Arrhenius bases, named after Svante Arrhenius, a Swedish chemist, are an essential concept in the study of chemistry. Bases play a vital role in countless chemical reactions and have significant practical applications in various fields. Understanding the intriguing characteristics and properties of Arrhenius bases can provide valuable insights into the world of chemistry.
In this article, we will explore 15 mind-blowing facts about Arrhenius bases that will leave you amazed and deepen your appreciation for the fascinating world of chemistry. From their fundamental definition to their role in neutralizing acids, these facts will shed light on the importance of Arrhenius bases and their impact on our everyday lives. So, let’s dive into the realm of Arrhenius bases and unveil the remarkable secrets they hold!
Key Takeaways:
- Arrhenius bases release hydroxide ions in water, making them feel soapy and taste bitter. They play a vital role in biology and industry, but can be corrosive and harmful if not handled properly.
- Arrhenius bases neutralize acids, adjust water pH, and are found in common household products. However, their improper disposal can harm the environment and aquatic life.
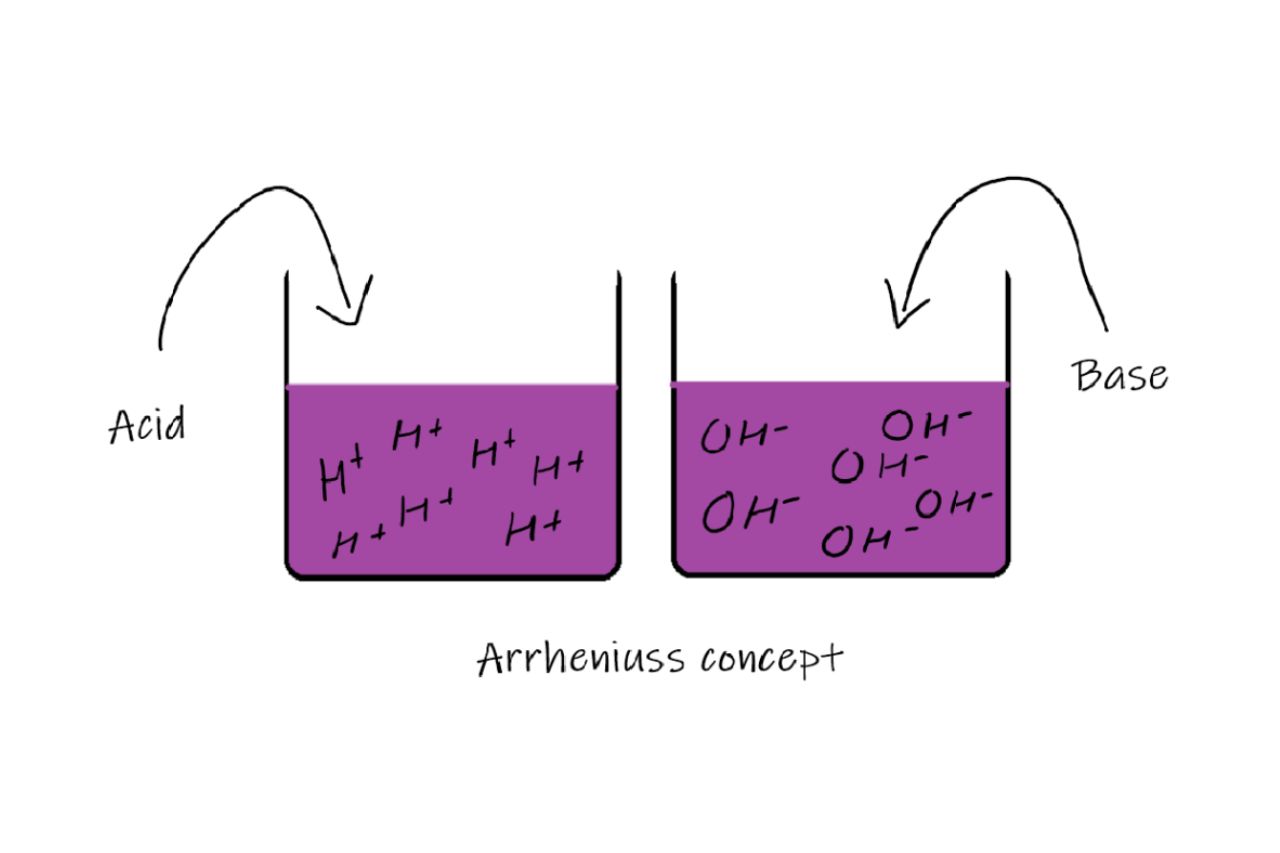
Arrhenius Base Definition
An Arrhenius Base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, releases hydroxide ions (OH-) which then react with hydrogen ions (H+) to form water.
