The renal cortex, also known as the cortical region of the kidney, is a vital component of the complex renal system. This outermost layer of the kidney plays a crucial role in the filtration and reabsorption of waste products, regulation of blood pressure, and maintenance of electrolyte balance. It is a fascinating and intricate part of the human anatomy that deserves further exploration.
In this article, we will delve into the depths of the renal cortex and uncover 19 fascinating facts that will not only expand your knowledge of this remarkable organ but also leave you in awe of its complexity. From its anatomical features to its essential functions, we will journey through the incredible world of the renal cortex, shedding light on its significance in maintaining overall health and well-being. So, prepare to be amazed as we uncover the hidden wonders of the renal cortex!
Key Takeaways:
- The renal cortex, located in the outer region of the kidney, filters waste products, reabsorbs essential nutrients, and produces hormones crucial for maintaining overall body health.
- The renal cortex plays a vital role in regulating the body’s acid-base balance, protecting the kidneys, and determining the kidney’s ability to filter blood, making it a fascinating and essential part of the human body.
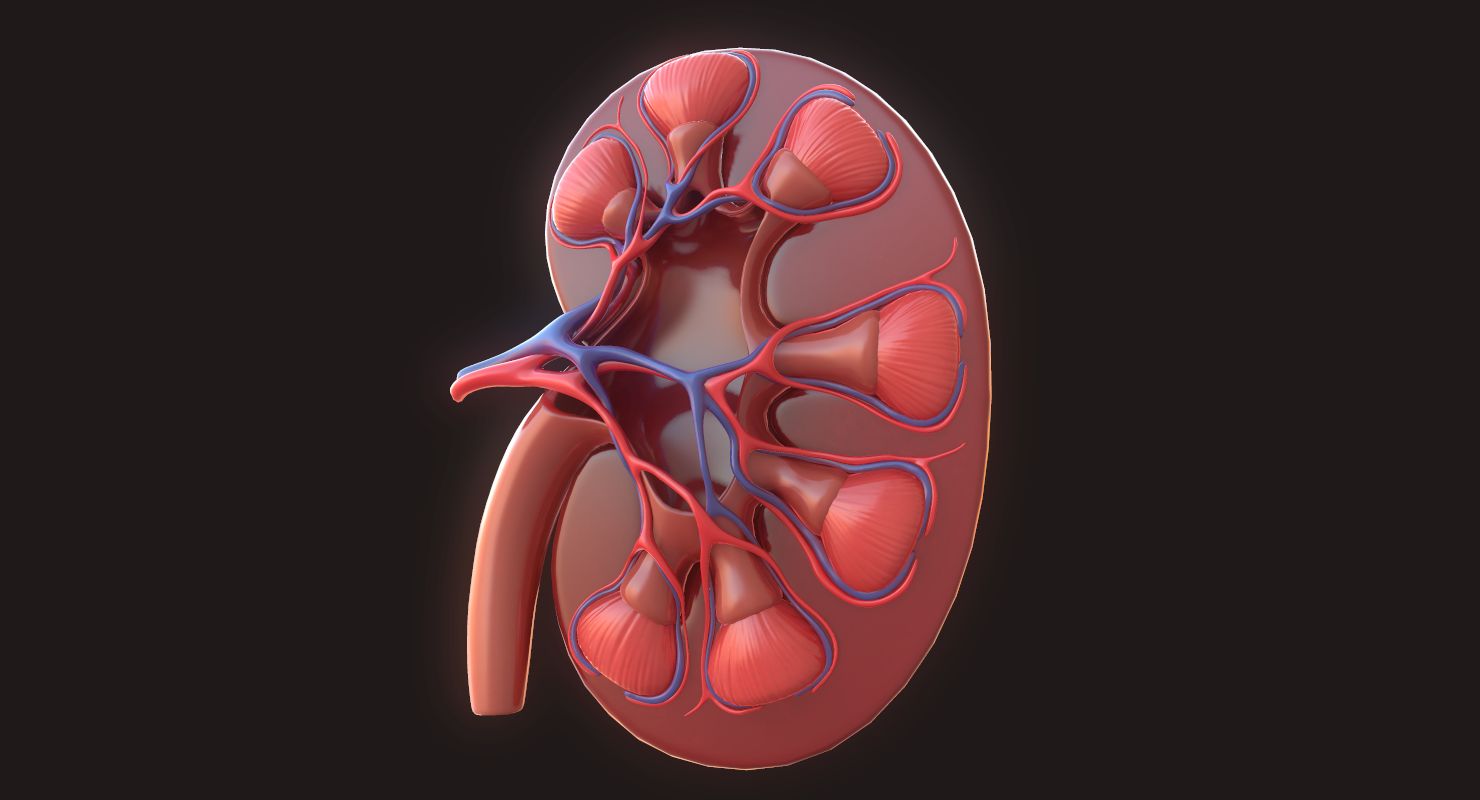
Location within the Kidney
The renal cortex is the outer region of the kidney, located just beneath the renal capsule. It extends from the renal capsule to the renal medulla.
