When it comes to semiconductors, there are two types that dominate the industry: direct band gap and indirect band gap. While direct band gap semiconductors are widely known for their efficiency and effectiveness in electronic devices, indirect band gap semiconductors often take a backseat in terms of popularity.
However, what many people don’t realize is that indirect band gap semiconductors have some fascinating properties and applications that make them just as important in the world of technology. In this article, we will uncover 17 mind-blowing facts about indirect band gap semiconductors that will leave you in awe.
Key Takeaways:
- Indirect band gap semiconductors like silicon and indium phosphide are crucial for optoelectronic devices, but they have limitations in solar cells. Quantum dots and ongoing research aim to overcome these limitations for better performance.
- Indirect band gap semiconductors have unique properties like long carrier lifetimes and high electron mobility, making them important for integrated circuits and high-speed electronic applications. Ongoing research continues to unlock their potential for diverse applications.
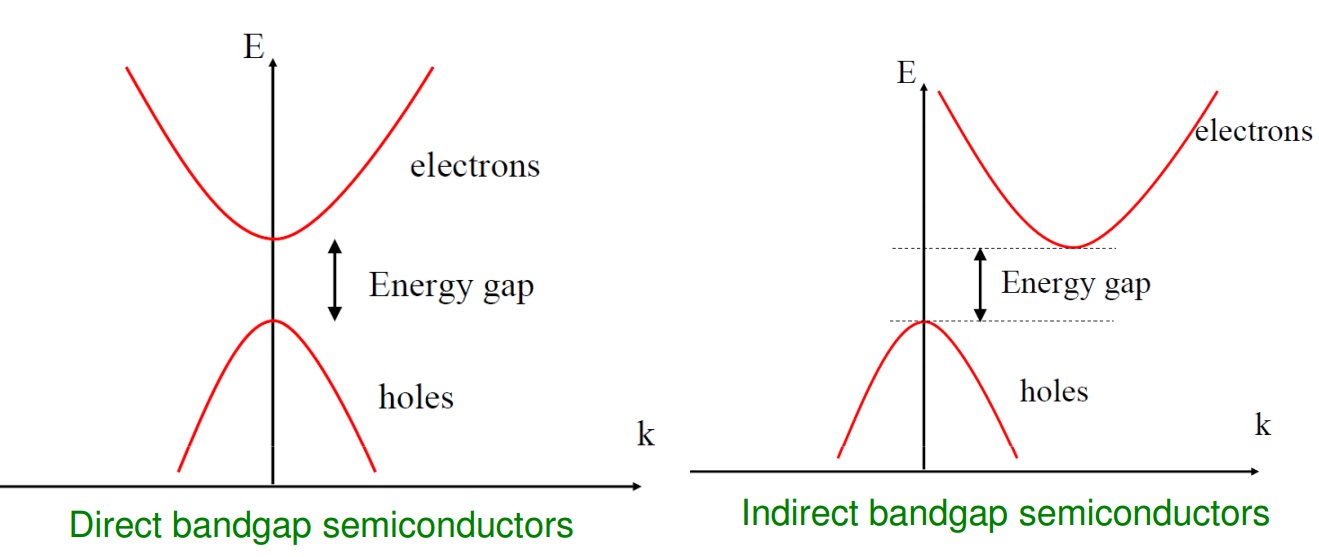
What is an Indirect Band Gap Semiconductor?
An indirect band gap semiconductor is a type of semiconductor material that has a band gap in which the minimum energy level for electrons is not at the same momentum value as the maximum energy level for holes. This means that the transition of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band requires the assistance of a phonon or lattice vibration.
Widely Used in Optoelectronic Devices
Indirect band gap semiconductors are widely used in optoelectronic devices such as photodiodes, LEDs (light-emitting diodes), and lasers. This is because their indirect band gap allows for efficient photon emission and absorption processes.
Silicon is an Indirect Band Gap Semiconductor
One of the most well-known examples of an indirect band gap semiconductor is silicon. It is widely used in the electronics industry due to its abundance and excellent semiconductor properties.
Limited Use in Solar Cells
Indirect band gap semiconductors have limited use in solar cells compared to direct band gap semiconductors. This is because the absorption of photons and the generation of electron-hole pairs are less efficient in indirect band gap materials.
Indium Phosphide is an Example of an Indirect Band Gap Semiconductor
Indium phosphide (InP) is another example of an indirect band gap semiconductor. It is commonly used in high-speed electronic and optoelectronic applications due to its excellent electrical and optical properties.
Quantum Dots can Overcome the Limitations
Quantum dots, which are nanoscale semiconductor particles, can overcome the limitations of indirect band gap semiconductors in solar cell applications. Their unique properties allow for more efficient light absorption and electron-hole pair generation.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Have Long Carrier Lifetimes
Due to the requirement of lattice vibrations for electron transitions, indirect band gap semiconductors typically have longer carrier lifetimes compared to direct band gap materials. This can be advantageous in certain device applications.
