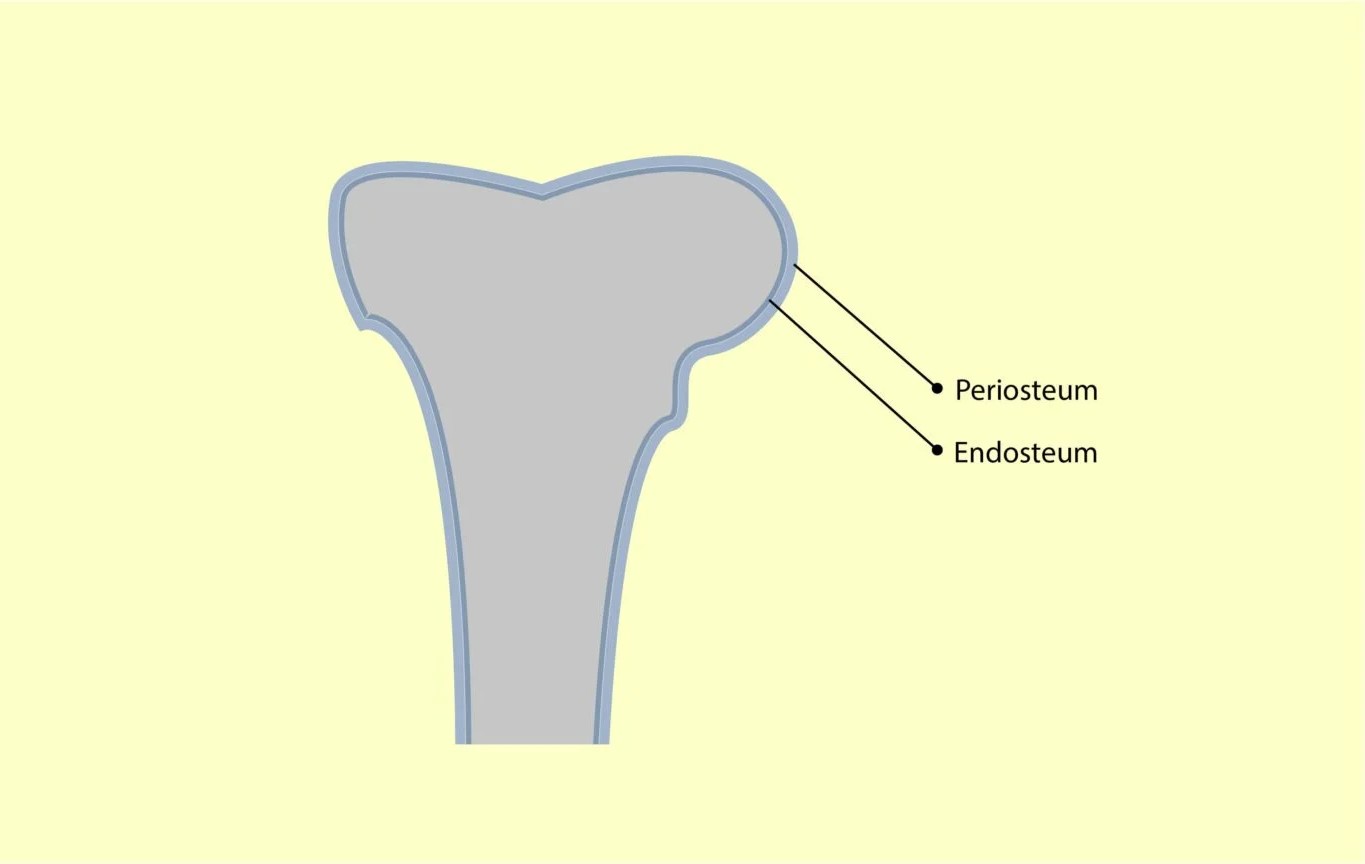
The endosteum is a fascinating and vital part of the human anatomy. It may not be as well-known as other structures like the heart or the brain, but its role in our bodies is just as crucial. The endosteum is a thin layer of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of our bones. It plays a significant role in bone development, maintenance, and repair. Despite its size, the endosteum is a bustling hub of activity, housing various types of cells and serving as a crucial site for bone remodeling. In this article, we will delve into 16 fascinating facts about the endosteum, shedding light on its importance and unveiling some lesser-known details about this remarkable structure.
Key Takeaways:
- Endosteum is like the body’s bone caretaker, helping bones grow, heal, and stay strong by regulating bone density, protecting bone tissue, and even sensing mechanical strain.
- Understanding endosteum’s role in bone biology can lead to new treatments for bone diseases and therapies for bone regeneration, making bones healthier and stronger.
What is Endosteum?
Endosteum is a thin layer of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of bones. It contains various types of cells, including osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which are involved in bone remodeling and repair.
Structure of Endosteum
The endosteum is composed of a single layer of cells called endosteal cells. These cells are flattened and contain osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoprogenitor cells. The endosteum also contains blood vessels that supply nutrients to the bone tissue.