Composition and Structure
The renal cortex consists of millions of tiny functional units called nephrons. These nephrons are responsible for filtering waste products and regulating the balance of electrolytes and water in the body.
Blood Supply
The renal cortex receives a rich blood supply through the renal arteries. These arteries branch out to form a network of arterioles, which supply the nephrons with oxygen and nutrients.
Urine Formation
In the renal cortex, the nephrons filter blood plasma to remove waste products and excess water, forming urine. This urine then travels through the renal medulla and into the renal pelvis before being excreted from the body.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
The renal cortex plays a crucial role in determining the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is a measure of the kidney’s ability to filter blood. Proper functioning of the renal cortex is essential for maintaining optimal GFR.
Reabsorption of Nutrients
Within the renal cortex, nutrients such as glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed by the nephrons and returned to the bloodstream. This ensures that essential substances are not lost during the filtration process.
Production of Hormones
The renal cortex is involved in the production of important hormones such as erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells, and renin, which regulates blood pressure and fluid balance.
Protection of the Kidneys
The dense layer of the renal cortex acts as a protective barrier for the kidneys, shielding them from external injuries and providing structural support.
Role in Acid-Base Balance
The renal cortex plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s acid-base balance by regulating the excretion of hydrogen ions and the reabsorption of bicarbonate ions.
Diagnostic Imaging
Medical professionals often use imaging techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans to visualize the renal cortex and diagnose any abnormalities or diseases affecting this region of the kidney.
Regional Differences
The thickness and composition of the renal cortex may vary in different regions of the kidney, with the outer cortical region differing from the inner cortical area.
Relationship with Renal Medulla
The renal cortex and renal medulla work together to perform the vital functions of the kidney. While the cortex is involved in filtration and reabsorption, the medulla is responsible for concentrating and collecting urine.
Nephron Density
The renal cortex contains a high density of nephrons, enabling efficient filtration and waste removal from the blood.
Oxygen Consumption
The renal cortex has a high oxygen consumption rate due to its role in filtration and reabsorption processes, which require energy.
Susceptibility to Damage
The renal cortex can be vulnerable to damage caused by certain medications, toxins, or diseases that specifically target the kidney.
Role in Drug Metabolism
Some drugs are metabolized within the renal cortex, which can impact their efficacy and interactions with other medications.
Development and Differentiation
During fetal development, the renal cortex undergoes complex differentiation processes to form the nephrons and establish its functional characteristics.
Age-Related Changes
The renal cortex undergoes changes with age, including a decrease in size and a decline in renal function, which can lead to age-related kidney diseases.
Influence of Hormones
Hormones such as aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) can have direct effects on the renal cortex, regulating water and electrolyte balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the renal cortex is a crucial part of the kidney that plays a vital role in the filtration and reabsorption of substances in our body. It is responsible for the production of urine, which helps to eliminate waste products and maintain water and electrolyte balance. The renal cortex contains millions of nephrons, each contributing to the overall function of the kidney. Understanding the anatomy and function of the renal cortex is essential for diagnosing and treating various kidney disorders. By delving into the fascinating facts about the renal cortex, we can appreciate the complexity and importance of this remarkable organ.
FAQs
1. What is the renal cortex?
The renal cortex is the outermost layer of the kidney. It contains the nephrons, which are the functional units of the kidney, responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and regulating water and electrolyte balance.
2. What is the role of the renal cortex?
The renal cortex plays a crucial role in filtering the blood and reabsorbing essential substances, such as water, electrolytes, and nutrients. It also helps in eliminating waste products through the production of urine.
3. How does the renal cortex produce urine?
The renal cortex filters blood through the glomerulus, where waste products and excess water are removed. The filtered fluid then passes through the tubules in the renal cortex, where essential substances are reabsorbed, and waste products form urine.
4. Can kidney diseases affect the renal cortex?
Yes, kidney diseases can affect the renal cortex. Conditions like chronic kidney disease, kidney infections, and kidney tumors can cause damage to the renal cortex, leading to impaired kidney function and various symptoms.
5. How can I keep my renal cortex healthy?
To keep your renal cortex healthy, it is essential to maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, exercise regularly, avoid excessive alcohol consumption, and refrain from smoking. It is also essential to monitor and manage any underlying medical conditions that may affect kidney health.
Exploring the renal cortex is just the beginning of your journey into understanding kidney function. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of the glomerulus, where blood filtration takes place. Discover how maintaining optimal kidney health is essential for overall well-being. Learn about the crucial role of renal medications in managing various kidney conditions and supporting proper kidney function.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


