Electronegativity is a fundamental concept in chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of chemical elements. It refers to the ability of an atom to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. The electronegativity of an element can determine various properties, such as its reactivity, polarity, and the nature of its chemical bonds.
In this article, we will delve into twelve mind-blowing facts about electronegativity that will expand your knowledge of this captivating concept. From the electronegativity trend across the periodic table to its significance in various chemical reactions, get ready to be astounded by the fascinating world of electronegativity.
Key Takeaways:
- Electronegativity determines how atoms behave in chemical bonds, affecting reactivity and bond type. It’s like a magnet for electrons, shaping the world of chemistry!
- Understanding electronegativity helps predict bond polarity, acidity, and reactivity. It’s like a secret code that unlocks the mysteries of chemical reactions!
Electronegativity determines the ability of an atom to attract electrons.
Electronegativity is a fundamental concept in chemistry that quantifies the attraction an atom has for electrons in a chemical bond. It helps to predict the nature of chemical bonding and the behavior of molecules.
The electronegativity of an element is determined by its atomic number.
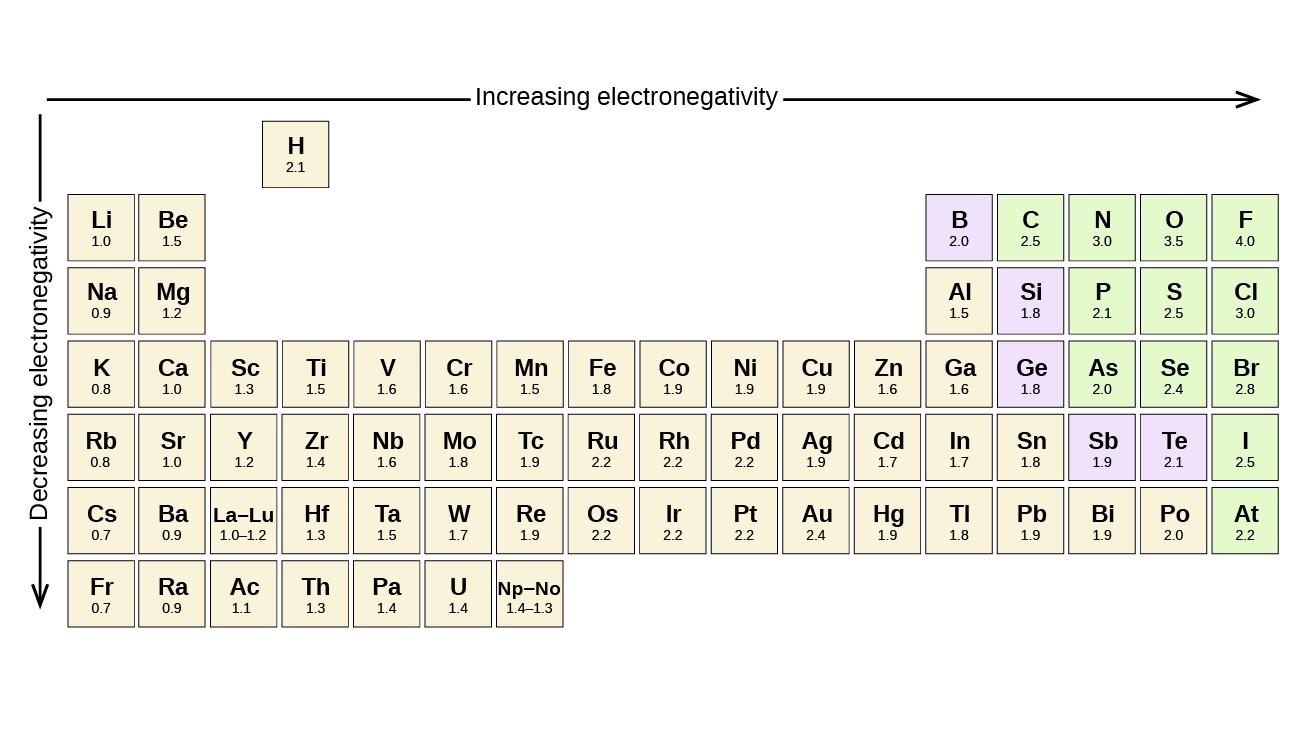
Generally, electronegativity increases as you move across a period from left to right on the periodic table. It also increases as you move up a group.
