Substrates are a fundamental concept in the field of chemistry, and understanding their properties and applications is essential for any aspiring chemist. Substrates are the materials or compounds upon which a chemical reaction takes place. They play a crucial role in various chemical processes, ranging from industrial applications to biological reactions within our bodies.In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of substrates and uncover nine unbelievable facts that will leave you amazed. From their role in enzyme-catalyzed reactions to their significance in organic synthesis, substrates are the unsung heroes behind many scientific breakthroughs. So, sit back, grab your lab coat, and prepare to be astounded by the incredible properties and functions of substrates. Let’s dive into the intriguing world of chemistry and discover what makes substrates truly remarkable.
Key Takeaways:
- Substrates are essential for chemical reactions, like the ingredients in a recipe. They interact with enzymes and can be organic or inorganic, influencing everything from drug development to the functioning of our bodies.
- Understanding substrates is like unlocking the secrets of a magical potion. Their unique properties and interactions with enzymes drive the complex reactions that sustain life and hold the key to scientific breakthroughs.
Substrate is an essential component in enzymatic reactions
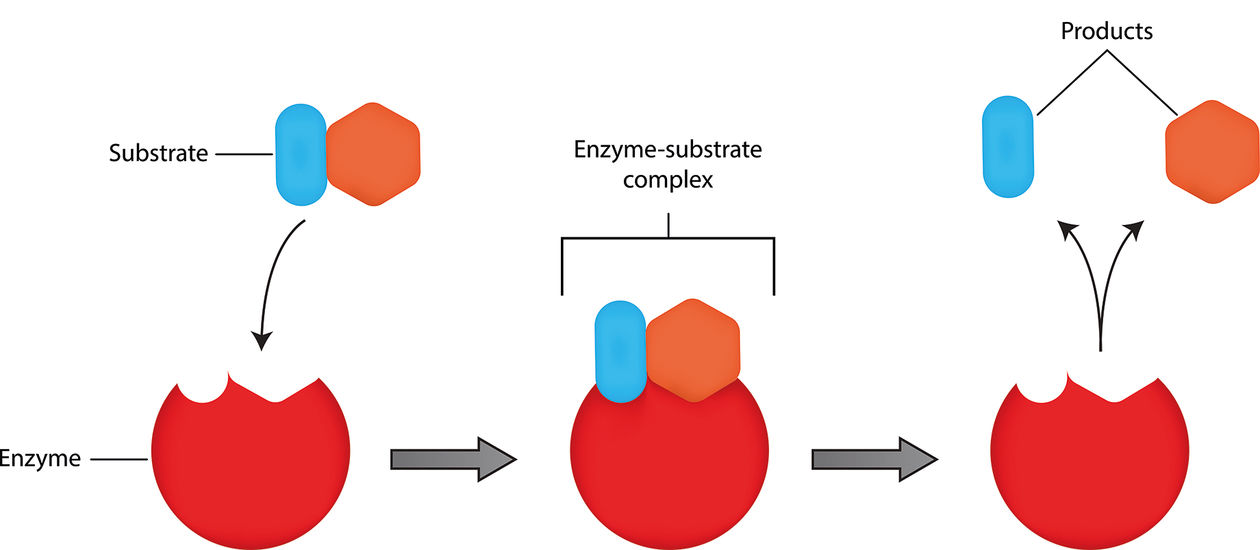
Enzymes are remarkable catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. Substrates serve as the specific molecules upon which enzymes act, initiating the reaction. Without substrates, these biological reactions would not occur, disrupting vital cellular processes.
Substrate specificity is a key characteristic
Each enzyme has a unique active site that can only accommodate specific substrates. This substrate specificity plays a crucial role in the precise functioning of biochemical pathways. It ensures that the right substrates are acted upon by the appropriate enzyme, preventing unwanted reactions.
Substrate concentration affects reaction rate
The rate of an enzymatic reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the substrate. Increasing substrate concentration enhances the likelihood of substrate-enzyme collisions, leading to a higher reaction rate. However, there is a saturation point beyond which adding more substrate does not further increase the reaction rate.
Substrates can undergo chemical transformations
During a chemical reaction, the substrate interacts with the enzyme’s active site and can undergo various chemical transformations. This includes bond breaking, formation of new bonds, and rearrangement of atoms, resulting in the formation of new products.
