The standard electrode potential is a fundamental concept in electrochemistry that measures the ability of an electrode to gain or lose electrons during a redox reaction. It plays a crucial role in determining the spontaneity and direction of electron flow in chemical reactions. While it may sound like a complex topic, learning about standard electrode potential can be both fascinating and mind-boggling.
In this article, we will delve into the world of standard electrode potential and explore some unbelievable facts that will surely amaze you. From the astonishing values of standard electrode potentials to their practical applications, we will unravel the mysteries behind these electrical phenomena. So, get ready to be electrified with these 16 unbelievable facts about standard electrode potential!
Key Takeaways:
- Standard electrode potential determines how likely metals are to rust or corrode, helping scientists predict and prevent damage to metal objects.
- By comparing standard electrode potentials, scientists can rank metals by reactivity and use this knowledge to design better batteries and fuel cells.
Standard electrode potential determines the reactivity of metals.
Standard electrode potential is a measure of the tendency of a metal to lose or gain electrons and undergo oxidation or reduction reactions.
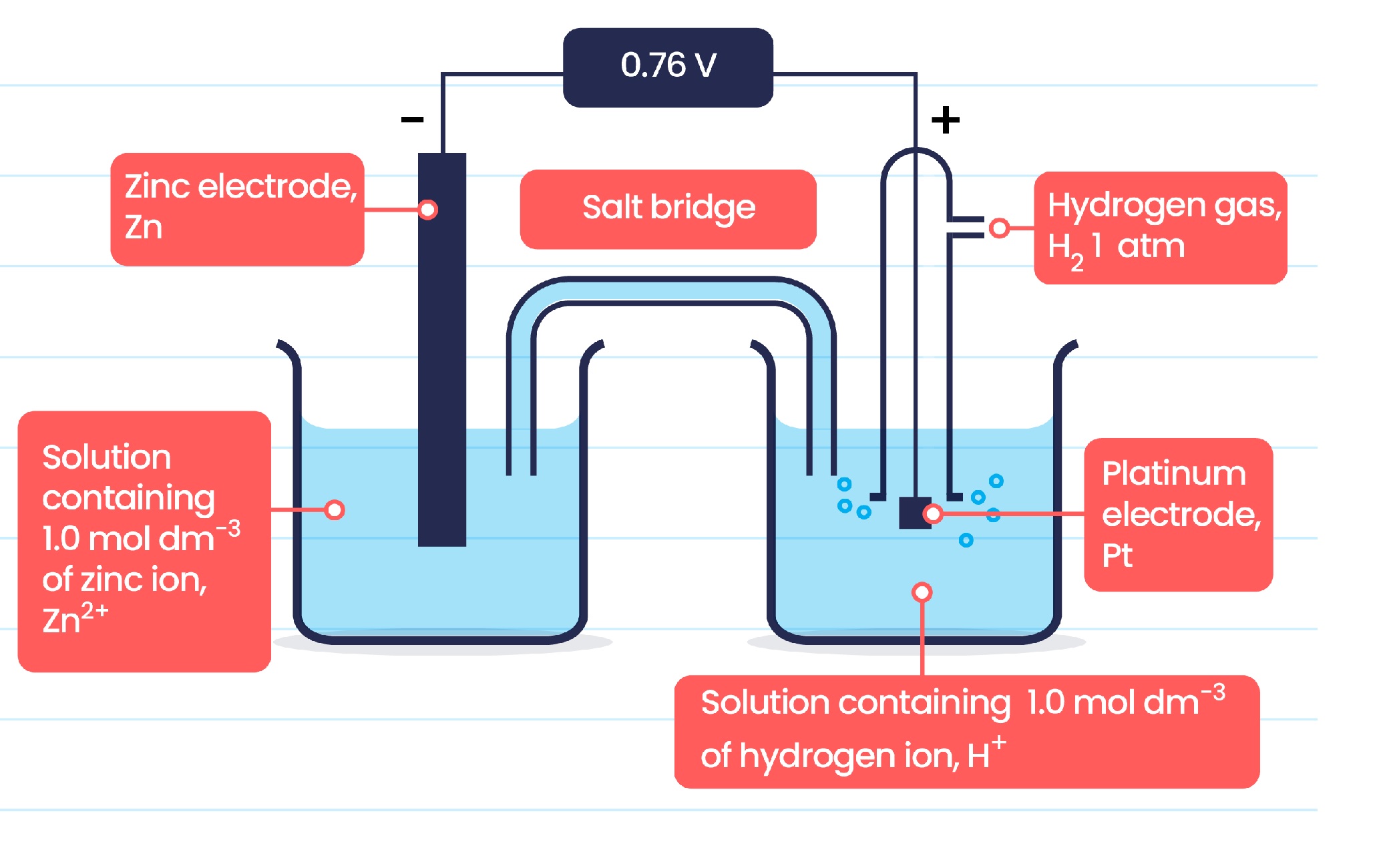
The standard hydrogen electrode is used as a reference point.