Alkali Substances
Arrhenius bases are commonly known as alkalis, and examples include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)?).
Corrosive Properties
Arrhenius bases are highly corrosive and can cause severe burns and damage to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Proper safety precautions should be taken when handling these substances.
pH Levels
Arrhenius bases have pH values above 7 on the pH scale, indicating their alkaline nature.
Common Household Bases
Many common household products are Arrhenius bases, including baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO?) and antacids.
Neutralization Reactions
Arrhenius bases can neutralize acids through a chemical reaction called neutralization, resulting in the formation of water and a salt.
Soapy Feel
Arrhenius bases, when dissolved in water, feel soapy to the touch due to their ability to react with fatty acids and form soap.
Bitter Taste
Arrhenius bases exhibit a bitter taste, which can be observed in substances like quinine or caffeine.
Biological Importance
Arrhenius bases play a crucial role in various biological processes, including enzyme activity and maintaining the pH balance in living organisms.
Industrial Applications
Arrhenius bases are widely used in industries such as agriculture, food production, and manufacturing, where they are employed in the production of fertilizers, cleaning agents, and paper products.
Arrhenius Base vs. Bronsted-Lowry Base
The Arrhenius base definition focuses specifically on the release of hydroxide ions in water, while the Bronsted-Lowry base definition is more general and includes substances that accept protons.
Dissociation of Arrhenius Bases
Arrhenius bases dissociate in water to form hydroxide ions (OH-) and a cation, which determines the specific properties of the base.
Relationship Between Arrhenius Acid and Base
An Arrhenius acid and an Arrhenius base can combine to undergo a neutralization reaction, producing water and a salt.
Arrhenius Bases in Water Treatment
Arrhenius bases are used in water treatment processes to adjust the pH level, neutralize harmful acidic pollutants, and maintain the proper alkalinity of water.
Environmental Impact
Improper disposal of Arrhenius bases can lead to environmental pollution, as they can react with other substances in the environment and potentially harm aquatic life.
Conclusion
Arrhenius bases are fascinating compounds that play a vital role in chemistry. From their unique properties to their various applications, these bases hold a wealth of knowledge waiting to be explored. Understanding the fundamentals of Arrhenius bases is essential for any student or enthusiast in the field of chemistry.
By delving into the 15 mind-blowing facts about Arrhenius bases outlined above, we have gained a deeper appreciation for their significance. Whether it’s their ability to neutralize acids, their role in chemical reactions, or their impact on the pH scale, Arrhenius bases are fundamental to our understanding of chemical processes.
Exploring the diverse range of Arrhenius bases and uncovering the inner workings of these compounds can unlock countless opportunities for innovation and discovery in chemistry. So, let us continue to explore, experiment, and expand our knowledge of Arrhenius bases, and unlock the secrets they hold.
FAQs
1. What is an Arrhenius base?
An Arrhenius base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, releases hydroxide ions (OH-) and increases the concentration of these ions.
2. How are Arrhenius bases different from other bases?
Arrhenius bases are specifically defined based on their behavior in water. They are different from other bases, such as Lewis bases, which are defined based on their ability to donate an electron pair.
3. Can you provide examples of Arrhenius bases?
Some common examples of Arrhenius bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
4. How do Arrhenius bases neutralize acids?
Arrhenius bases neutralize acids by reacting with hydrogen ions (H+) from the acid to form water and a salt. This process is known as neutralization.
5. What are the uses of Arrhenius bases?
Arrhenius bases have various applications, including in the production of soaps and detergents, water treatment processes, and as ingredients in household cleaning products.
6. Are all bases Arrhenius bases?
No, not all bases are Arrhenius bases. Other types of bases include Bronsted-Lowry bases, which are defined based on their ability to accept a proton, and Lewis bases, which are based on their electron donation ability.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
