The greater omentum is a fascinating part of the human anatomy that often goes unnoticed. However, it plays a crucial role in protecting our internal organs and supporting immune functions.
In this article, we will dive into the world of the greater omentum and explore 12 mind-blowing facts about this remarkable structure. From its unique location in the abdominal cavity to its role in fat storage and disease prevention, you’ll discover why the greater omentum is truly one of the hidden gems of human anatomy.
So, get ready to be amazed by the incredible intricacies of the greater omentum as we unravel its secrets one mind-blowing fact at a time!
Key Takeaways:
- The Greater Omentum is like a superhero organ that protects the abdomen from infections and helps in healing wounds by acting as a barrier and providing nourishment through its blood vessels.
- It also plays a role in regulating body temperature, metabolism, and appetite, and may even hold the key to future medical advancements through its potential as a source of stem cells.
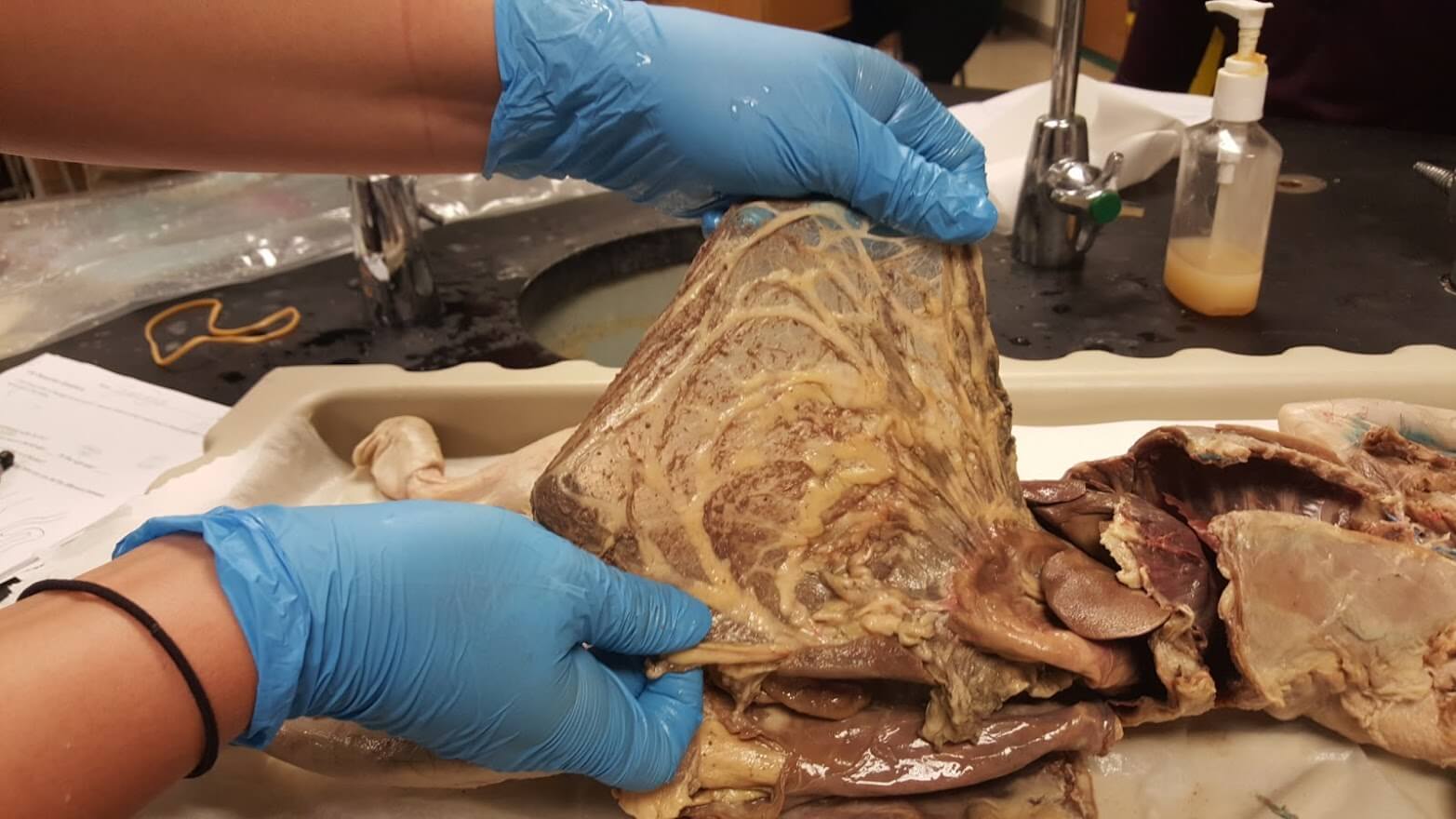
The Greater Omentum is part of the peritoneum
The Greater Omentum is a large fold of fatty tissue that hangs down from the stomach and extends over the intestines. It is considered a double-layered apron-like structure that is part of the peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity.
