Isotopes are a fascinating aspect of the world of chemistry. These variations of elements have unique properties that make them essential in various fields, such as medicine, energy production, and environmental studies. Understanding isotopes is crucial for scientists and researchers as they delve deeper into the intricacies of atomic structure and chemical reactions.
In this article, we will explore 18 astounding facts about isotopes that will leave you in awe of the wonders of the atomic world. From their discovery to their applications, isotopes have a significant impact on our daily lives. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the captivating world of isotopes!
Key Takeaways:
- Isotopes are different versions of elements with unique properties. They help in dating fossils, treating diseases, and even solving crimes. They are like secret agents with special missions in science!
- Isotopes are like cosmic detectives, revealing secrets about the universe, Earth, and even ancient civilizations. They are crucial in fields like medicine, energy, and environmental studies, making them superstars of the scientific world!
What is an Isotope?
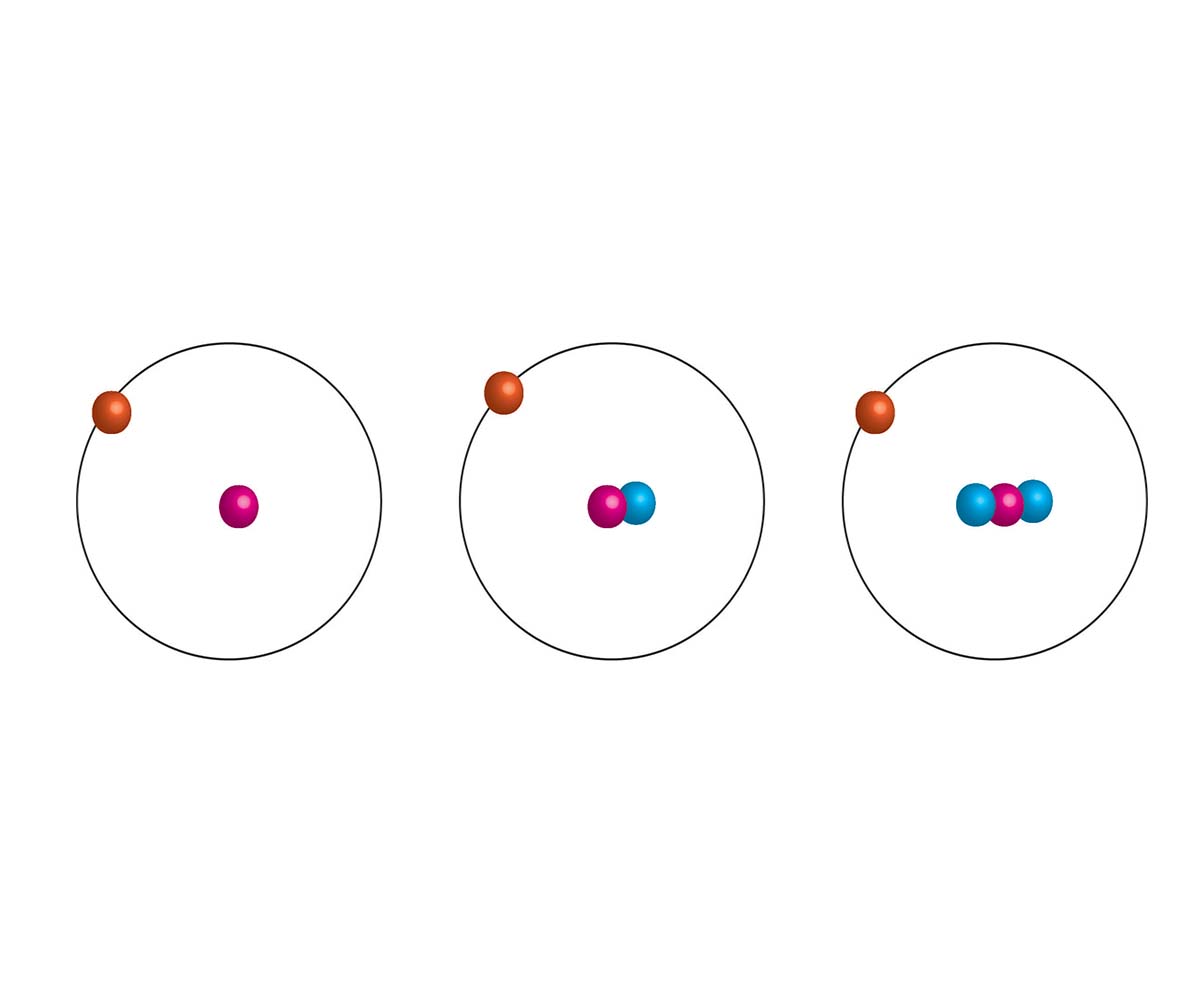
An isotope is a variant of a particular chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in its nucleus. This difference in neutron count gives each isotope a unique mass number. Isotopes can be stable or unstable, and they play a crucial role in several scientific fields, including chemistry, physics, and geology.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, while the mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are two isotopes of carbon, with 6 protons each but 6 and 8 neutrons, respectively.
Stable Isotopes
Stable isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay and do not change over time. They have a long half-life, making them useful for various applications, such as tracing chemical reactions, studying biological processes, and determining the origin of elements in the environment.
