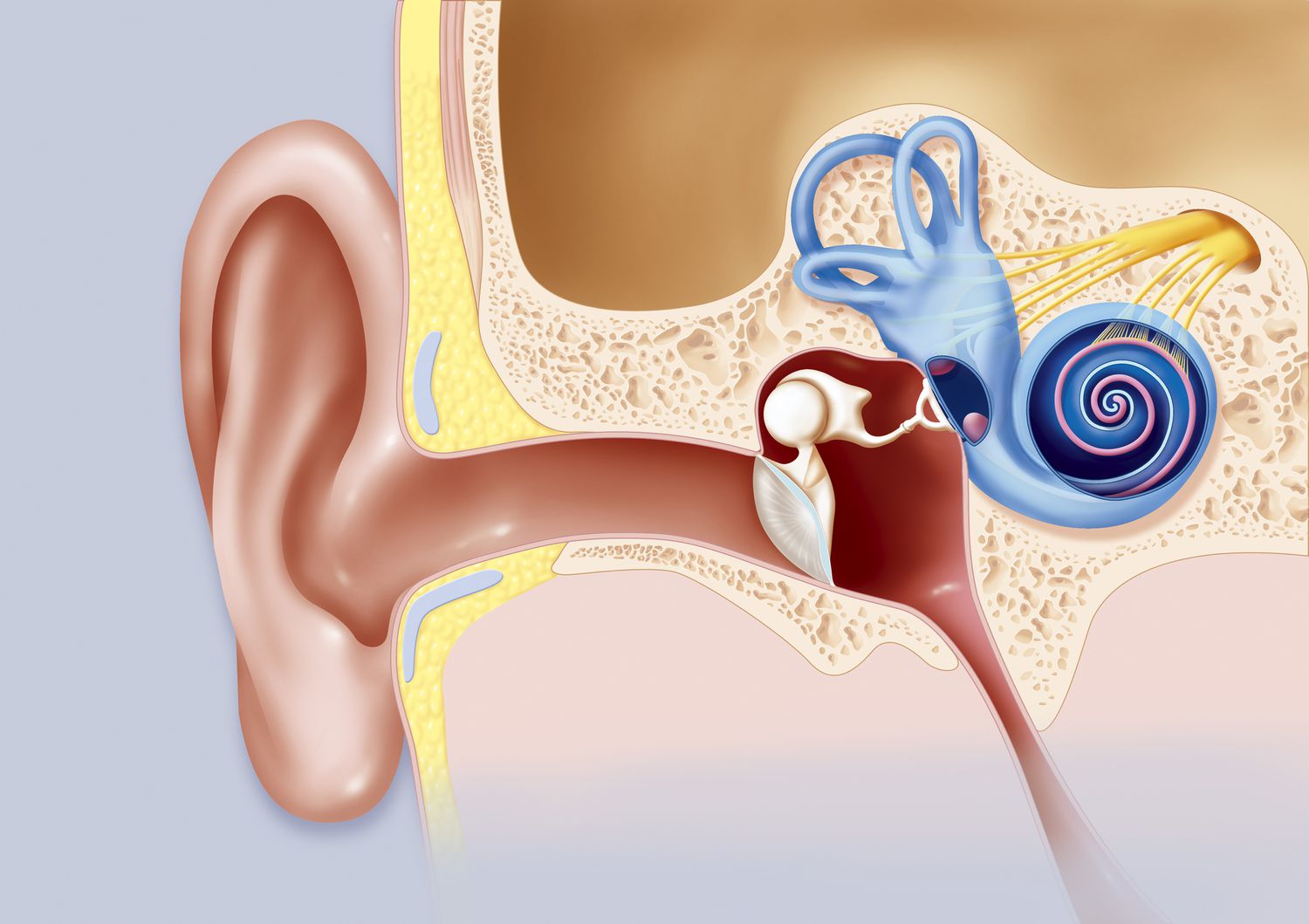
The cochlear nerve, also known as the acoustic nerve, is a critical component of our auditory system. It plays a vital role in transmitting sound signals from the cochlea to the brain, allowing us to perceive and interpret sounds. While the cochlear nerve may seem like a straightforward part of our anatomy, it holds some fascinating secrets that continue to intrigue scientists and medical professionals alike.
In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic nature of the cochlear nerve and uncover 10 intriguing facts that shed light on its importance and complexity. From its microscopic structure to its role in hearing loss and innovative research developments, the cochlear nerve is a captivating subject that exemplifies the wonders of human anatomy and the intricacies of our perception of sound.
Key Takeaways:
- The cochlear nerve is a crucial part of our ability to hear, carrying electrical impulses from the inner ear to the brain for sound interpretation.
- Protecting our ears from loud noises is important to preserve the integrity of the cochlear nerve and prevent hearing loss.
The Cochlear Nerve: A Vital Connection
The cochlear nerve, also known as the auditory nerve, plays a crucial role in our ability to hear. It is responsible for transmitting sound signals from the inner ear, specifically the cochlea, to the brain for processing and interpretation.