The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is assigned a standard electrode potential of 0 volts and is used as a reference point to compare the electrode potentials of other elements.
The more positive the standard electrode potential, the greater the tendency for reduction.
A positive standard electrode potential indicates a greater tendency for reduction, while a negative standard electrode potential indicates a greater tendency for oxidation.
Standard electrode potentials are measured under standard conditions.
Standard electrode potentials are determined under standard conditions of temperature (298K), pressure (1 atmosphere) and concentration (1 molar).
The Nernst equation relates standard electrode potential to concentration and temperature.
The Nernst equation allows for the calculation of electrode potential under non-standard conditions, taking into account the concentration of reactants and products and the temperature.
The standard electrode potential of hydrogen is crucial in determining cell voltages.
The standard electrode potential of hydrogen is involved in many electrochemical reactions and is used to calculate the cell voltages of various redox reactions.
The standard electrode potential of an element can vary depending on the phase.
The standard electrode potential of an element can differ depending on whether it is in its solid, liquid, or gaseous form.
Standard electrode potentials are used to predict the feasibility of redox reactions.
If the difference in standard electrode potentials between two half-cells is positive, the reaction is likely to be spontaneous. If the difference is negative, an external voltage source is needed to drive the reaction.
The standard electrode potential of an element can change with pH.
The standard electrode potential of some elements, such as manganese and chromium, can vary depending on the pH of the solution.
Standard electrode potentials can be used to rank metals in order of reactivity.
By comparing the standard electrode potentials of different metals, it is possible to determine their relative reactivity and their suitability for various applications.
Standard electrode potentials are essential in understanding corrosion processes.
The knowledge of standard electrode potentials helps in predicting and preventing corrosion of metals by understanding their tendency to undergo oxidation.
Changes in temperature can affect standard electrode potentials.
Standard electrode potentials are temperature-dependent, and as the temperature increases, the electrode potentials can change.
Standard electrode potentials can be used to calculate the equilibrium constant.
By using the Nernst equation and the standard electrode potentials of the reactants and products, the equilibrium constant of a reaction can be determined.
The standard electrode potential of lithium is the most negative.
Lithium has the most negative standard electrode potential among all the elements, indicating its strong tendency to undergo oxidation.
Variation in standard electrode potentials is observed for different oxidation states of an element.
The standard electrode potential of an element can vary depending on its oxidation state, as different oxidation states involve different electron transfer processes.
Standard electrode potentials are used in the construction of electrochemical cells.
Standard electrode potentials are essential in designing and building electrochemical cells for various applications, including batteries and fuel cells.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding standard electrode potential is crucial in the field of chemistry. It provides valuable insights into the stability and reactivity of redox reactions. The concept of standard electrode potential helps us predict the direction in which a reaction will proceed and determine the feasibility of electrochemical processes.
Through this article, we have explored 16 unbelievable facts about standard electrode potential. From the origins of the concept to its applications in various fields, we have delved into the fascinating world of electrochemistry. We have discovered how electrode potentials are measured, how they relate to the thermodynamics of reactions, and the factors that affect their value.
By understanding standard electrode potential, we have gained an appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern electrochemical processes. Whether it is in the development of new batteries, the study of corrosion, or the analysis of redox reactions in biological systems, electrode potentials play a vital role in advancing our understanding of the world around us.
FAQs
Q: What is standard electrode potential?
A: Standard electrode potential is a measure of the tendency of a half-cell to undergo reduction compared to a standard hydrogen electrode under standard conditions.
Q: How is standard electrode potential measured?
A: Standard electrode potential is measured using a reference electrode, such as the standard hydrogen electrode, and a working electrode of interest.
Q: What is the significance of standard electrode potential?
A: Standard electrode potential allows us to predict the direction of redox reactions and determine the feasibility of electrochemical processes.
Q: Can standard electrode potential change?
A: Standard electrode potential can change with temperature and concentration, but it remains constant under standard conditions.
Q: How does standard electrode potential relate to the thermodynamics of reactions?
A: Standard electrode potential is directly related to the Gibbs free energy change of a reaction, providing insights into its spontaneity.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