Gallium Antimonide is Another Example of an Indirect Band Gap Semiconductor
Gallium antimonide (GaSb) is a compound that exhibits indirect band gap behavior. It is used in various applications, including infrared detectors, lasers, and high-speed transistors.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Have Lower Absorption Coefficients
Indirect band gap semiconductors typically have lower absorption coefficients compared to direct band gap materials. This means that they require thicker layers to absorb the same amount of light, making them less favorable for certain optical device applications.
Research Focus on Enhancing Indirect Band Gap Device Performance
There is ongoing research to enhance the performance of devices based on indirect band gap semiconductors. This includes exploring new materials, device structures, and fabrication techniques.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Can Exhibit Higher Thermal Conductivity
Some indirect band gap semiconductors, such as diamond, can exhibit higher thermal conductivity compared to direct band gap materials. This makes them suitable for high-power electronic applications where efficient heat dissipation is crucial.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Have Lower Radiative Recombination Rates
The radiative recombination rates in indirect band gap semiconductors are typically lower compared to direct band gap materials. This can affect the efficiency of certain light-emitting devices.
Germanium is Another Indirect Band Gap Semiconductor
Germanium (Ge) is a classic example of an indirect band gap semiconductor. It was widely used in early electronic devices and is still studied for its unique properties and potential applications.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Can Exhibit High Electron Mobility
Some indirect band gap semiconductors, such as gallium arsenide (GaAs), can exhibit high electron mobility. This makes them suitable for high-speed electronic applications.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Are Important for Integrated Circuits
Indirect band gap semiconductors, like silicon, play a vital role in integrated circuits (ICs). Their properties allow for the construction of transistors, diodes, and other electronic components required for modern electronic devices.
Indirect Band Gap Semiconductors Can Be Engineered for Specific Applications
Through precise material engineering and device design, indirect band gap semiconductors can be tailored for specific applications. This includes optimizing their performance for different wavelengths, temperatures, and power requirements.
Research Continues to Unlock the Potential of Indirect Band Gap Semiconductor
The exploration of indirect band gap semiconductors is an active area of research in semiconductor physics and materials science. Scientists aim to uncover new materials and device concepts that harness the unique characteristics of these semiconductors for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, indirect band gap semiconductors are fascinating materials with unique properties that play a crucial role in various electronic devices. Understanding the concepts behind their behavior is essential for advancements in the field of semiconductor technology. From their diverse applications in solar cells to their contribution to the development of optoelectronic devices, indirect band gap semiconductors continue to amaze scientists and engineers alike. Their ability to emit and absorb light, combined with their efficient electron mobility, makes them indispensable in modern technology.As researchers delve deeper into the properties and potential applications of indirect band gap semiconductors, we can expect further breakthroughs in fields such as telecommunications, energy storage, and quantum computing. Exciting times lie ahead as we uncover more mind-blowing facts about these remarkable materials.
FAQs
1. What exactly is an indirect band gap semiconductor?
An indirect band gap semiconductor refers to a material in which the minimum energy required for an electron to move from the valence band to the conduction band occurs at a different momentum or wavevector. This results in a lower probability of direct transitions, leading to a longer recombination time.
2. What are the unique characteristics of indirect band gap semiconductors?
Indirect band gap semiconductors have several distinctive traits, including lower absorption coefficients for specific wavelengths of light, longer recombination times, and lower luminescence efficiency compared to direct band gap semiconductors.
3. What are some applications of indirect band gap semiconductors?
Indirect band gap semiconductors are commonly used in optoelectronic devices such as solar cells, infrared detectors, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). They are also being explored for their potential applications in quantum computing, where their long recombination times can help maintain quantum states.
4. How do indirect band gap semiconductors differ from direct band gap semiconductors?
Unlike indirect band gap semiconductors, direct band gap semiconductors have a minimum energy for electron transitions that occurs at the same momentum or wavevector. This allows for more efficient absorption and emission of light, making direct band gap semiconductors ideal for applications such as lasers and optical devices.
5. Are indirect band gap semiconductors more or less efficient than direct band gap semiconductors?
Indirect band gap semiconductors are generally less efficient than direct band gap semiconductors in terms of luminescence. However, they have their own advantages, such as longer recombination times, which can be beneficial in certain applications, like infrared detectors and optoelectronic devices.
Fascinating facts about indirect band gap semiconductors spark curiosity, don't they? Delving deeper into material science reveals even more surprising discoveries. For those interested in electronic engineering, exploring VHDL for hardware description offers invaluable insights. And if you're captivated by the intricacies of semiconductor physics, prepare to be astonished by the wonders of pn junctions. Each topic unveils a unique facet of the scientific world, inviting us to expand our knowledge and appreciate the marvels that surround us. So, which fascinating realm will you explore next?
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