Fluorine has the highest electronegativity among all elements.
With an electronegativity value of 3.98 on the Pauling scale, fluorine has the strongest ability to attract electrons. This makes it highly reactive and often a part of compounds with other elements.
Electronegativity plays a crucial role in chemical reactions and bond formations.
The difference in electronegativity between atoms determines the type of bond formed. In ionic bonds, the electronegativity difference is large, while in covalent bonds, the difference is small.
Electronegativity affects the polarity of a chemical bond.
When atoms with different electronegativity values are bonded, the bond becomes polar. This results in the formation of partial positive and partial negative charges in the molecule.
The electronegativity of an atom influences its chemical reactivity.
Atoms with higher electronegativity values tend to attract electrons more strongly, making them more reactive in chemical reactions.
Electronegativity helps determine the acidity or basicity of a compound.
Electronegativity differences between atoms can influence the distribution of electrons in a molecule and the strength of acid-base interactions.
The concept of electronegativity was introduced by Linus Pauling.
Linus Pauling, a renowned American chemist, developed the concept of electronegativity in the early 1930s. His work laid the foundation for understanding chemical bonding.
There are multiple scales to measure electronegativity.
The Pauling scale is the most commonly used scale for measuring electronegativity. Other scales, such as the Mulliken scale and the Allen scale, also exist.
Electronegativity values can be used to predict bond type.
If the electronegativity difference between two atoms is less than 0.5, the bond is considered nonpolar covalent. If the difference is between 0.5 and 1.7, the bond is considered polar covalent. Anything above 1.7 indicates an ionic bond.
Electronegativity can vary within a molecule.
Even in a single molecule, electronegativity can differ among different atoms. This phenomenon can lead to the presence of polar regions within a molecule.
The concept of electronegativity extends beyond individual atoms.
Electronegativity can also be applied to functional groups in organic compounds, providing insights into their reactivity and behavior in chemical reactions.
In conclusion, understanding the 12 Mind-blowing Facts About Electronegativity is crucial to comprehend the nature of chemical bonding, reactivity, and the behavior of molecules. These facts provide a glimpse into the fascinating world of chemistry and the role that electronegativity plays in shaping our understanding of the atomic realm.
Conclusion
Electronegativity is a fascinating concept in chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of atoms and molecules. Hopefully, these 12 mind-blowing facts about electronegativity have shed some light on this important topic:
1. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
2. The electronegativity values of elements are calculated using various scales, such as the Pauling scale.
3. The most electronegative element on the periodic table is fluorine, while the least electronegative is cesium.
4. Electronegativity tends to increase across a period and decrease down a group on the periodic table.
5. Electronegativity differences determine the type of chemical bond formed between atoms: ionic or covalent.
6. Polar covalent bonds occur when there is a significant electronegativity difference between atoms.
7. Nonpolar covalent bonds occur when there is an insignificant difference in electronegativity between atoms.
8. Electronegativity values can be used to predict the polarity of molecules.
9. The concept of electronegativity is closely related to bond dissociation energy and bond strength.
10. Electronegativity plays a crucial role in determining how atoms interact in chemical reactions.
11. Electronegativity can also influence physical properties such as boiling and melting points.
12. Understanding electronegativity is essential for predicting the behavior of molecules in various chemical reactions.
By exploring these mind-blowing facts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of electronegativity in the world of chemistry.
FAQs
Q: What is electronegativity?
A: Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
Q: How is electronegativity calculated?
A: Electronegativity values are calculated using scales such as the Pauling scale.
Q: Which element is the most electronegative?
A: Fluorine is the most electronegative element on the periodic table.
Q: What determines the type of chemical bond formed between atoms?
A: The electronegativity difference between atoms determines the type of bond formed: ionic or covalent.
Q: What are polar covalent bonds?
A: Polar covalent bonds occur when there is a significant electronegativity difference between atoms.
Q: How are electronegativity values used to predict the polarity of molecules?
A: The difference in electronegativity values between atoms in a molecule can indicate its polarity.
Q: How does electronegativity influence chemical reactions?
A: Electronegativity plays a crucial role in determining how atoms interact in chemical reactions.
Q: Can electronegativity affect physical properties?
A: Yes, electronegativity can influence physical properties such as boiling and melting points.
Q: Why is understanding electronegativity important in chemistry?
A: Understanding electronegativity is essential for predicting the behavior of molecules in chemical reactions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
