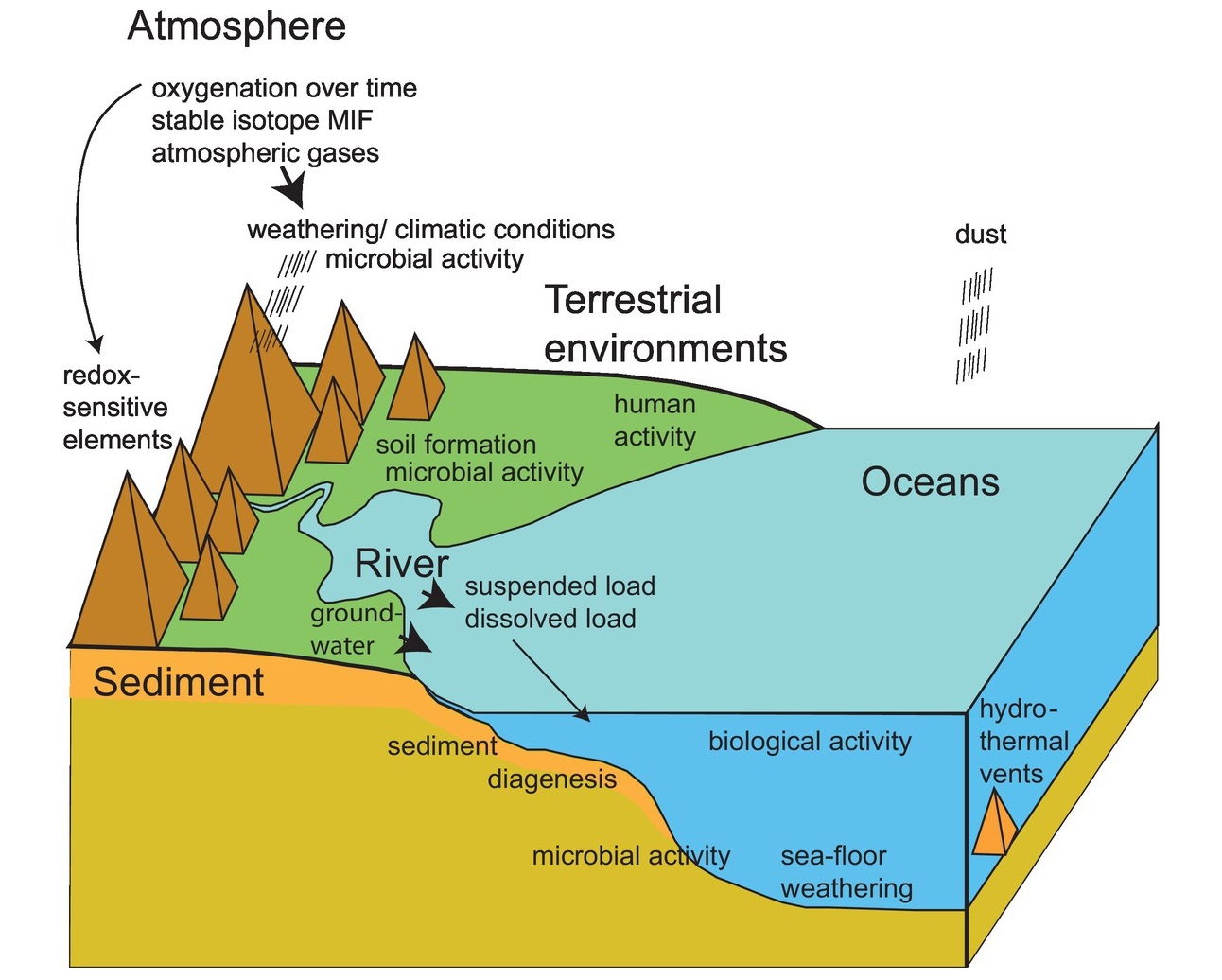
Geochemistry is a fascinating field that combines the principles of chemistry and geology to understand the composition, structure, and processes of the Earth. It explores how elements and compounds are distributed and interact within various natural systems, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. From the formation of rocks to the dynamics of volcanic eruptions, geochemistry unravels the mysteries of the Earth’s past and present.
In this article, we present 15 enigmatic facts about geochemistry that will ignite your curiosity and deepen your understanding of this captivating discipline. Get ready to delve into the world of isotopes, mineral formations, elemental abundances, and much more. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast, a geology student, or simply someone intrigued by the wonders of the Earth, these intriguing facts will shed light on the intricacies of geochemistry.
Key Takeaways:
- Diamonds are made of pure carbon, formed deep within the Earth. Geochemistry helps us understand their origin and value, shedding light on Earth’s hidden treasures.
- Geochemistry unravels Earth’s mysteries, from ancient environments to natural hazards. It plays a vital role in sustainable resource management and understanding the solar system’s formation.
Diamonds are made of pure carbon.
Diamonds, known for their brilliance and value, are formed deep within the Earth’s mantle under intense heat and pressure. They are composed solely of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice structure. This unique composition gives diamonds their hardness and remarkable optical properties.
The composition of seawater is predominantly made up of water and dissolved salts.
Seawater, a vital part of Earth’s hydrosphere, contains a multitude of dissolved substances. However, the most abundant elements found in seawater are oxygen and hydrogen, forming water molecules, along with various salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, and calcium carbonate.
