Although hydrogen is the simplest and lightest element in the periodic table, it’s nothing short of impressive. Hydrogen is the most abundant element, and it makes up most of the matter in the universe. This powerful chemical can also fuel stars, cars, and rocket ships. It’s also one of the most promising sources of clean fuel. Learn more about this valuable element with these fascinating hydrogen facts.
- Hydrogen’s atomic number is 1 and its chemical symbol is H.
- The alchemist and physician Paracelsus unknowingly observed hydrogen at around 1520 when he noted that gas formed as a byproduct of acids attacking metals.
- Another physician, Théodore de Mayerne, later repeated Paracelsus’s experiment in 1650. Mayerne noted that the gas was flammable, but neither Paracelsus nor Mayerne considered the gas as a new element.
- In 1766, English scientist Henry Cavendish first described hydrogen gas as a unique substance. He called this gas “inflammable air”.
- Hydrogen has a boiling point of 20.271 K (−423.182 °F; −252.879 °C) and a melting point of 13.99 K (−434.49 °F; −259.16 °C).
- Hydrogen is the first element in the periodic table.
- Hydrogen can bond with itself to form a diatomic hydrogen molecule (H2).
- This chemical does not have any color, odor, or taste.
- Hydrogen is nonmetallic and non-toxic.
- Hydrogen is extremely flammable when combined with oxygen. It forms water on combustion with oxygen. This property prompted French chemist Antoine Lavoisier to give it the name “hydrogen”, which is the Greek term for “water-former”.
- Hydrogen has a standard atomic weight of 1.008 and is the lightest element on the periodic table.
- The boiling and melting points of hydrogen molecules are among the lowest of all substances, second only to helium.
- Hydrogen combines with electronegative elements (such as chlorine, fluorine, and oxygen) through hydrogen bonds.
- Hydrogen’s electron configuration is 1s1. It has one valence electron.
- Gaseous hydrogen has a specific gravity of 0.0696 and only has around 7% the density of air.
- In 1995, scientists first produced antihydrogen, the antimatter counterpart of hydrogen. Antihydrogen contains a positron and an antiproton.
- Hydrogen is around 14 times lighter than air.
- In 1800, Anthony Carlisle, William Nicholson, and Johann Ritter first decomposed water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis.
- According to data from 2018, the United States of America alone produces 10 million metric tons of hydrogen per year.
- Although hydrogen is non-toxic, it may displace the oxygen in the air and result in asphyxiation.
Hydrogen makes up most of the matter in the universe.

One of the most essential hydrogen facts is that it makes up a huge portion of all the normal matter in the universe. It makes up about more than 90% of normal matter by number and around 75% by mass. Most stars, molecular clouds, and gas giants consist of hydrogen.
Hydrogen typically exists throughout the universe in its atomic state or as plasma.
On Earth, however, hydrogen typically exists either as a gas or in combination with other elements. Despite hydrogen being so abundant, its diatomic gaseous form (H2) is a rather rare resource in our atmosphere. Gaseous hydrogen only makes up about 0.00005% of the air we breathe.
Hydrogen has three naturally-occurring isotopes.
There are three naturally-occurring variants or isotopes of hydrogen. Hydrogen is the only element whose isotopes have distinct names, and these are protium, deuterium, and tritium. As isotopes, these atoms have the same number of protons and only differ in the number of neutrons. Two of these isotopes are stable, while one isotope is radioactive.
The hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1, is the most common isotope of hydrogen, with an abundance of around 99.98%. This is a stable isotope, and its chemical symbol is 1H. It is the simplest of all elements, containing a single proton and electron. Protium gets its name from the fact that it only has a single proton in its nucleus. It’s also worth noting that the hydrogen atom is the only element that can exist in a stable state without a neutron.
