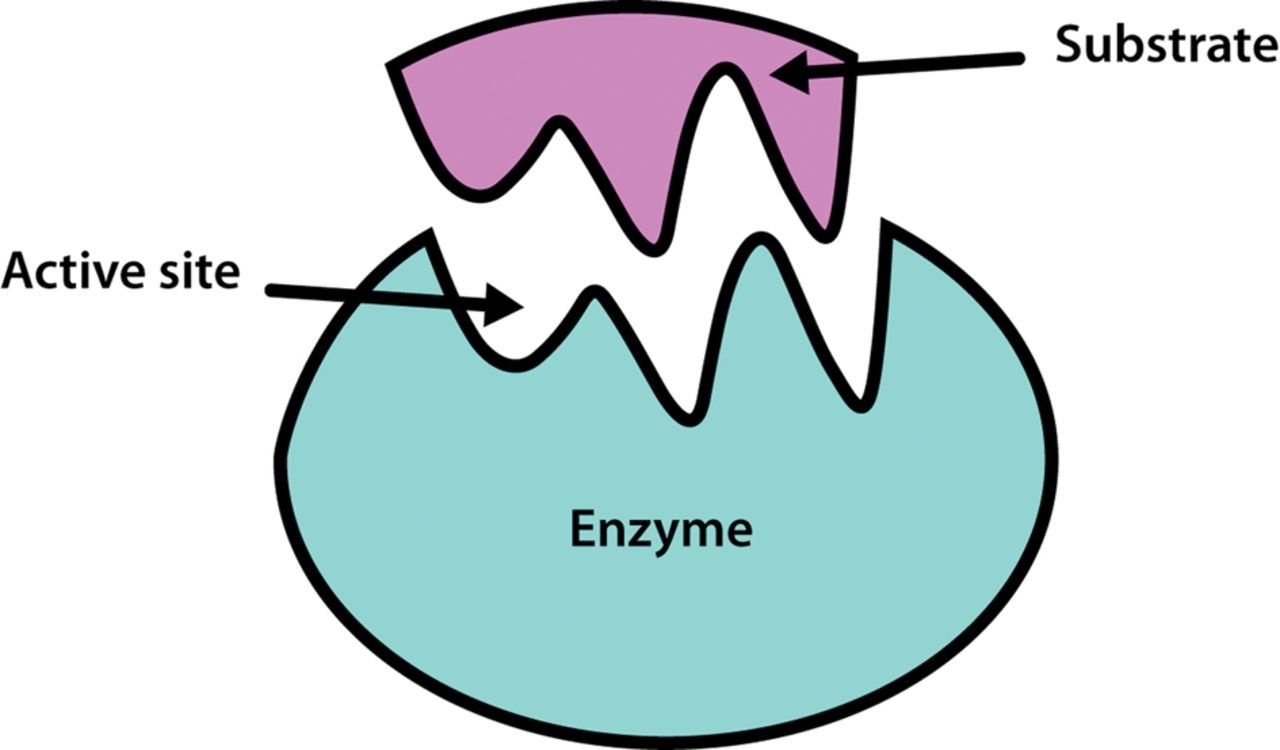
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of enzymes and their role in chemical reactions, the active site is a topic that cannot be overlooked. The active site is a crucial part of an enzyme where the actual reaction takes place. It serves as a binding site for substrates and catalyzes the conversion of reactants into products.
Delving deeper into the active site can reveal fascinating insights into how enzymes function and the mechanisms behind their catalytic abilities. In this article, we will explore 16 intriguing facts about the active site, shedding light on its structure, specificity, regulation, and other intriguing features.
So, if you’re ready to dive into the fascinating world of enzymes and unravel the mysteries of the active site, let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Active sites are like special locks that only fit specific keys, making chemical reactions happen efficiently.
- Understanding active sites helps scientists design drugs to target enzymes, opening doors to new medical treatments.
The Active Site is the Catalyst of Chemical Reactions
The active site is the region in an enzyme where the substrate binds and chemical reactions take place. It acts as a catalyst, facilitating the conversion of reactants into products.
Active Sites Are Highly Specific
Each active site is uniquely shaped to accommodate a specific substrate. This high degree of specificity ensures that only the appropriate substrate molecules can bind and react, enhancing the efficiency of the enzyme.
Active Sites Can Undergo Conformational Changes
Active sites are not static structures. They can undergo conformational changes to enhance or inhibit enzyme activity. These changes allow for precise control over the rate of chemical reactions in the cell.
