Substitution reaction is a fundamental concept in chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding organic and inorganic reactions. It involves the replacement of one atom or group of atoms with another within a molecule. This reaction type holds significant importance in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental studies.
In this article, we will explore 13 extraordinary facts about substitution reactions that will deepen your understanding of this fascinating chemical phenomenon. From the diverse types of substitution reactions to their relevance in everyday life, these facts will highlight the significance and applications of substitution reactions in the world of chemistry.
So, let’s dive into the world of substitution reactions and uncover some captivating facts that will broaden our knowledge and appreciation for this fundamental chemical process.
Key Takeaways:
- Substitution reactions are like chemical makeovers, where atoms or groups of atoms are replaced with others. They’re super important in making medicines, plastics, and even cleaning up the environment!
- Substitution reactions are like the superheroes of chemistry, helping to create new drugs, materials, and even recreate natural compounds. They’re like the secret sauce behind many amazing scientific discoveries!
Substitution Reaction – A Key Concept in Organic Chemistry
Substitution reaction is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that involves the replacement of one atom or group of atoms with another. It plays a crucial role in various chemical processes and has wide-ranging implications in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Two Types of Substitution Reactions
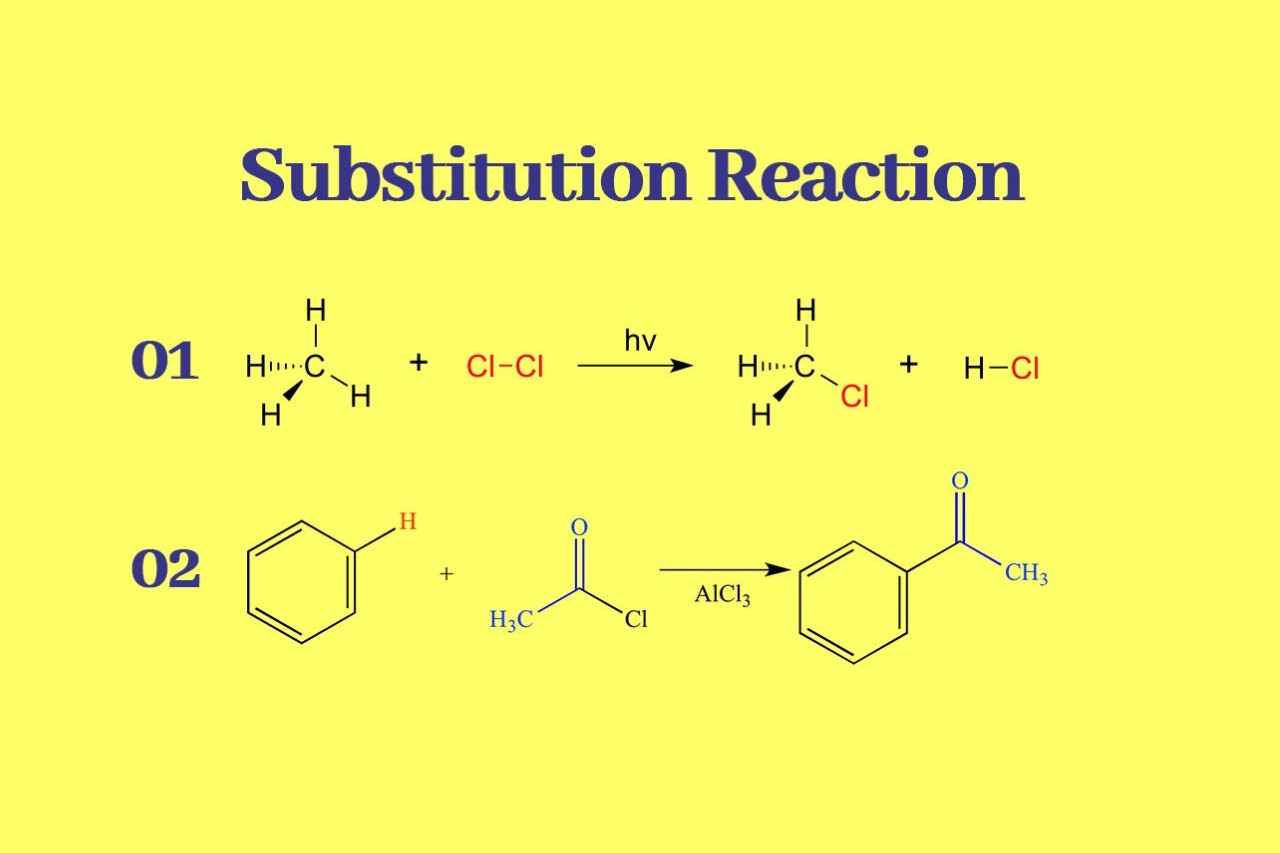
There are two main types of substitution reactions: nucleophilic substitution and electrophilic substitution. Nucleophilic substitution involves the attack of a nucleophile on an electrophilic center, while electrophilic substitution occurs when an electrophile replaces a hydrogen atom in a molecule.
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
In nucleophilic substitution reactions, a nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to an electrophilic center, resulting in the displacement of a leaving group. This process is commonly used for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds of industrial importance.
Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
Electrophilic substitution reactions involve the replacement of a hydrogen atom in a molecule with an electrophile. This type of reaction is frequently encountered in aromatic compounds and is responsible for the synthesis of a wide range of products, such as dyes, fragrances, and polymers.
