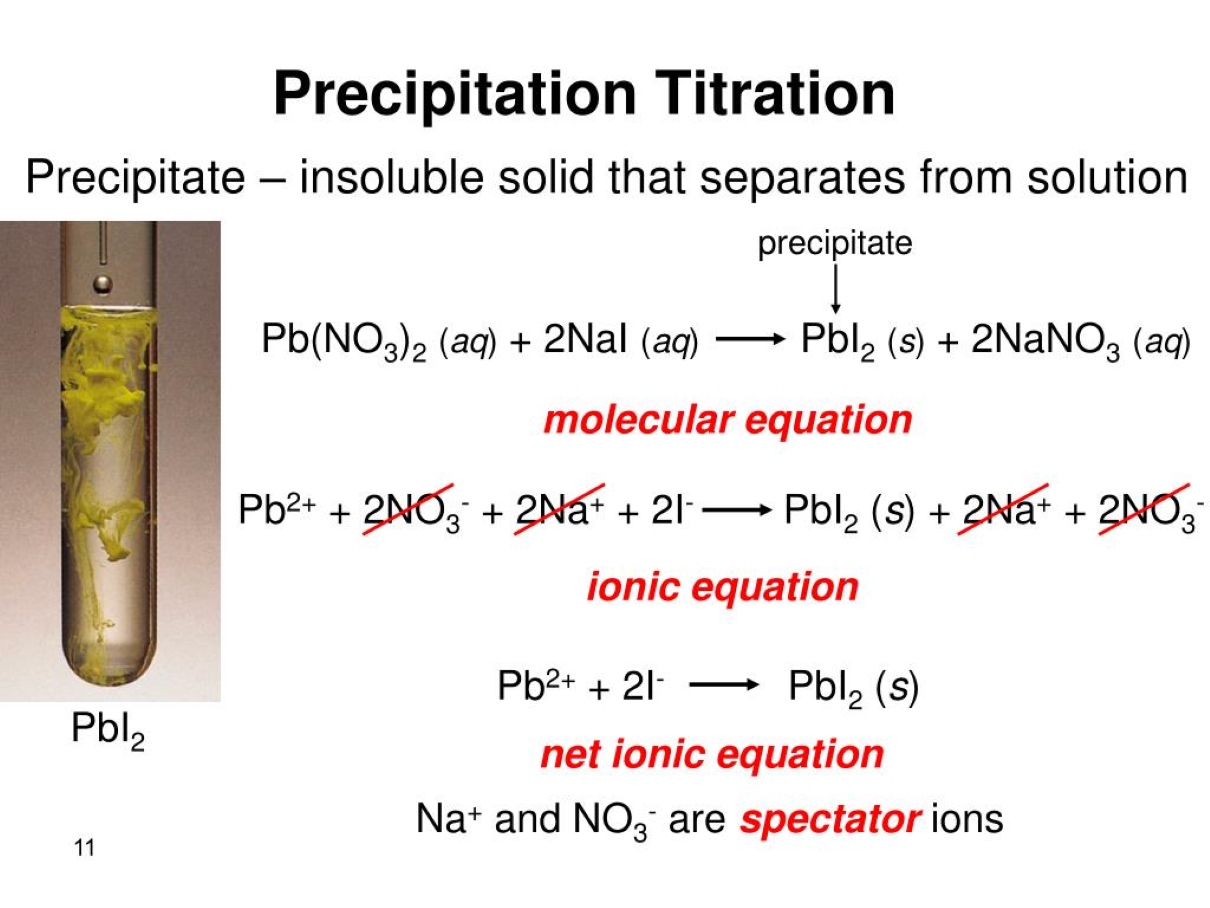
Precipitation titration is a widely used technique in analytical chemistry for determining the concentration of a substance in a solution. It involves the formation of a solid precipitate through a chemical reaction between the analyte and a titrant. This method is particularly useful for measuring the concentration of ions, such as chloride, sulfate, and bromide, in various samples.
Key Takeaways:
- Precipitation titration is a common and versatile technique used to determine the concentration of ions in a solution, making it essential for environmental and pharmaceutical analysis.
- Factors such as pH and temperature can influence the accuracy of precipitation titration, highlighting the need for careful control of these variables to obtain reliable results.
Precipitation titration is a commonly used analytical technique.
Precipitation titration is a widely used technique in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of an analyte in a solution. It involves the formation of a solid precipitate when a titrant reacts with the analyte.
The titrant and analyte react to form an insoluble product.
In precipitation titration, the titrant is added to the analyte solution to form an insoluble product (precipitate) that can be easily detected and measured. This allows for the determination of the analyte concentration.
Common precipitating agents used in precipitation titration include silver nitrate and potassium iodide.
Silver nitrate and potassium iodide are frequently used as precipitating agents in precipitation titrations due to their ability to form insoluble compounds with various analytes.
Precipitation titration can be used to determine the concentration of ions in a solution.
By selecting a suitable precipitating agent, precipitation titration can be employed to determine the concentration of specific ions in a solution. This is particularly useful in environmental and pharmaceutical analysis.