Radioactive Isotopes
Radioactive isotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive decay, emitting radiation in the form of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. They have various applications in medicine, including cancer treatment, diagnostic imaging, and sterilization of medical equipment.
Carbon Dating
Carbon-14, an isotope of carbon, is widely used in archaeological and geological dating. By measuring the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in organic materials, scientists can determine the age of once-living organisms and estimate the age of fossils and artifacts.
Isotopes in Medicine
Medical isotopes are crucial in diagnosing and treating various diseases. For example, technetium-99m is used in nuclear medicine imaging, while iodine-131 is employed in the treatment of thyroid disorders.
Isotopes in Agriculture
Stable isotopes play an important role in agriculture and food science. By tracking isotopic ratios, scientists can determine the origin, authenticity, and quality of food products. Isotopic analysis also helps in studying nutrient uptake in plants and understanding food chains.
Isotopes in Environmental Studies
Isotopic analysis provides valuable insights into environmental processes such as the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nutrient cycles. It helps scientists understand climate change, pollution sources, and ecosystem dynamics.
Isotopes in Forensic Science
Forensic scientists use isotopic analysis to determine the origin and history of evidence such as bones, teeth, hair, and soils. Isotopic signatures can provide clues about a person’s geographic origin, diet, and even travel history.
Isotopes in Geology
Isotope analysis is used extensively in geology to study the age of rocks, minerals, and geological events. It helps determine the timing of volcanic eruptions, the formation of minerals, and the dating of ancient geological formations.
Isotopes in Energy Production
Nuclear power plants use isotopes, such as uranium-235 and plutonium-239, in the process of nuclear fission to generate electricity. Isotope separation techniques are crucial for producing enriched fuel and ensuring the safe operation of nuclear reactors.
Heavy Water
Heavy water, or deuterium oxide, is an isotopic form of water in which the hydrogen atoms are replaced by deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen with both a proton and a neutron. Heavy water is used in nuclear reactors as a neutron moderator.
Isotope Hydrology
Isotopic analysis of water is essential in hydrology to study the movement and origin of groundwater, understand water availability, and manage water resources effectively. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in water molecules serve as tracers for tracking the water cycle.
Isotopes in Climate Studies
Isotopic analysis of ice cores, tree rings, and sediment records provides valuable insights into past climate conditions. By studying the isotopic composition of these archives, scientists can reconstruct temperature changes, atmospheric composition, and even ancient weather patterns.
Isotopes in Cosmology
Isotopes are fundamental to understanding the origin and evolution of the universe. By studying the abundance of isotopes in stars, galaxies, and cosmic rays, astronomers can unravel the mysteries of stellar nucleosynthesis and the formation of elements in the cosmos.
Isotope Hydrology
Isotopic analysis of water is essential in hydrology to study the movement and origin of groundwater, understand water availability, and manage water resources effectively. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in water molecules serve as tracers for tracking the water cycle.
Application in Anthropology
Isotope analysis has revolutionized the field of anthropology by providing insights into ancient diets, migration patterns, and social structures. By studying the isotopic composition of human remains and archaeological artifacts, scientists can uncover fascinating details about past civilizations.
Isotopes in Space Exploration
Isotopes are vital in studying extraterrestrial materials and understanding the formation of planets and asteroids. Isotopic analysis of meteorites and lunar samples has shed light on the early history of the solar system and the processes that shaped celestial bodies.
Conclusion
Isotopes are truly remarkable and fascinating elements. From their impact on various scientific fields to their applications in medicine and industry, isotopes have proven to be invaluable. We have learned that isotopes are variants of an element that have different numbers of neutrons, leading to unique properties and behaviors. These distinct characteristics allow researchers to study and manipulate isotopes to uncover new insights into atomic structure and chemical processes.
Additionally, isotopes play a crucial role in fields such as radiocarbon dating, nuclear medicine, and sustainable energy production. Their ability to act as tracers and markers enables scientists to track chemical reactions, monitor pollutants, and diagnose medical conditions. Isotopes are also utilized in various industries, including agriculture, forensics, and environmental sciences.
Understanding the properties and applications of isotopes is essential for researchers, students, and anyone interested in the world of chemistry. By delving deeper into the study of isotopes, we can unlock new findings and advancements that contribute to our understanding of the natural world and improve our everyday lives.
FAQs
Q: What is an isotope?
An isotope is a variant of an element that has the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in its nucleus.
Q: How are isotopes used in medicine?
Isotopes are used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic purposes, such as in PET scans or radioisotope therapy to treat certain types of cancer.
Q: What isotope is used in radiocarbon dating?
Carbon-14 is the isotope used in radiocarbon dating to determine the age of ancient artifacts, fossils, and archaeological sites.
Q: How are isotopes used in environmental science?
Isotopes are used as tracers to track the movement and fate of various substances in the environment, helping scientists understand pollution sources and environmental dynamics.
Q: Are all elements found naturally as isotopes?
Yes, all elements have naturally occurring isotopes, although some isotopes may only exist in trace amounts.
Q: Can isotopes be used to detect counterfeit money?
Yes, isotopes can be used to detect counterfeit money. Certain isotopes, such as stable isotopes of elements like sulfur or oxygen, can act as unique signatures that can be used to identify counterfeit banknotes.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
