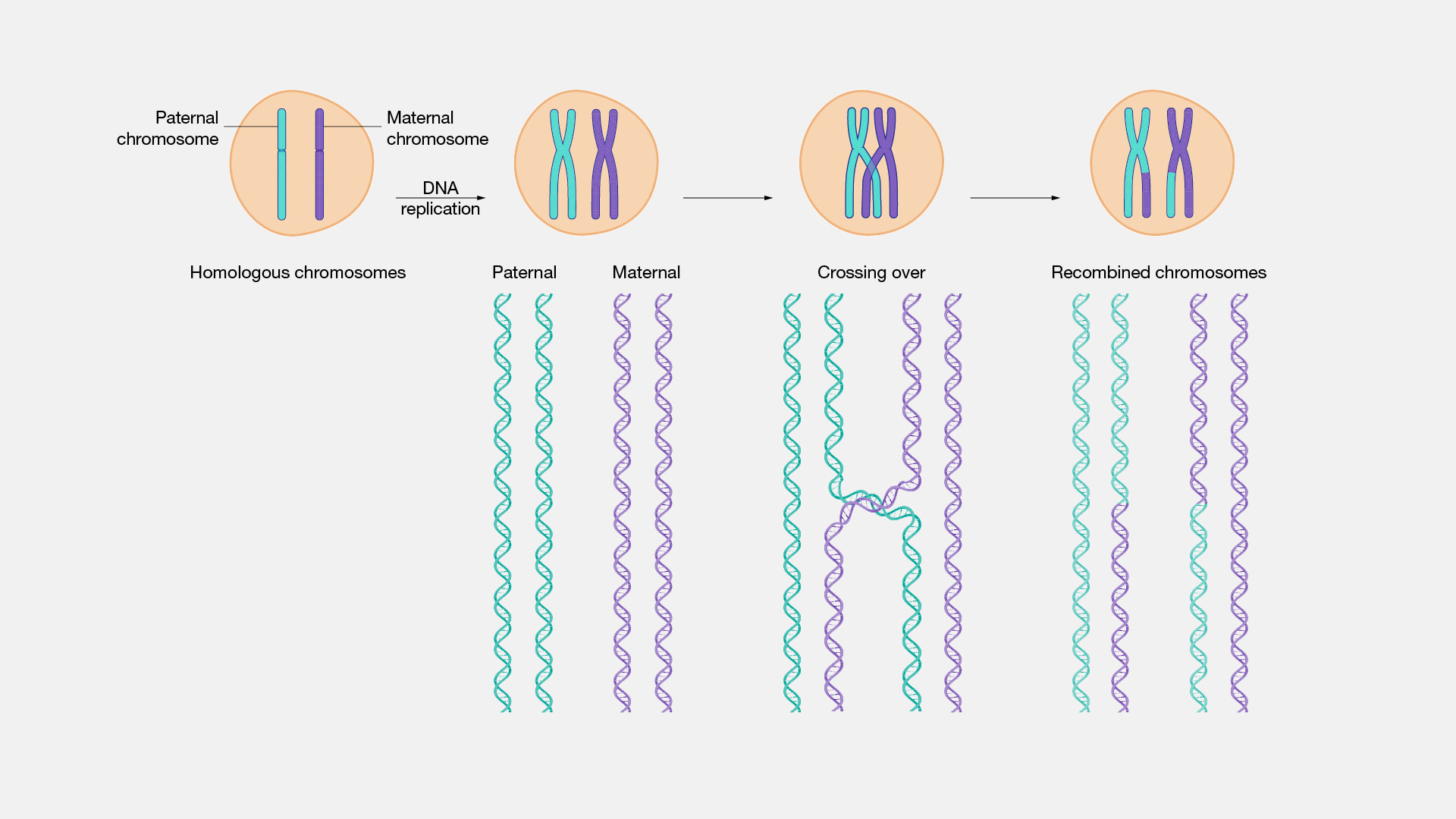
Recombination, a fascinating process in genetics, holds the key to genetic diversity and evolution. It involves the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during the formation of reproductive cells. This crucial mechanism not only ensures the proper distribution of genetic information but also contributes to the creation of novel genetic combinations.
In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of recombination and explore ten intriguing facts about this fundamental process. From the evolutionary benefits of genetic shuffling to the role of recombination in disease prevention, we will uncover the mysteries surrounding this intricate mechanism. So, fasten your seatbelts and prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of recombination!
Key Takeaways:
- Recombination is like a genetic mix-and-match game that creates new gene combinations, promoting diversity and helping organisms adapt to changing environments.
- Recombination is a genetic superhero, repairing DNA damage, influencing evolution, and even playing a role in the formation of new species.
Recombination plays a crucial role in genetic diversity
Recombination is a fundamental process that occurs during meiosis, the cell division responsible for producing sperm and egg cells. It involves the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, resulting in new combinations of genes. This mechanism is essential for creating genetic diversity within a population and plays a vital role in evolution.
Recombination can repair DNA damage
One intriguing aspect of recombination is its ability to repair DNA damage. When a cell’s DNA is damaged, recombination can act as a repair mechanism by using the intact DNA strand as a template to restore the damaged region. This process, known as homologous recombination repair, ensures the integrity of the genome and helps prevent the accumulation of mutations.