Another one of the two stable isotopes of hydrogen is deuterium or hydrogen-2. Its nucleus consists of a single proton and a single neutron, and its chemical symbols are either 2H or D. American chemist Harold Urey discovered deuterium in 1931. Urey named it deuterium after the Greek word deuteros, which means “second”. This refers to the two particles in its nucleus. Many also refer to this isotope as “heavy hydrogen”.
The third isotope of hydrogen is tritium or hydrogen-3, which contains one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. Its symbols are 3H or T. Tritium is a radioactive isotope that has a half-life of 12.32 years. It occurs naturally when cosmic rays interact with atmospheric gases.
Hydrogen also has heavier isotopes, but those are man-made and do not occur naturally. One of these synthetic isotopes, hydrogen-7 (7H), has the shortest half-life of any known isotope.
It was one of the first elements produced after the Big Bang.
The famous Big Bang theory postulates that the universe was once in a hot, dense state and it began expanding rapidly, giving rise to the universe we know today. After the universe started cooling down, subatomic particles began to form and combine into atoms.
Hydrogen was one of the first elements that came into existence after the Big Bang, along with helium and lithium. These primordial elements later came together through gravity and formed early nebulae, stars, and galaxies. Now that’s one of the hydrogen facts that are truly out of this world!
Hydrogen is essential in the production of ammonia and the processing of fossil fuels.
All three isotopes of hydrogen have a multitude of industrial uses, making hydrogen a valuable resource. It’s essential for the production of ammonia for plant fertilizers and also has its uses in processing fossil fuels and treating metals, among others.
The isotopes deuterium and tritium are useful for nuclear energy and biochemical research. Both deuterium and tritium also play a role in making nuclear weapons, such as the fearsome hydrogen bomb.
Because hydrogen mostly exists on Earth in compounds with other elements, such as methane (CH4) or water (H2O), it must be separated from the other elements. To do this, industries must produce hydrogen through methods such as steam reforming, gasification, or electrolysis. These methods separate the elements in various compounds, producing the usable H2 molecules.
It was once used to lift airships.
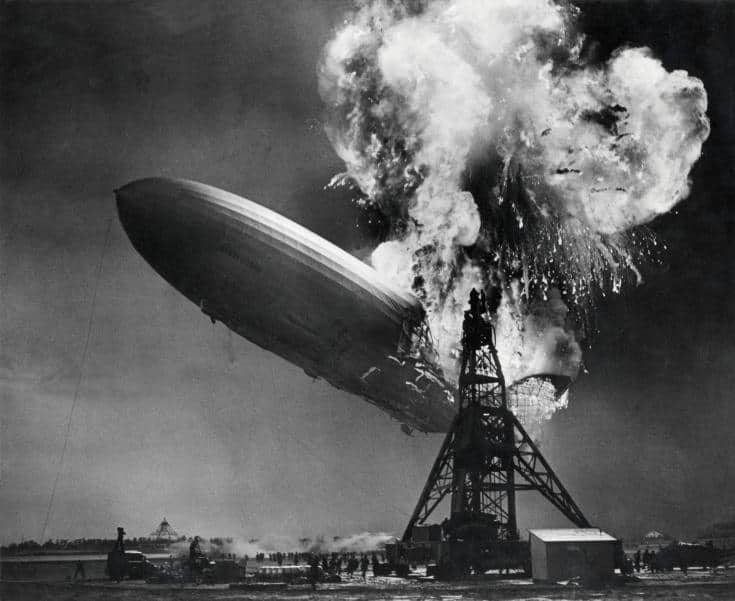

Hydrogen is the lightest chemical in the periodic table, and it is 14 times lighter than air. It thus has the ability to lift objects, similar to how helium can lift balloons. Because hydrogen is cheaper and more readily available than helium, early airships used hydrogen as a lifting gas. Hydrogen used to lift even the most massive airships such as the German Zeppelin Hindenburg.
Unfortunately, hydrogen is highly flammable. This made it a dangerous lifting gas for manned airship flights. Hydrogen-filled airships, and airships in general, eventually fell out of favor especially after Hindenburg caught fire in 1937.