Substrates can be organic or inorganic
Substrates are not limited to organic compounds; they can also include inorganic molecules. Organic substrates commonly involve carbon-based compounds found in living organisms, whereas inorganic substrates can encompass minerals, metals, and other non-carbon-based substances.
Substrates play a role in drug development
Understanding the interaction between substrates and enzymes is essential in drug development. Drugs often target specific enzymes by binding to their substrates, inhibiting or modulating their activity. This knowledge is crucial in designing effective medications with minimal side effects.
Enzyme-substrate complexes are highly dynamic
When a substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site, an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. This complex undergoes dynamic changes, including conformational shifts and induced fit. These alterations optimize the molecular interactions necessary for the catalytic conversion of substrates.
Substrate concentration affects enzyme inhibition
Substrate concentration can influence enzyme inhibition. In competitive inhibition, increasing substrate concentration can overcome the inhibition by effectively outcompeting the inhibitor for the active site. However, in non-competitive inhibition, substrate concentration does not alleviate the inhibition as the inhibitor binds to a separate site on the enzyme.
Substrates can be transformed by multiple enzymes
Some substrates can be acted upon by multiple enzymes, leading to different products. This versatility allows for complex metabolic pathways, as one substrate can be involved in various biochemical reactions, contributing to the diversity of chemical processes in living organisms.
Substrates are the foundation of chemistry, driving countless reactions that occur within our bodies and the natural world. Understanding their remarkable properties and role in enzymatic processes opens up a world of possibilities for scientific discoveries and advancements.
So, next time you encounter the term “substrate,” remember the 9 unbelievable facts about substrate and appreciate the amazing complexity and beauty of the chemical world!
Conclusion
In conclusion, substrates play a critical role in various chemical processes. From supporting enzyme activity to acting as a surface for chemical reactions, substrates are a fundamental component in the world of chemistry. Understanding the properties and characteristics of substrates can provide insights into numerous scientific fields, including biochemistry, materials science, and environmental chemistry. By exploring the nine unbelievable facts about substrates, we have gained a deeper appreciation for their significance and impact. Whether it’s the versatility of graphene as a substrate or the complex interactions between enzymes and their substrates, the world of substrates continues to awe and inspire scientists. As our knowledge in chemistry advances, we can anticipate even more remarkable discoveries and applications revolving around substrates.
FAQs
Q: What is a substrate?
A substrate refers to the material or compound that undergoes a specific chemical reaction or is acted upon by an enzyme or catalyst.
Q: What is the role of substrates in enzymes?
Enzymes rely on substrates to bind to their active sites, initiating a specific chemical reaction. Substrates are essential for enzyme activity and catalysis.
Q: Can substrates influence the outcome of a chemical reaction?
Yes, the properties of substrates, such as their composition, geometry, and surface characteristics, can impact the rate and outcome of a chemical reaction.
Q: Are all substrates organic compounds?
No, substrates can include both organic and inorganic compounds. Examples of inorganic substrates include metals, minerals, and various solid surfaces.
Q: Can a substrate be a gas or a liquid?
Yes, substrates can be in the form of gases, liquids, or solids, depending on the specific chemical reaction or process involved.
Q: Are there any limitations or constraints to substrate utilization?
Certain enzymes or catalysts may have specific requirements for substrate size, shape, or functional groups, limiting the range of substrates that can be utilized.
Q: What is the significance of substrates in materials science?
In materials science, substrates act as a base upon which thin films or coatings can be deposited, influencing properties such as adhesion, conductivity, and optical characteristics.
Q: Can substrates be modified or tailored for specific applications?
Yes, substrates can be modified or engineered to enhance their properties or to create surfaces with specific functionalities for various applications, such as in electronics or biomedical devices.
Q: Are there any recent advancements or breakthroughs related to substrates?
Yes, ongoing research has led to advancements in substrate materials, such as the discovery of 2D materials like graphene, which has opened up new possibilities in electronics, energy storage, and sensing applications.
Unraveling substrate's secrets is just the beginning! Explore induced fit model's astounding adaptability, where enzymes and substrates dance in perfect harmony. Enzyme-substrate complexes hold mindblowing mysteries waiting to be solved. Substrate binding's surprising intricacies will leave you craving more fascinating insights into the world of biochemistry.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
