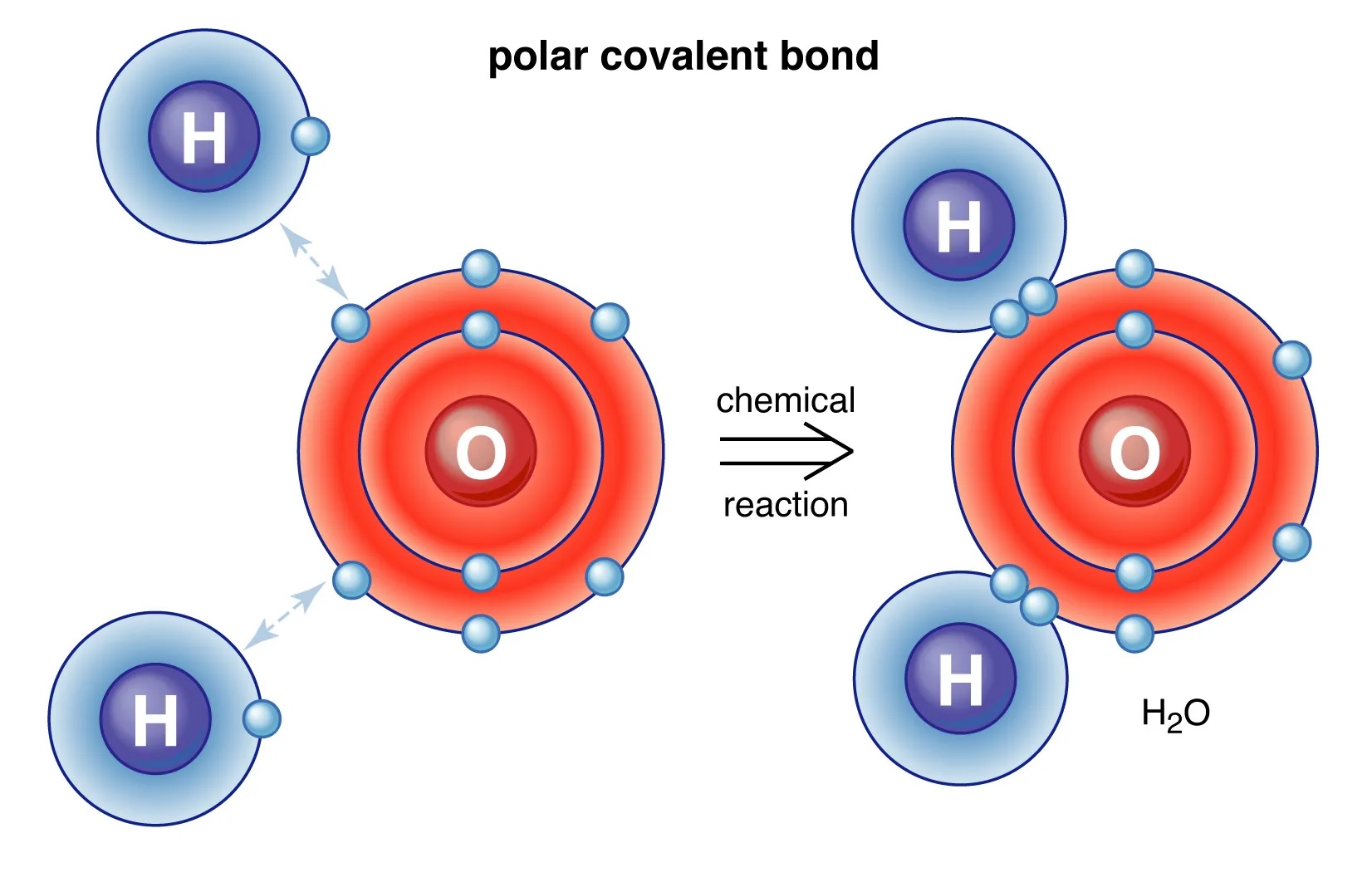
When it comes to understanding the building blocks of matter, the concept of covalent bonds is truly intriguing. Covalent bonds play a critical role in chemistry and have a profound impact on our daily lives, often shaping the properties and behavior of the substances we encounter. These bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons, creating a strong connection that allows them to share resources and work together harmoniously.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of covalent bonds and explore some unbelievable facts about them. From their unique ability to create stable compounds to their influence on molecular structures, covalent bonds have a plethora of secrets waiting to be uncovered. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries behind this essential chemistry concept!