The Sun and other stars use hydrogen as fuel.
Perhaps one of the most well-known hydrogen facts is that hydrogen fuels the Sun and other stars. Like most stars, the Sun consists of hydrogen atoms, and its core fuses these atoms together under extremely high pressure. This process of nuclear fusion produces the heat and light that the Sun emits, which in turn powers most living beings on Earth.
As an added fact, the fusion of atoms in the core of stars eventually results in the creation of heavier chemical elements. Essentially, many of the elements in the universe heavier than lithium-7 came to existence because of hydrogen. Without it, you probably would not exist. How’s that for fascinating hydrogen facts?
Hydrogen made it possible for humans to explore space.
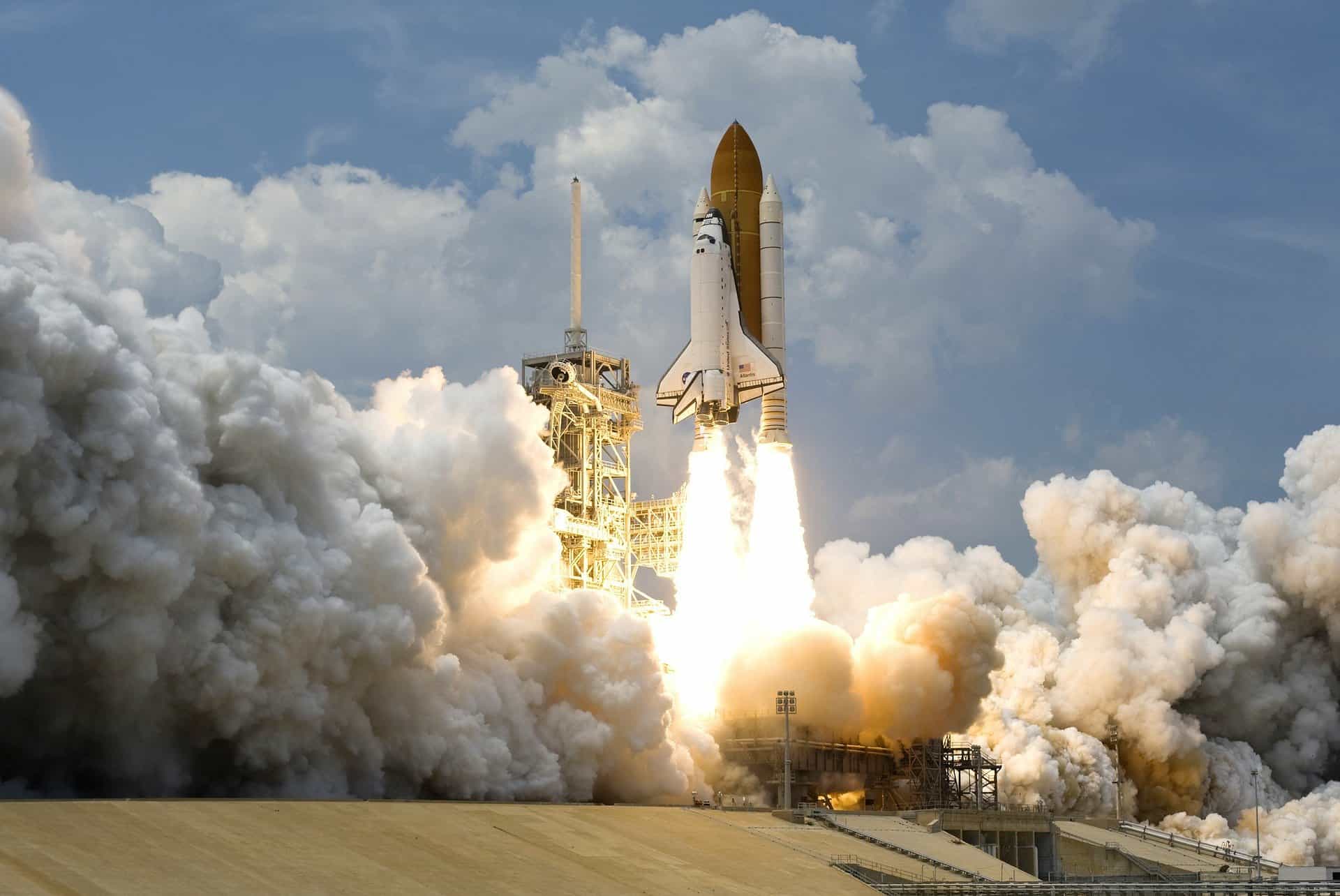

Although hydrogen has its fair share of dangers and accidents, it also paved the way for humans to explore outer space. Liquid hydrogen is the most favorable choice when it comes to fueling spacecraft because it’s a lightweight substance that can pack a lot of power. In combination with liquid oxygen, it can provide the most efficient sources of energy to travel through space. Hydrogen fuel made it possible for humans to explore space and even achieve the famous Apollo missions.