Geochemistry plays a crucial role in studying the formation and evolution of Earth’s crust.
By analyzing rocks, minerals, and geological processes, geochemists can unravel the intricate history of our planet. They study how elements and compounds interact and transform over time, shedding light on the geological phenomena that shape Earth’s crust.
Volcanoes provide valuable insights into geochemistry.
The eruptions of volcanoes release gases and molten rock from deep within the Earth’s mantle. These materials can contain important clues about the composition and chemical processes occurring beneath the Earth’s surface. Analyzing volcanic gases and lava can help scientists understand the Earth’s interior.
Isotopes are fundamental to geochemical research.
Scientists use isotopic analysis to determine the origin and history of various substances. Isotopes are variants of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. By examining the ratios of isotopes in a sample, geochemists can draw conclusions about its source or the processes it has undergone.
Geochemistry plays a critical role in understanding the Earth’s climate history.
By analyzing sediments, ice cores, and other geological records, scientists can reconstruct past climates and understand how Earth’s temperature and atmospheric conditions have changed over millions of years. Geochemical data can provide insights into ancient weather patterns, ocean temperatures, and the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Mineral exploration heavily relies on geochemistry.
Geochemical techniques are essential in determining the presence and distribution of valuable minerals in the Earth’s crust. By analyzing soil, rock samples, and groundwater, geologists can identify mineral deposits and make informed decisions about their potential for commercial extraction.
Geochemistry helps in understanding the water quality of natural sources.
By analyzing the chemical composition of water sources, geochemists can assess their quality and identify any potential contaminants. This information is crucial for ensuring the safety of drinking water supplies and maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems.
The carbon cycle is a cornerstone of geochemical processes.
From the atmosphere to the oceans, plants to animals, carbon is continuously cycling through different reservoirs on Earth. Geochemists study the movement and transformations of carbon compounds, providing valuable insights into climate change, ecosystem dynamics, and the impact of human activities.
Geochemistry plays a vital role in understanding natural hazards.
By studying the chemical signatures of rocks and minerals, geochemists can decipher the history of geological events such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. This knowledge is crucial for predicting and mitigating the impact of natural hazards on human populations.
Geochemistry is an interdisciplinary field.
Geochemistry draws upon principles from geology, chemistry, physics, biology, and environmental science. This interdisciplinary approach allows scientists to tackle complex questions and explore the intricate relationships between Earth’s systems.
Geochemistry helps in understanding ancient environments.
Through the analysis of sedimentary rocks, fossils, and chemical traces, geochemists can unravel the mysteries of ancient environments. They can reconstruct past climates, decipher the history of ancient oceans, and explore the conditions that prevailed on Earth millions of years ago.
Oceanic plate subduction plays a vital role in geochemical processes.
When oceanic plates collide with continental plates, subduction occurs, leading to complex chemical reactions between the two types of crust. This process influences the composition of volcanic eruptions, the formation of mountain ranges, and the recycling of elements within Earth’s interior.
The discovery of isotopic anomalies in meteorites has revolutionized our understanding of the solar system’s formation.
By studying isotopic compositions in meteorites, scientists have gained insights into the origin and evolution of the solar system. These anomalies provide clues about the processes that occurred during the formation of planets and shed light on the abundance of elements in space.
Geochemistry contributes to sustainable resource management.
By understanding the geochemical processes involved in the formation of mineral resources, scientists can develop strategies for sustainable mining practices. This knowledge helps optimize resource extraction, minimize environmental impacts, and ensure the long-term availability of essential minerals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, geochemistry is a fascinating field that studies the chemical composition and processes of the Earth. It plays a crucial role in understanding the formation of rocks, minerals, and the distribution of elements in the environment. Through geochemical analysis, scientists are able to unravel the mysteries of our planet’s history and gain insights into global processes such as climate change, volcanic activity, and the origin of life.The enigmatic facts about geochemistry presented in this article highlight the complexity and beauty of this scientific discipline. From the discovery of new elements to the identification of ancient climates through chemical signatures, geochemistry continues to amaze us with its ability to unlock the secrets of the Earth.Whether you are a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about how our planet works, exploring the world of geochemistry is sure to ignite your curiosity and deepen your understanding of the world we live in.
FAQs
1. What is geochemistry?
Geochemistry is the study of the chemical composition and processes of the Earth, including the distribution of elements and isotopes in rocks, minerals, soils, water, and the atmosphere.
2. How is geochemistry used in practical applications?
Geochemistry is used in various practical applications such as environmental monitoring, resource exploration, understanding natural hazards, and assessing the impact of human activities on Earth’s ecosystems.
3. What are some major areas of study in geochemistry?
Major areas of study in geochemistry include isotope geochemistry, organic geochemistry, geochemical modeling, biogeochemistry, and planetary geochemistry.
4. How do geochemists analyze samples?
Geochemists employ various techniques such as spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, and electron microscopy to analyze the chemical composition of samples.
5. How does geochemistry contribute to our understanding of climate change?
Geochemistry helps scientists reconstruct past climates by analyzing isotopes and trace elements preserved in ice cores, sediments, and fossil records. This data provides valuable insights into long-term climate patterns and helps predict future changes.
6. Is geochemistry only limited to Earth?
No, geochemistry also extends its scope to other celestial bodies such as planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. It helps shed light on the origin and evolution of these celestial bodies.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