It Carries Electrical Impulses
The cochlear nerve is composed of thousands of individual nerve fibers that carry electrical impulses generated by the hair cells in the cochlea. These impulses travel along the nerve and ultimately reach the auditory cortex in the brain, allowing us to perceive and understand sound.
It’s Part of the Eighth Cranial Nerve
The cochlear nerve is one component of the eighth cranial nerve, also known as the vestibulocochlear nerve. This nerve is responsible for both hearing (via the cochlear nerve) and balance (via the vestibular nerve).
It’s a Bilateral Structure
The cochlear nerve is present on both sides of the head, meaning we have a cochlear nerve in each ear. This bilateral arrangement ensures that we can perceive sound in a stereo or three-dimensional manner.
It Carries Different Frequencies
The cochlear nerve is specialized to carry different frequencies of sound. The nerve fibers closest to the base of the cochlea are responsible for transmitting high-frequency sounds, while the fibers towards the apex carry low-frequency sounds.
Damage to the Cochlear Nerve Causes Hearing Loss
If the cochlear nerve is damaged or compromised, it can result in hearing loss or even complete deafness in the affected ear. This can occur due to various reasons such as trauma, infections, or certain medical conditions.
It’s Vulnerable to Noise-Induced Damage
Prolonged exposure to loud noises can cause damage to the cochlear nerve, leading to noise-induced hearing loss. This emphasizes the importance of protecting our ears from excessive noise levels to preserve the integrity of the cochlear nerve.
It’s Essential for Speech Perception
The cochlear nerve is essential for speech perception and understanding. It allows us to differentiate between different sounds, words, and tones, enabling effective communication and language comprehension.
It Can be Affected by Tumors
In some cases, tumors can develop along the path of the cochlear nerve. This can lead to various symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and imbalance. Treatment options for these tumors may include surgical removal or radiation therapy.
Advances in Cochlear Nerve Stimulation
Advancements in medical technology have led to the development of cochlear implants, a remarkable solution for individuals with severe hearing loss or deafness. Cochlear implants directly stimulate the cochlear nerve, bypassing the damaged hair cells and allowing individuals to regain some level of hearing.
These 10 enigmatic facts about the cochlear nerve highlight its vital role in our ability to hear and perceive sound. Understanding the complexities of this intricate neural pathway enhances our appreciation for the wonders of human anatomy and the incredible capacity of our auditory system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cochlear nerve is a fascinating aspect of human anatomy that plays a crucial role in our ability to hear and perceive sound. This nerve carries electrical signals from the inner ear to the brain, allowing us to interpret and understand the world of sound around us. Understanding the enigmatic facts about the cochlear nerve helps us appreciate the complexity and intricacy of our auditory system. From its unique structure to its remarkable ability to transmit signals, the cochlear nerve is truly a vital component of our overall hearing function. By delving into the depths of this nerve, we gain a deeper understanding of the remarkable mechanisms that enable us to experience the rich tapestry of sounds that surround us each day.
FAQs
1. What is the cochlear nerve?
The cochlear nerve, also known as the auditory nerve, is a section of the eighth cranial nerve that carries electrical signals from the cochlea (inner ear) to the brain, enabling us to perceive sound.
2. How does the cochlear nerve transmit signals?
The cochlear nerve transmits signals through a complex network of fibers and cells. It converts sound vibrations into electrical signals, which are then relayed to the brain for interpretation and understanding.
3. What happens if the cochlear nerve is damaged?
If the cochlear nerve is damaged, it can result in hearing loss or difficulties in perceiving and understanding sound. This can impact an individual’s quality of life and may require medical intervention or the use of hearing aids or cochlear implants.
4. Can the cochlear nerve be repaired?
Currently, there is no known way to repair or regenerate the cochlear nerve. However, advancements in medical technology and research offer hope for potential treatments in the future.
5. Is the cochlear nerve different from the auditory nerve?
No, the cochlear nerve and the auditory nerve refer to the same nerve. The term “cochlear nerve” is more commonly used in reference to the specific function of transmitting auditory signals from the cochlea to the brain.
6. How long is the cochlear nerve?
The length of the cochlear nerve varies among individuals. It extends from the cochlea to the brainstem, covering a distance of approximately 20 to 30 millimeters.
7. Can the cochlear nerve be affected by certain medical conditions?
Yes, certain medical conditions such as acoustic neuroma or infections can affect the function of the cochlear nerve, leading to hearing loss or other auditory impairments.
8. Can exercise or lifestyle changes improve the health of the cochlear nerve?
While exercise and healthy lifestyle choices promote overall well-being, there is no direct evidence to suggest that they specifically target or improve the health of the cochlear nerve.
9. Is the cochlear nerve involved in balance and spatial orientation?
No, the cochlear nerve is primarily associated with transmitting auditory signals. Balance and spatial orientation are managed by a different portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve, known as the vestibular nerve.
10. Are there any treatment options available for cochlear nerve-related disorders?
Depending on the specific disorder or condition affecting the cochlear nerve, treatment options may include medication, hearing aids, cochlear implants, or other assistive devices. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
