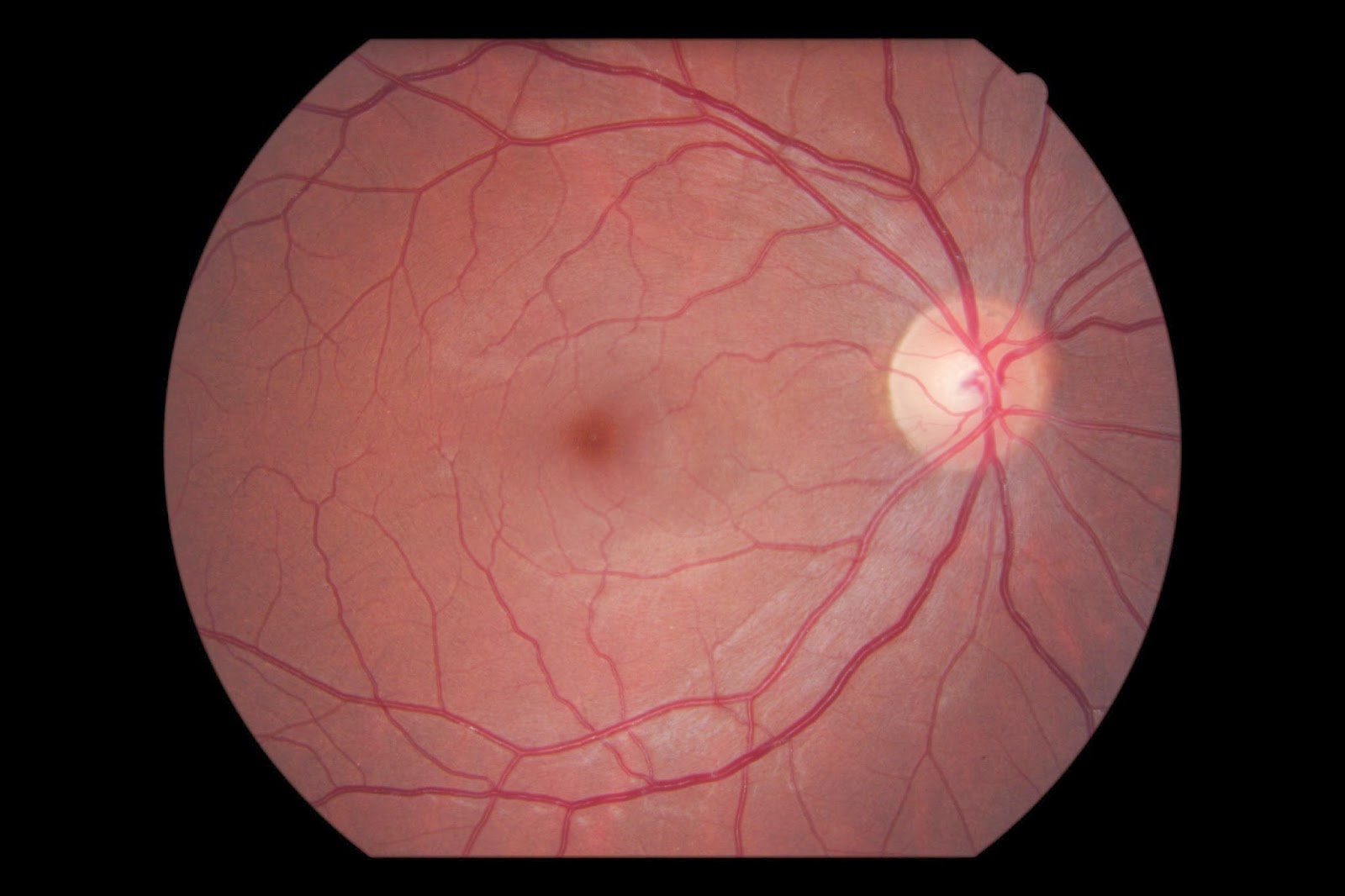
The optic nerve is a remarkable and vital component of our visual system. It serves as an information superhighway, carrying visual signals from the eye to the brain, allowing us to perceive the world around us. While most of us are familiar with the basic function of the optic nerve, there are several astonishing facts about this complex structure that you may not be aware of. From its incredible ability to transmit data to the brain at lightning speed to its vulnerability to certain conditions, the optic nerve is truly a marvel of human anatomy. In this article, we will explore 13 astonishing facts about the optic nerve that will deepen your understanding of this crucial part of our visual system.
Key Takeaways:
- The optic nerve, also known as cranial nerve II, is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain, allowing us to see and perceive the world around us.
