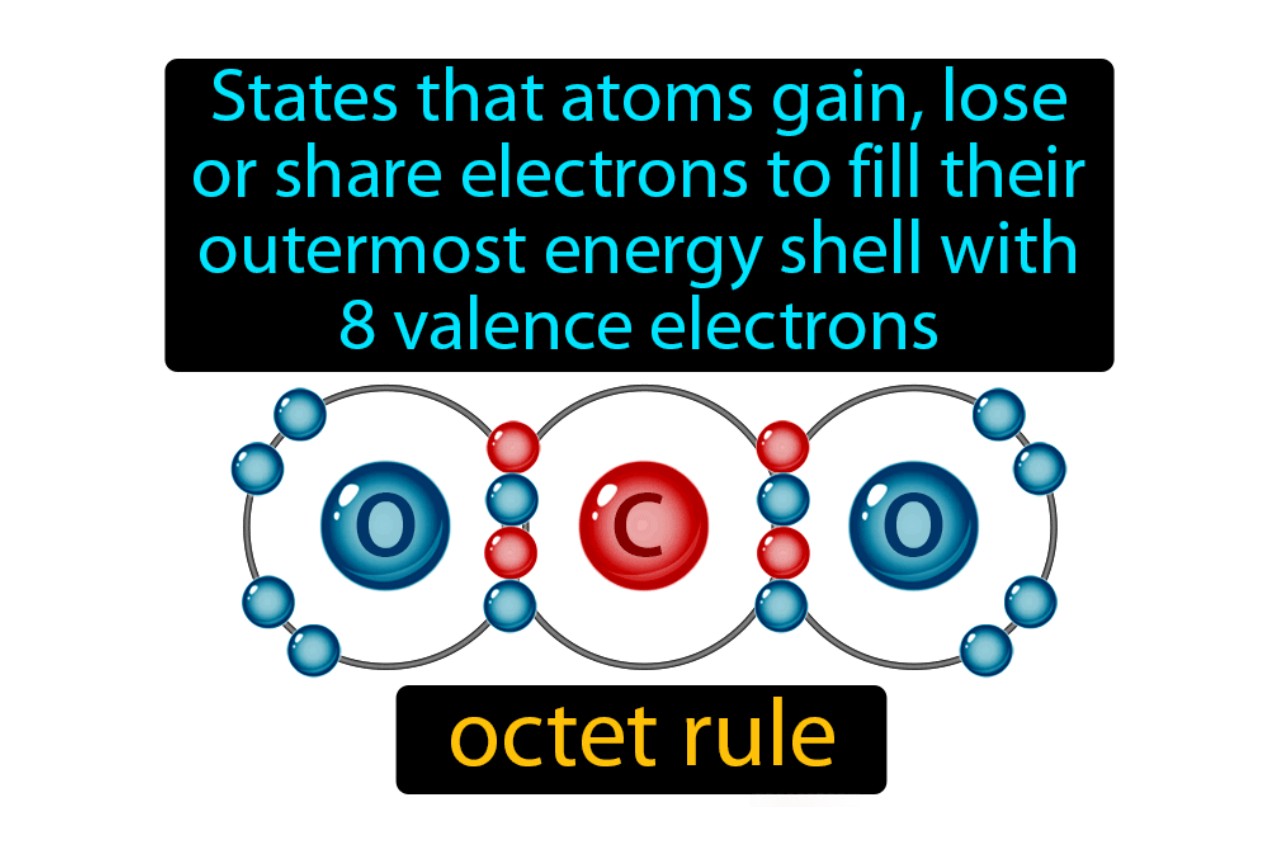
The concept of the octet rule is a fundamental principle in chemistry that helps us understand the behavior and stability of atoms. It states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a stable configuration with a full outer shell of eight electrons. This rule, proposed by Gilbert N. Lewis in the early 20th century, has revolutionized our understanding of chemical bonding and the formation of compounds.
In this article, we will explore 13 unbelievable facts about the octet rule. From its significance in determining the properties of elements to its exceptions and limitations, we will delve into the captivating world of octet rule chemistry. So, buckle up and get ready to discover some mind-blowing insights into the octet rule and how it influences the atomic behavior of elements.
Key Takeaways:
- The Octet Rule is a fundamental concept in chemistry, helping us understand how atoms bond to form molecules and why some elements form ions. It’s like a rulebook for atoms to achieve stability!
- While the Octet Rule is a useful guideline, there are exceptions, like atoms with expanded octets. It’s like a general rule that most atoms follow, but some like to break the rules and have more than eight electrons!