Role in Bone Growth
Endosteum plays a crucial role in bone growth and development. It provides a surface for bone-forming cells to attach, allowing for the deposition of new bone tissue. It also helps in the remodeling of existing bone tissue.
Regulates Bone Density
The endosteum helps regulate bone density by promoting the differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation, while osteoclasts are involved in bone resorption. This balance between bone formation and resorption is essential for maintaining healthy bone density.
Interaction with Bone Marrow
Endosteum is closely associated with bone marrow, which is found inside the central cavity of long bones and in the spaces between trabeculae in cancellous bone. It helps in the exchange of nutrients and waste products between bone cells and the surrounding bone marrow.
Protection and Support
The endosteum provides a protective and supportive environment for bone tissue. It helps maintain the integrity of the bone structure and prevents damage from external forces.
Healing of Bone Fractures
During the healing process of a bone fracture, the endosteum plays a crucial role in the recruitment of cells necessary for bone repair. It also helps in the formation of a new callus, which eventually bridges the fracture site.
Role in Calcium Homeostasis
Endosteum is involved in maintaining calcium homeostasis in the body. It regulates the release of calcium from bone tissue into the bloodstream and helps in the deposition of calcium back into the bone when needed.
Sensory Function
Recent studies suggest that the endosteum may have sensory functions and play a role in detecting mechanical strain and transmitting signals to bone-forming cells. This allows for the adaptation and remodeling of bone in response to mechanical stimuli.
Importance in Bone Diseases
The endosteum is implicated in various bone diseases, including osteoporosis and osteomalacia. Changes in the endosteum’s structure and function can disrupt the balance between bone formation and resorption, leading to bone loss and increased fracture risk.
Therapeutic Applications
The understanding of the endosteum’s role in bone biology has led to the development of therapeutic strategies for bone regeneration and repair. Researchers are exploring the use of endosteal cells and their manipulation to enhance bone healing and treat bone disorders.
Vascularization of Bone
Endosteum plays a critical role in the vascularization of bone tissue. It provides a route for blood vessels to enter and traverse bone, supplying essential nutrients and oxygen to bone cells.
Response to Hormonal Changes
Endosteal cells are responsive to hormonal changes in the body, such as those occurring during puberty or menopause. These hormonal shifts can influence bone remodeling and affect the overall health and strength of the skeleton.
Communication with Other Bone Cells
The endosteum facilitates communication between different bone cells, allowing for the coordination of bone remodeling and repair processes. It acts as a signaling interface, enabling cells to exchange information and regulate their activity.
Endosteum and Bone Cancer
Studies have shown that the endosteum may play a role in the initiation and progression of bone cancer, such as osteosarcoma. Understanding the interactions between cancer cells and the endosteum could provide insights into developing targeted therapies.
Constant Remodeling Process
The endosteum is involved in the constant remodeling process of bone tissue throughout life. It allows for the removal of old or damaged bone and the replacement with newly formed bone, ensuring the maintenance of a healthy and functional skeletal system.
These 16 fascinating facts about endosteum highlight its essential role in bone biology, from bone growth to repair and maintenance. Understanding the intricate functions of the endosteum opens up possibilities for advancements in bone research and the development of new therapies for bone-related conditions.
Conclusion
Endosteum is a vital component of the human anatomy that plays a crucial role in bone health and function. Its thin membrane-like structure lines the inner surface of bones, providing a protective layer and facilitating various physiological processes. The endosteum contains osteoprogenitor cells that contribute to bone remodeling, repair, and maintenance.Understanding the fascinating facts about endosteum helps shed light on its significance in the overall functioning of the skeletal system. From its role in mediating bone growth during development to its involvement in bone regeneration after fractures, endosteum proves to be a dynamic and essential part of our bodies.By delving deeper into the intricacies of endosteum, researchers and medical professionals can continue to uncover new insights into bone biology and discover innovative treatment approaches for conditions such as osteoporosis and bone injuries. The study of endosteum opens up exciting avenues for further exploration, leading to advancements in the field of skeletal health and improving the quality of life for individuals worldwide.
FAQs
1. What is the function of endosteum?
The endosteum serves multiple functions, including facilitating bone growth during development, participating in bone remodeling, and aiding in bone repair after fractures.
2. How does the endosteum contribute to bone health?
The endosteum contains osteoprogenitor cells that differentiate into osteoblasts, which are responsible for bone formation. It also helps maintain the balance between bone resorption and bone formation, crucial for overall bone health.
3. Can endosteum be damaged or affected by diseases?
Yes, various diseases, such as osteoporosis and osteomyelitis, can affect the endosteum and disrupt its normal functioning. Traumatic injuries to the bone can also damage the endosteum.
4. Does endosteum have any role in bone regeneration?
Yes, the endosteum plays a significant role in bone regeneration by providing a niche for the proliferation and differentiation of osteoprogenitor cells, leading to the formation of new bone tissue.
5. Can the endosteum be visualized in medical imaging?
Typically, the endosteum is not clearly visible in routine medical imaging techniques such as X-rays. However, advanced imaging modalities like CT scans and MRI can provide better visualization of the endosteum.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