Containing liquid hydrogen does come with its unique set of challenges. For example, for the hydrogen to remain in a liquid phase, it needs to be in temperatures no higher than -423 °F (-252.78 °C; 20.37 K). This requires copious amounts of insulation and other protective measures. Because of this, NASA boasts that the taming of liquid hydrogen is one of its most significant technological achievements.
Some cars also run on hydrogen fuel.
Hydrogen fuel is one of the most environmentally-friendly fuels in the world. Because hydrogen readily combusts with oxygen to form water and release energy, it does not require or release any carbon dioxide which contributes to global warming. As a clean source of energy, hydrogen fuel made its way to commercial use as an alternative to fossil fuel. Many fuel cell vehicles and fuel cell buses now make use of hydrogen fuel cells to roam the roads.
Although hydrogen fuel is a promising alternative to fossil fuel, the production and containment of hydrogen remain a significant problem in practice. Liquid hydrogen needs special containers with good insulation to remain in a liquid state. Moreover, it can easily leak out of its container. Hydrogen fuel is also highly flammable, and there have been some records of explosions in hydrogen filling stations. Certainly one of the more controversial hydrogen facts.
The concentration of hydrogen ions dictates whether a solution is basic or acidic.
An aqueous compound may be acidic, basic, or neutral depending on its pH. The term “pH” stands for “potential of hydrogen” or “power of hydrogen”, which indicates the concentration of H+ ions (hydrogen atoms with positive electric charges) in the solution. A higher concentration of H+ ions leads to a lower pH. If a solution’s pH is lower than 7, then it is acidic. A pH higher than 7, on the other hand, indicates a basic or alkaline solution.
Hydrogen atoms turn into hydrogen ions when they lose or gain electrons. If a hydrogen atom loses an electron, then it will have a positive charge and turns into a hydron or proton (H+). If it gains an electron, however, it will have a negative charge and turn into a hydride or protide (H-).
Hydrogen can act as a metal under immense pressures and temperatures.
Although hydrogen is not a metal, it can have metallic properties under certain conditions. Metallic hydrogen occurs when hydrogen is subjected to extreme pressures and temperatures. Specifically, it needs to be in pressures of no less than 25 GPa (3,600,000 psi; 250,000 atm). In this phase, hydrogen exists in a liquid form and acts as an electrical conductor similar to metallic elements.
Physicists Eugene Wigner and Hillard Bell Huntington first predicted the existence of metallic hydrogen in 1935. Because of the extreme pressures required for hydrogen to exhibit metallic properties, metallic hydrogen is notoriously difficult to produce in laboratories. Scientists suggest that metallic hydrogen exists in large quantities within the interior parts of the gas giants, Jupiter and Saturn. Metallic hydrogen could also exist in various planets outside of our solar system.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.