- Damage to the optic nerve can lead to vision loss, and conditions such as glaucoma and optic neuritis can affect its health and function, leading to vision problems.
Optic Nerve is the Second Cranial Nerve
The optic nerve, also known as cranial nerve II, is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain.
More Than One Million Nerve Fibers
The optic nerve consists of approximately one million nerve fibers, which carry visual signals to the brain for interpretation.
Connects the Eye to the Brain
The optic nerve connects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, to the visual centers in the brain, allowing us to see and perceive the world around us.
No Photoreceptors in the Optic Nerve
Unlike the retina, which contains photoreceptor cells to capture light, the optic nerve does not contain any photoreceptors. Its main function is to transmit visual signals.
The Optic Nerve is Myelinated
The nerve fibers of the optic nerve are surrounded by a protective myelin sheath, which helps to facilitate the efficient transmission of visual signals.
Optic Nerve Damage Can Lead to Vision Loss
If the optic nerve is damaged or injured, it can result in partial or complete vision loss, depending on the severity and location of the damage.
Optic Nerve Disorders
Conditions such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, and optic nerve tumors can affect the health and function of the optic nerve, leading to vision problems.
The Optic Nerve is About 50-55mm in Length
The average length of the optic nerve is approximately 50-55mm, extending from the back of the eye to the optic chiasm, where the nerve fibers partially cross.
Optic Nerve Can Transmit Signals at High Speeds
The optic nerve is capable of transmitting visual signals at incredible speeds, allowing us to perceive the world in real-time.
Optic Nerve Supply
The optic nerve receives its blood supply from a network of blood vessels called the ciliary arteries, which provide oxygen and nutrients to sustain its function.
Each Eye has its Own Optic Nerve
Each eye has its own optic nerve, which transmits visual information independently to the brain. This allows for binocular vision and depth perception.
The Optic Nerve Can Be Examined by an Ophthalmologist
An ophthalmologist can perform a comprehensive eye examination, including the evaluation of the optic nerve, to assess its health and detect any abnormalities or signs of disease.
Optic Nerve Regeneration
Research is being conducted to explore the possibility of regenerating damaged or injured optic nerves, which could potentially restore vision in individuals affected by optic nerve diseases or injuries.
Conclusion
The optic nerve is truly a remarkable part of the human anatomy. Its intricate structure and functions are essential for our visual perception and overall well-being. From transmitting visual information to the brain to playing a role in maintaining eye health, the optic nerve plays a crucial role in our lives.Understanding the optic nerve can help us appreciate its importance and the remarkable capabilities of our visual system. Its complexity and vulnerability make it an area of interest for researchers and medical professionals alike. By staying informed about the optic nerve and taking steps to maintain its health, we can ensure that our vision remains clear and vibrant for years to come.
FAQs
1. What is the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.
2. How does the optic nerve work?
The optic nerve receives signals from the light-sensitive cells in the retina and carries them to the brain, where they are interpreted as visual images.
3. Can the optic nerve be damaged?
Yes, the optic nerve can be damaged due to various factors such as trauma, glaucoma, or other diseases.
4. What are the symptoms of optic nerve damage?
Symptoms of optic nerve damage may include vision loss, blurred vision, loss of peripheral vision, and changes in color perception.
5. How can I keep my optic nerve healthy?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular eye exams, protecting your eyes from injury, and managing underlying health conditions can help keep your optic nerve healthy.
6. Can optic nerve damage be treated?
Treatment options for optic nerve damage depend on the cause and severity of the damage. It’s important to consult with an eye specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
7. Are there any natural ways to support optic nerve health?
While there is no direct evidence, a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, along with regular exercise and avoiding smoking, may contribute to overall eye health.
8. Can optic nerve damage lead to permanent vision loss?
Depending on the extent of the damage, optic nerve damage can lead to partial or complete vision loss. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing optic nerve conditions.
9. Can optic nerve damage be prevented?
Some causes of optic nerve damage, such as trauma, can be prevented by taking safety precautions. Regular eye exams and managing underlying health conditions can also help detect and manage potential optic nerve issues.
10. Can the optic nerve regenerate?
Currently, the optic nerve has limited regenerative capabilities. However, ongoing research aims to find ways to stimulate nerve regeneration and restore visual function.
Exploring astonishing facts about the optic nerve sparks curiosity for more intriguing discoveries. Have you ever wondered about the optic disc's blind spot and its enigmatic nature? Unraveling the mysteries surrounding this fascinating aspect of our visual system will leave you captivated and eager to learn more.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