The Octet Rule is a fundamental concept in chemistry.
The Octet Rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to have a full outer shell of eight electrons, resembling the stable configuration of noble gases.
The Octet Rule helps predict the bonding behavior of atoms.
By following the Octet Rule, chemists can make accurate predictions about how atoms will bond with each other to form molecules.
The Octet Rule applies to most elements on the periodic table.
Elements in groups 1 to 7 typically follow the Octet Rule, as they strive to achieve a stable electron configuration.
The Octet Rule explains why atoms form ions.
Atoms that do not have a complete outer shell of electrons will either gain or lose electrons to achieve stability, resulting in the formation of ions.
The Octet Rule is a simplified model.
While the Octet Rule is a useful guideline, there are exceptions and cases where atoms may have more or fewer than eight electrons in their valence shell.
The Octet Rule is essential for understanding covalent bonding.
In covalent bonds, atoms share electrons to achieve an octet in their valence shell, creating a stable molecule.
The Octet Rule can be violated by atoms with an expanded octet.
In elements from the third period and beyond, such as phosphorus and sulfur, atoms can accommodate more than eight electrons in their valence shell.
The Octet Rule helps explain the stability of noble gases.
Noble gases have a complete outer shell of eight electrons, making them highly stable and unreactive.
The Octet Rule is not applicable to transition metals.
Transition metals can have variable numbers of electrons in their outer shell, causing them to exhibit different bonding behavior.
The Octet Rule is named after the Latin word “octo,” meaning eight.
This reflects the significance of achieving eight electrons in the valence shell for stability.
The Octet Rule was first proposed by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1916.
Gilbert N. Lewis, an American physical chemist, introduced the concept of the Octet Rule to explain the bonding patterns observed in chemical compounds.
The Octet Rule makes understanding electron configurations easier.
By applying the Octet Rule, chemists can determine the electron configuration of elements and molecular compounds, aiding in the understanding of their properties.
The Octet Rule plays a crucial role in organic chemistry.
In organic compounds, atoms follow the Octet Rule to form stable covalent bonds, enabling the vast diversity of organic molecules found in nature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Octet Rule is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the behavior of atoms and their tendency to attain a stable electron configuration. It states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a full outer shell with eight electrons, similar to the noble gas configuration. This rule not only explains the formation of chemical bonds but also provides insights into the stability and reactivity of elements.Understanding the Octet Rule is crucial in various areas of chemistry, including molecular structure, electron distribution, and predicting chemical reactions. By following this rule, scientists can explain why certain molecules are more stable than others and predict the types of bonds that will form between different elements.Overall, the Octet Rule plays a vital role in our understanding of chemical behavior and helps us make significant advancements in various fields, from drug development to environmental chemistry. By continuing to explore and refine our understanding of this rule, we can unlock new possibilities and deepen our knowledge of the molecular world.
FAQs
1. What is the Octet Rule?
The Octet Rule is a principle in chemistry which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight electrons in their outer shell.
2. Why is the Octet Rule important?
The Octet Rule is important because it helps us understand the behavior of atoms and their tendency to form chemical bonds. It allows us to predict the stability and reactivity of elements, as well as understand how molecules are formed.
3. How does the Octet Rule explain chemical bonding?
The Octet Rule explains chemical bonding by stating that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a full outer shell and attain a stable electron configuration similar to the noble gases. This rule helps us understand why certain atoms bond with each other to form compounds.
4. Are there any exceptions to the Octet Rule?
Yes, there are exceptions to the Octet Rule. Some atoms can have fewer or more than eight electrons in their outer shell, depending on the element and the specific circumstances. These exceptions occur primarily with elements from the third period onwards, such as phosphorus and sulfur.
5. How does the Octet Rule influence molecular stability?
The Octet Rule influences molecular stability by guiding the formation of bonds that allow atoms to achieve a full outer shell. Molecules that follow the Octet Rule are generally more stable than those that do not, as they have achieved a balanced electron configuration.
6. Can the Octet Rule be applied to all elements?
The Octet Rule is primarily applicable to elements in the second period of the periodic table and a few elements beyond that. Elements in the first period, such as hydrogen and helium, do not require eight electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration and have different rules governing their electron distribution.
Mastering the octet rule is just the beginning of your chemistry journey. Dive deeper into atomic structure by exploring valence electron configurations, which hold the key to understanding chemical bonding and reactivity. Unraveling these fundamental concepts will help you build a solid foundation in chemistry and appreciate the elegance of the periodic table.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