Substitution Reaction Mechanisms
Substitution reactions follow different mechanisms depending on the type of reaction and the nature of the reactants. The most common mechanisms include SN1 (unimolecular nucleophilic substitution), SN2 (bimolecular nucleophilic substitution), and SE2 (bimolecular electrophilic substitution).
Influence of Substrate Structure
The structure of the substrate greatly influences the rate and outcome of a substitution reaction. Factors such as steric hindrance, electronic effects, and resonance stabilization can significantly impact the reactivity and selectivity of the reaction.
Substitution Reactions in Biochemical Processes
Substitution reactions are not limited to synthetic chemistry but also play a vital role in biochemical processes. Enzymes catalyze numerous substitution reactions in living organisms, facilitating essential metabolic pathways and molecular transformations.
Substitution Reactions and Medicinal Chemistry
Medicinal chemists extensively utilize substitution reactions for the development and synthesis of new drugs. Through targeted modifications of existing drug molecules, substitution reactions can enhance potency, selectivity, and other desirable properties.
Environmental Impacts of Substitution Reactions
Understanding substitution reactions is essential for assessing the environmental impacts of various chemicals. For instance, the degradation of pollutants in the environment often involves substitution reactions that transform harmful substances into less toxic forms.
Cross-Coupling Reactions
Cross-coupling reactions, a type of substitution reaction, enable the selective linking of two carbon atoms using transition metal catalysts. These reactions have revolutionized organic synthesis, allowing for the construction of complex carbon frameworks with high efficiency.
Substitution Reactions in Industrial Production
The application of substitution reactions is widespread in industrial production, especially in the manufacturing of plastics, polymers, and various chemical intermediates. These reactions enable the synthesis of a wide range of products essential for our daily lives.
Substitution Reactions in Material Science
Substitution reactions are vital in material science for the synthesis and modification of advanced materials. By selectively replacing specific atoms or functional groups within a material, scientists can tailor its properties, leading to improved performance and functionality.
Substitution Reactions in Natural Product Synthesis
Natural product synthesis often relies on substitution reactions to recreate complex molecules found in nature. These reactions enable chemists to access valuable natural compounds, including pharmaceuticals, flavors, fragrances, and agricultural chemicals.
In conclusion, the 13 extraordinary facts about substitution reactions highlight their significance in organic chemistry, their diverse applications in various fields, and their impact on the development of new materials and drugs. Understanding the mechanisms and intricacies of substitution reactions enriches our knowledge of chemical processes and paves the way for innovative scientific discoveries.
Conclusion
Substitution reactions are a fascinating aspect of chemistry that play a crucial role in various biological, industrial, and environmental processes. From the basic principles of substitution reactions to their wide range of applications, we have explored some extraordinary facts that shed light on the significance and complexity of this reaction type.
Substitution reactions occur when an atom, ion, or group of atoms is replaced by another atom, ion, or group of atoms within a molecule. They are commonly categorized as nucleophilic or electrophilic substitutions, depending on the nature of the reactants involved. These reactions are fundamental in organic chemistry, as they allow for the synthesis of new compounds and the modification of existing ones.
Some extraordinary facts about substitution reactions include the diverse mechanisms employed, such as SN1, SN2, and SNi, which dictate the rate and stereochemistry of the reaction. Additionally, the presence of leaving groups, solvents, and temperature can greatly impact the outcome of a substitution reaction.
Understanding the intricacies of substitution reactions is vital for numerous applications, including drug development, chemical synthesis, and environmental remediation. By harnessing the power of these reactions, scientists can create new compounds with unique properties and contribute to advancements in various fields.
FAQs
Q: What is a substitution reaction?
A substitution reaction is a chemical reaction in which an atom, ion, or group of atoms is replaced by another atom, ion, or group of atoms within a molecule. It is a fundamental process in organic chemistry and plays a critical role in various biological, industrial, and environmental processes.
Q: What are the different types of substitution reactions?
There are two main types of substitution reactions: nucleophilic substitution and electrophilic substitution. Nucleophilic substitution involves the replacement of an atom or group by a nucleophile, while electrophilic substitution occurs when an electrophile replaces an atom or group in a molecule. These reactions can further be classified based on factors such as reaction mechanisms, reactant characteristics, and reaction conditions.
Q: What are some common examples of substitution reactions?
Some common examples of substitution reactions include the hydrolysis of esters, the haloalkane substitution reactions, and the nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl halides. These reactions are often encountered in organic synthesis, drug development, and other chemical processes.
Q: How do reaction conditions affect substitution reactions?
Reaction conditions such as the presence of a leaving group, the nature of the solvent, and the temperature can have a significant impact on substitution reactions. These factors can influence the mechanism, rate, and selectivity of the reaction, leading to different outcomes and products.
Q: Why are substitution reactions important?
Substitution reactions play a vital role in various scientific and industrial applications. They allow for the synthesis of new compounds, the modification of existing ones, and the production of key intermediates in drug development. Additionally, substitution reactions are critical for environmental remediation processes, where contaminants are substituted with less harmful substances.
Substitution reactions play a crucial role in organic chemistry, biochemistry, and various industries. Understanding their mechanisms, types, and applications is essential for anyone interested in this fascinating field. If you're curious to learn more about substitution reactions, consider exploring our other articles on astounding facts about substitution reactions and the intriguing world of electrophilic substitution. These articles will provide you with even more in-depth knowledge and captivating insights into this fundamental chemical process, allowing you to expand your understanding and appreciate the significance of substitution reactions in our world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