Recombination can cause genetic diseases
While recombination is generally a beneficial process, it can sometimes lead to genetic disorders. Errors in recombination can result in chromosomal abnormalities, such as deletions, duplications, or translocations, which can cause diseases like Down syndrome or certain types of cancer. Understanding the factors that influence recombination and its potential errors is crucial for diagnosing and treating these disorders.
Recombination can influence the evolution of pathogens
In pathogens like bacteria and viruses, recombination can have significant implications for their evolution and ability to evade the host’s immune system. By shuffling genetic material between different strains or species, recombination can generate new combinations of genes that may confer advantages in terms of virulence, drug resistance, or host specificity.
Recombination is mediated by specific enzymes
The process of recombination is catalyzed by a group of enzymes, including the recombinase proteins, which are responsible for recognizing and cutting DNA strands at specific sites called recombination hotspots. These enzymes play a key role in facilitating the exchange of genetic material and ensuring the accuracy of the process.
Recombination can occur between non-homologous DNA sequences
Although recombination commonly occurs between homologous chromosomes, it can also take place between non-homologous DNA sequences. This phenomenon, known as non-homologous recombination, can result in genetic rearrangements and is often associated with certain diseases, including cancer.
Recombination rates can vary across the genome
Recombination rates are not uniform throughout the genome but instead vary across different regions. Some regions, known as recombination hotspots, have a higher likelihood of undergoing recombination, while others, known as recombination cold spots, have a lower probability. These variations in recombination rates can have implications for genetic mapping studies and the understanding of complex genetic diseases.
Recombination can influence the speed of evolution
Recombination plays a crucial role in speeding up the process of evolution by allowing for the mixing and reorganization of genetic material. It facilitates the transfer of beneficial genetic variations across individuals, generating new combinations of genes that can potentially enhance an organism’s survival and reproductive success.
Recombination can promote speciation
By generating new combinations of genes, recombination can contribute to the formation of new species through a process called sympatric speciation. When populations become reproductively isolated and undergo different selective pressures, recombination can lead to the divergence and accumulation of genetic differences, ultimately resulting in the emergence of distinct species.
Recombination is influenced by environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature, nutrient availability, and exposure to certain chemicals or stressors, can influence recombination rates. These factors can either promote or inhibit recombination, shaping the genetic composition of populations and potentially influencing their adaptability to changing environments.
Conclusion:
The 10 enigmatic facts about recombination highlight its significance in genetic diversity, DNA repair, evolution, and disease development. Understanding the intricacies of recombination can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms driving genetic variation and adaptation. Moreover, unraveling the mysteries surrounding recombination can have far-reaching implications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and ecology.
Conclusion
Recombination is a fascinating biological process that plays a critical role in genetic diversity and evolution. Throughout this article, we have explored ten enigmatic facts about recombination that shed light on its significance and complexity.
From the generation of genetic variation to the repair of damaged DNA, recombination is essential for the survival and adaptation of organisms. Its ability to shuffle and exchange genetic material during meiosis leads to the production of unique offspring with diverse traits.
Recombination not only allows for the elimination of harmful mutations but also facilitates the combination of beneficial mutations, leading to the evolution of new traits that can enhance survival and reproductive success. It is truly a driving force behind the remarkable diversity of life on our planet.
By unraveling the mysteries of recombination, scientists can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms of genetic inheritance and contribute to advancements in various fields, such as agriculture, medicine, and conservation biology.
As our understanding of recombination continues to expand, it is certain to uncover even more enigmatic facts that will further deepen our appreciation for the intricate workings of the biological world.
FAQs
1. What is recombination?
Recombination is a biological process where genetic material is exchanged or shuffled between different DNA molecules or chromosomes during cellular reproduction.
2. Why is recombination important?
Recombination is crucial for generating genetic diversity, repairing damaged DNA, and facilitating the evolution of new traits in organisms.
3. How does recombination occur during meiosis?
During meiosis, recombination occurs when homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo a process called crossing over, where genetic material is exchanged between the chromosomes.
4. What is the role of recombination in evolution?
Recombination plays a significant role in evolution by generating genetic variation, allowing for the elimination of harmful mutations, and facilitating the combination of beneficial mutations.
5. Are there any diseases or disorders associated with recombination?
Defects in the recombination process can lead to certain diseases or disorders, such as infertility, chromosomal abnormalities, and genetic disorders.
6. Can recombination be artificially manipulated?
Yes, recombination can be artificially manipulated in the laboratory using techniques such as genetic engineering and gene editing.
7. Is recombination limited to sexual reproduction?
No, recombination can also occur in organisms that reproduce asexually, although the frequency may be lower compared to sexually reproducing organisms.
8. Can recombination occur between different species?
While rare, there have been instances of recombination occurring between different species, leading to the transfer of genetic material across species boundaries.
9. Are there any ethical considerations associated with manipulating recombination?
Yes, the manipulation of recombination raises ethical concerns, particularly when it involves human genetic engineering and gene editing.
10. Are there any ongoing research areas focused on understanding recombination?
Yes, researchers are continually exploring various aspects of recombination, including its molecular mechanisms, its role in disease development, and its potential applications in biotechnology and evolutionary biology.
Recombination's enigmatic nature leaves many questions unanswered, but fear not! Delving deeper into genetic recombination's intricacies reveals even more captivating facts that will leave you in awe. Curious about how often recombination events occur? Prepare to have your mind blown by the astonishing truths behind recombination frequency. And if you're ready to explore the cutting-edge world of recombinant DNA, buckle up for a thrilling ride through its most fascinating aspects.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
