The Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental concept that holds great significance in the field of chemistry. It was first proposed by the English chemist John Dalton in the early 19th century and has since played a crucial role in understanding the composition of compounds. This law states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the ratios of the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are always small whole numbers. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Law of Multiple Proportions and explore 14 enigmatic facts about it. From its historical background to its practical applications in modern research, we will uncover intriguing details that highlight the profound implications of this law. So, prepare to embark on a journey through the complexities of chemical composition and discover why the Law of Multiple Proportions is at the core of understanding the building blocks of matter.
Key Takeaways:
- The Law of Multiple Proportions helps chemists understand how different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds, providing a foundation for stoichiometry and atomic theory.
- By studying the Law of Multiple Proportions, scientists can classify elements, determine atomic ratios, and apply these principles in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to environmental chemistry.
The Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry.
The Law of Multiple Proportions states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in a ratio of small whole numbers.
The Law of Multiple Proportions was first proposed by John Dalton in the early 19th century.
Dalton’s theory of atoms and the Law of Multiple Proportions revolutionized the field of chemistry, providing a framework for understanding the composition of compounds.
The Law of Multiple Proportions helps to determine the atomic ratios in compounds.
By analyzing the masses of elements in different compounds, scientists can determine the ratios of atoms present and gain insights into the chemical formulae of these compounds.
The Law of Multiple Proportions is crucial in understanding the concept of stoichiometry.
Stoichiometry involves the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction, and the Law of Multiple Proportions provides a basis for these calculations.
The Law of Multiple Proportions applies to both simple and complex compounds.
Whether it’s a simple binary compound or a complex molecule, the Law of Multiple Proportions holds true in all cases.
The Law of Multiple Proportions supports the concept of atomic masses.
By examining the ratios of different elements in compounds, scientists can determine the relative atomic masses of those elements.
The Law of Multiple Proportions is consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass.
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. The Law of Multiple Proportions aligns with this principle as it describes how elements combine in fixed proportions.
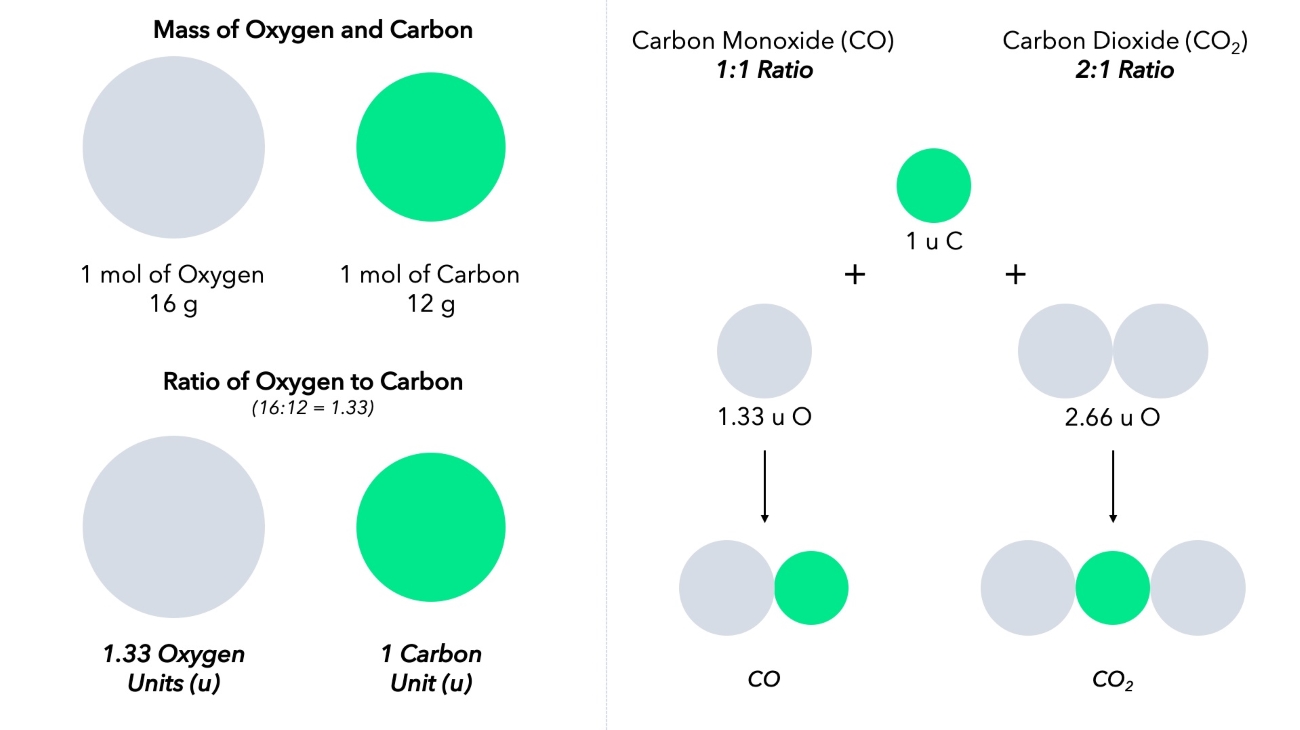
The Law of Multiple Proportions can be explained using simple examples.
