculate the concentration of metal ions in the sample solution.
Complexometric titration's fascinating, but there's more to explore in chemistry! Dive into analytical chemistry and its captivating facts. Discover extraordinary truths about indicators used in acid-base titrations. Struggling with water hardness? Check out our top water softener recommendations.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