Key Takeaways:
- Covalent bonds are incredibly strong and play a vital role in shaping the molecules around us, from simple diatomic molecules to complex macromolecules like DNA.
- Understanding covalent bonds helps us explore the properties and behaviors of a wide range of molecules, including those found in everyday biological processes.
Covalent bonds are formed between nonmetal atoms.
In a covalent bond, two nonmetal atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing allows the atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration.
They are incredibly strong.
Covalent bonds are some of the strongest chemical bonds, resulting in the formation of stable molecules.
Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar.
If the electrons are shared equally between the atoms, the bond is nonpolar. However, if the electron distribution is uneven, the bond is polar.
Electronegativity determines bond polarity.
The electronegativity difference between atoms is crucial in determining the polarity of a covalent bond. The greater the electronegativity difference, the more polar the bond becomes.
Multiple bonds can form between atoms.
In covalent bonding, atoms can share more than one pair of electrons, forming double or triple bonds. These multiple bonds result in stronger connections between atoms.
Covalent bonding is essential in organic compounds.
Most organic compounds, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, are held together by covalent bonds.
Covalent bonds are found in both small and large molecules.
From simple diatomic molecules like oxygen (O?) to complex macromolecules like DNA, covalent bonds hold atoms together to form a wide range of molecules.
Covalent bonds exhibit localized electron density.
The electrons involved in covalent bonding tend to be localized between the two atoms, creating distinct regions of electron density.
Covalent bonds can be flexible.
The nature of covalent bonding allows for some flexibility within the molecular structure, allowing atoms to rotate or vibrate without breaking the bond.
Covalent bonds contribute to the shape of molecules.
The arrangement of covalent bonds determines the three-dimensional shape of a molecule, which in turn affects its chemical properties and interactions.
Covalent bonds are directional.
The sharing of electrons in covalent bonds occurs in specific directions, resulting in the alignment and orientation of atoms within a molecule.
Covalent bonds play a vital role in biological processes.
From the building blocks of DNA to the complex enzymes involved in metabolism, covalent bonds are crucial in countless biological processes.
Covalent bonds can be broken in chemical reactions.
During chemical reactions, covalent bonds can be broken, allowing for the rearrangement and formation of new molecules.
The 13 Unbelievable Facts About Covalent Bond discussed above showcase the significance of covalent bonds in the world of chemistry. Understanding the intricacies of these bonds opens the door to exploring the properties and behaviors of a vast array of molecules in our everyday lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, covalent bonds are fascinating and essential to understanding the world of chemistry. These bonds play a crucial role in holding atoms together, forming molecules, and determining the physical and chemical properties of substances. From the sharing of electrons to the formation of double and triple bonds, covalent bonds offer a wide range of possibilities for creating new compounds and unlocking endless possibilities in various fields, including medicine, materials science, and environmental research.
By delving into the unbelievable facts about covalent bonds, we can appreciate the intricacies and marvel at the wonders of chemical bonding. From the strongest bond present to the existence of resonating structures, covalent bonds continue to surprise scientists and enthusiasts alike. So the next time you encounter a covalent bond, remember how truly remarkable and fundamental it is to the study of chemistry.
FAQs
Q: What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons with each other in order to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Q: How are covalent bonds formed?
Covalent bonds are formed through the overlapping or sharing of electrons between two atoms. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration.
Q: Are covalent bonds strong?
Yes, covalent bonds can be very strong. The strength of a covalent bond depends on factors such as the types of atoms involved and the number of shared electrons. Some covalent bonds, such as those in carbon-carbon double or triple bonds, are particularly strong.
Q: Can covalent bonds form between different elements?
Yes, covalent bonds can form between atoms of different elements. When atoms of different elements share electrons, it creates a polar covalent bond. The degree of electron sharing and the resulting polarity depends on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms.
Q: What are resonating structures?
Resonating structures, also known as resonance forms, are alternative ways of representing a molecule’s structure in which the placement of electrons is slightly different. These structures are used to describe the delocalization of electrons in molecules with multiple bonding possibilities.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