For instance, carbon and oxygen can form two different compounds—carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The ratio of oxygen to carbon in carbon monoxide is 1:1, while in carbon dioxide, it is 2:1, demonstrating the Law of Multiple Proportions.
The Law of Multiple Proportions helps to classify elements into different groups.
By analyzing the ratios of elements in compounds, scientists can group elements based on their similar chemical properties and behaviors.
The Law of Multiple Proportions has practical applications in various industries.
Understanding the stoichiometric relationships in chemical reactions is crucial in fields such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
The Law of Multiple Proportions led to the development of the atomic theory.
Dalton’s work on the Law of Multiple Proportions played a key role in establishing the atomic theory, which forms the basis of modern chemistry.
The Law of Multiple Proportions holds true for both inorganic and organic compounds.
Whether it’s a simple inorganic compound or a complex organic molecule, the Law of Multiple Proportions remains a fundamental principle in understanding their composition.
The Law of Multiple Proportions helps to explain empirical formulas.
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound, and the Law of Multiple Proportions aids in determining these ratios.
The Law of Multiple Proportions continues to be studied and applied in modern chemistry.
From understanding molecular structures to predicting reaction outcomes, the principles of the Law of Multiple Proportions remain relevant and essential in advancing the field of chemistry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental concept in chemistry that highlights the relationship between the ratios of elements in a compound. These enigmatic facts about the Law of Multiple Proportions unlock a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and the composition of substances. From the discovery by John Dalton to the exploration of stoichiometry, these facts shed light on the intricacies of chemical combinations. Whether it’s the existence of multiple compounds with different ratios or the role of atomic masses, the Law of Multiple Proportions continues to captivate chemists and researchers alike. By studying these facts, we gain valuable insights into the nature of matter and the principles that govern its behavior.
FAQs
Q: What is the Law of Multiple Proportions?
A: The Law of Multiple Proportions states that when two elements combine to form multiple compounds, the ratio of the masses of one element that combines with a fixed mass of the other element will always be a ratio of small whole numbers.
Q: Who discovered the Law of Multiple Proportions?
A: The Law of Multiple Proportions was first proposed by John Dalton in the early 19th century. His theory revolutionized the understanding of chemical reactions and laid the foundation for modern atomic theory.
Q: What are some examples of the Law of Multiple Proportions?
A: One example is carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2). In carbon monoxide, the ratio of carbon to oxygen is 1:1, while in carbon dioxide, the ratio is 1:2. Another example is nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), where the ratio of nitrogen to oxygen is 1:1 in the former and 1:2 in the latter.
Q: How does the Law of Multiple Proportions relate to stoichiometry?
A: The Law of Multiple Proportions is closely related to stoichiometry, which is the quantitative study of chemical reactions. Stoichiometry allows chemists to calculate the ratios of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction, based on the principles established by the Law of Multiple Proportions.
Q: What is the significance of the Law of Multiple Proportions?
A: The Law of Multiple Proportions provides important insights into the composition of compounds and the behavior of elements in chemical reactions. It has helped refine our understanding of atomic theory and has practical applications in fields such as materials science, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