Gravimetric analysis is often used to determine the endpoint in precipitation titrations.
Gravimetric analysis, which involves measuring the mass of the formed precipitate, is commonly used to determine the endpoint in precipitation titration. The endpoint is reached when no further precipitation occurs.
Precipitation titration can be performed using manual or automated techniques.
Precipitation titration can be carried out manually, where reagents are added by hand, or using automated techniques like automated burettes, which improve accuracy and precision.
Precipitation titration can be affected by factors such as pH and temperature.
The pH and temperature of the solution can influence the formation of the precipitate in precipitation titration. Therefore, careful control of these factors is crucial for accurate results.
Back titration is a variation of precipitation titration.
In back titration, an excess of the titrant is added to react with the analyte, and then the remaining excess titrant is titrated with another reagent. This technique is useful when direct titration is not feasible.
Precipitation titration can be used to determine the concentration of chloride ions in a sample.
AgNO3 is commonly used as a titrant to determine the concentration of chloride ions in a sample. The formation of a white precipitate of AgCl indicates the endpoint of the titration.
Precipitation titration is an essential technique in pharmaceutical analysis.
Precipitation titration is widely utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the analysis of drug formulations, ensuring the accurate determination of active ingredients and impurities.
Precipitation titration can be used for the determination of halides, sulfates, and many other analytes.
Precipitation titration is a versatile technique that can be applied to the determination of various analytes, including halides, sulfates, and many other ionic compounds.
Kaliumnitroferrocyanide is a precipitating agent used in precipitation titration of iron(II) ions.
Kaliumnitroferrocyanide, commonly known as potassium nitroprusside, is frequently used as a precipitating agent in the precipitation titration of iron(II) ions (Fe2+).
Precipitation titration is based on the principle of chemical equilibria.
The formation of a precipitate in the titration reaction is governed by the principles of chemical equilibria. The solubility product constant (Ksp) plays a crucial role in this process.
Complexometric titration can be used in conjunction with precipitation titration.
Complexometric titration, which involves the formation of a complex between the analyte and a reagent, can be combined with precipitation titration to enhance selectivity and accuracy.
Precipitation titration is widely used in environmental analysis.
Precipitation titration is an important technique in environmental analysis, allowing for the determination of pollutants and contaminants in water and soil samples.
Mohr’s method is commonly used for the precipitation titration of chloride ions.
Mohr’s method, which utilizes silver nitrate and potassium chromate as indicators, is frequently employed in the precipitation titration of chloride ions (Cl-) due to the formation of a red precipitate of silver chromate.
Precipitation titration is a cost-effective and widely employed analytical technique.
Due to its simplicity, versatility, and relatively low cost, precipitation titration remains a popular choice in various analytical applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, precipitation titration is a fascinating and crucial technique in the field of chemistry. It involves the formation of a solid precipitate through a chemical reaction, which is used to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution. By carefully controlling the reaction conditions and measuring the amount of precipitate formed, scientists can accurately analyze various compounds and ions in a solution.
Precipitation titration offers several advantages such as simplicity, affordability, and wide applicability across different industries. Its versatility makes it an essential tool in environmental analysis, drug development, and quality control in manufacturing processes. The precise and reliable results obtained through precipitation titration contribute to advancements in various scientific fields.
Understanding the fascinating facts about precipitation titration not only enhances our knowledge of chemical analysis techniques but also highlights the vital role it plays in scientific research and everyday life applications.
FAQs
Q: What is precipitation titration?
A: Precipitation titration is a technique used in chemistry to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution by measuring the formation of a solid precipitate through a chemical reaction.
Q: How is precipitation titration performed?
A: Precipitation titration involves adding a titrant, a solution of known concentration, to the analyte solution until a reaction occurs and a precipitate forms. The amount of titrant needed to reach the endpoint is then used to calculate the concentration of the analyte.
Q: What are the advantages of precipitation titration?
A: Precipitation titration is simple, affordable, and widely applicable. It can be used for a range of compounds and ions, making it a versatile tool in various industries such as environmental analysis, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
Q: What are some real-life applications of precipitation titration?
A: Precipitation titration is used in environmental analysis to determine pollutant concentrations in water samples, in pharmaceutical analysis to assess drug purity, and in quality control processes to monitor the concentration of ions in manufacturing operations.
Q: How does precipitation titration contribute to scientific research?
A: Precipitation titration provides precise and reliable results, enabling scientists to analyze and understand chemical compounds and ions in solution. This knowledge contributes to advancements in various scientific fields and helps in the development of new drugs, environmental monitoring, and quality control techniques.
Precipitation titration, a fascinating analytical technique, unravels the mysteries of chemical composition. Delving deeper into the world of analytical chemistry reveals even more captivating facts waiting to be discovered. Techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) offer powerful tools for unraveling the secrets hidden within substances. Exploring these methods further opens up a treasure trove of knowledge, enabling us to understand the intricate workings of matter at a fundamental level. Embark on a journey through the realms of analytical chemistry and chemical analysis with AAS, where each fact you uncover brings you one step closer to mastering the art of chemical analysis.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