Active Sites Can Bind Multiple Substrates Simultaneously
Some enzymes have active sites that are capable of binding multiple substrates at the same time. This enables complex reactions to occur in a coordinated manner, increasing the efficiency of the overall process.
Active Sites Can Be Affected by Temperature and pH
The activity of active sites can be influenced by factors such as temperature and pH. Changes in these conditions can alter the shape and function of the active site, impacting enzyme activity.
Active Sites Can Be Allosteric
Some enzymes have allosteric active sites, which can be regulated by the binding of molecules at sites other than the active site itself. This allows for additional control over enzyme activity.
Active Sites Can Bind Transition State Analogs
Transition state analogs are molecules that mimic the transition state of a reaction. Active sites have the ability to bind these analogs with high affinity, providing valuable insights into enzyme mechanisms.
Active Sites Are Essential for Enzyme-Substrate Specificity
The active site plays a crucial role in determining the specificity of an enzyme for its substrate. The precise arrangement of amino acids within the active site enables selective binding and catalysis.
Active Sites Are Often Located in Clefts or Pockets
The active sites of enzymes are frequently found in clefts or pockets on the enzyme surface. This arrangement provides a confined environment for the substrate, promoting efficient catalysis.
Active Sites Can Be Inhibited
Active sites can be inhibited by molecules known as inhibitors. These inhibitors can bind to the active site and prevent the substrate from binding, effectively blocking the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
Active Sites Can Serve as Binding Sites for Cofactors
Some active sites require the presence of cofactors, such as metal ions or coenzymes, for optimal activity. These cofactors can bind to the active site and participate in the catalytic process.
Active Sites Can Have Induced Fit
The concept of induced fit suggests that the active site undergoes conformational changes upon substrate binding. This adjustment enhances the fit between the enzyme and substrate, facilitating the catalytic reaction.
Active Sites Can Participate in Acid-Base Catalysis
Active sites may contain amino acid residues that can act as acids or bases, facilitating acid-base catalysis. These residues can donate or accept protons, aiding in the reaction process.
Active Sites Can Exhibit Covalent Catalysis
Covalent catalysis involves the formation of a transient covalent bond between the enzyme and the substrate. Active sites can contain amino acid residues that participate in covalent catalysis.
Active Sites Play a Role in Enzyme Specificity
The active site contributes to the overall specificity of an enzyme. The unique combination of amino acids within the active site determines which substrates can bind and undergo catalytic reactions.
Active Sites Can Be Targeted for Drug Design
Understanding the structure and function of active sites allows researchers to design drugs that can specifically target and inhibit the activity of particular enzymes. This approach has been instrumental in the development of various therapeutic agents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the active site in chemistry is a fascinating concept that plays a vital role in various chemical reactions. It serves as a site where substrates bind and undergo transformations, leading to the formation of products. The active site is highly specific and can accommodate only certain substrates due to its precise shape and chemical properties.Understanding the active site is crucial in the field of drug development, as many medications work by targeting and modulating the activity of enzymes at their active sites. Inhibitors can block the active site, preventing the enzyme from carrying out its function, while activators can enhance the activity of the enzyme.By exploring the 16 intriguing facts about the active site, we have gained a deeper appreciation for its significance in chemical reactions and its potential applications in various fields. The active site continues to be an area of ongoing research, and further discoveries in this field will undoubtedly expand our knowledge and provide new avenues for scientific exploration.
FAQs
1. What is an active site in chemistry?
The active site is a specific region on an enzyme or catalyst where the substrate molecule binds, leading to a chemical reaction.
2. How does the active site determine substrate specificity?
The active site’s shape, charge distribution, and chemical properties determine its ability to accommodate and react with specific substrate molecules.
3. Can the active site accommodate multiple substrates?
Some enzymes have the ability to accommodate and react with multiple substrates, while others are highly specific and can bind only to a single substrate.
4. How do inhibitors affect the active site?
Inhibitors can bind to the active site and prevent the substrate from binding, thereby blocking the enzyme’s activity.
5. Can the active site be modified?
Yes, modifications to the active site can occur through genetic mutations or by chemical modifications, altering the enzyme’s activity and substrate binding affinity.
6. What role does the active site play in drug development?
The active site is a target for designing drugs that can inhibit or activate specific enzymes, thus modulating their activity and treating various diseases.
7. Can the active site undergo conformational changes?
Yes, the active site can undergo conformational changes, allowing it to adjust and accommodate larger or differently shaped substrates.
8. How can the active site be visualized?
Techniques such as X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy can be used to visualize the active site’s structure and its interactions with substrates.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