It plays a crucial role in immune defense
The Greater Omentum is rich in immune cells and acts as a defense mechanism against infections. It contains macrophages, which are specialized cells that engulf and digest harmful pathogens, preventing them from causing further harm.
It acts as a protective barrier
One of the remarkable functions of the Greater Omentum is that it wraps around and isolates areas of infection or inflammation. This protective barrier helps to limit the spread of infection and reduces the risk of complications.
It aids in wound healing
The Greater Omentum has a high concentration of blood vessels, which provide nourishment and oxygen to injured or inflamed areas. This increased blood flow promotes tissue repair and accelerates the healing process.
It can help regulate body temperature
The Greater Omentum contains a network of blood vessels that can dilate or constrict depending on the body’s needs. This mechanism allows it to regulate body temperature by either dissipating heat or conserving warmth.
It assists in fat metabolism
As a fatty tissue, the Greater Omentum plays a role in lipid metabolism. It can store excess fat and release it when the body needs energy. This function helps maintain a balance in body fat distribution.
It contributes to the feeling of fullness
The Greater Omentum is involved in the sensation of satiety. It secretes various hormones that send signals to the brain, indicating that the stomach is full. This helps regulate appetite and prevents overeating.
It can be used for reconstructive surgeries
Due to its versatile nature, the Greater Omentum can be harvested and transplanted to repair or reconstruct areas in need of vascularized tissue. It has been employed in surgeries to restore blood supply and promote healing in different parts of the body.
It has an intricate network of lymphatic vessels
The Greater Omentum contains an extensive network of lymphatic vessels, which play a crucial role in the immune system. These vessels help transport lymph fluid, carrying waste products and immune cells to the lymph nodes for filtration.
It can form adhesions in certain conditions
In some cases, the Greater Omentum may become adhered to nearby organs or tissues due to inflammation, infection, or surgery. These adhesions can cause abdominal pain or discomfort and may require medical intervention to be resolved.
It may contribute to the development of visceral fat
In individuals with excess visceral fat, the Greater Omentum can become thickened and contribute to the accumulation of abdominal fat. Visceral fat has been associated with an increased risk of various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
It is a potential source of stem cells
Recent research suggests that the Greater Omentum may harbor a population of stem cells, known as omental adipose-derived stem cells (OASCs). These cells have the potential to differentiate into various cell types and hold promise for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
These 12 mind-blowing facts about the Greater Omentum showcase the fascinating role this organ plays in the human body. Its unique anatomy, immune functions, and contributions to overall health make it a vital and intriguing component of our abdominal cavity. From protecting against infections to assisting in wound healing, the Greater Omentum truly deserves its title as the “policeman of the abdomen.
Conclusion
The Greater omentum is truly a remarkable organ in the human body. Its functions extend far beyond what one might expect from a simple fold of fatty tissue. From providing protection and insulation to playing a role in immune responses, it is clear that the Greater omentum is a vital component of our anatomy.
Exploring the mind-blowing facts about the Greater omentum has allowed us to gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the human body. Whether it’s its ability to act as a “policeman” patrolling for inflammation or its role in helping to minimize the spread of cancer, the Greater omentum is a fascinating subject that continues to be studied by anatomists and medical professionals.
As our understanding of the human body continues to evolve, it is important to recognize the significance of organs like the Greater omentum. They not only contribute to our overall health and well-being but also serve as a reminder of the incredible complexity and ingenuity of our anatomical design.
FAQs
1. What is the Greater omentum?
The Greater omentum is a fold of fatty tissue that hangs down from the stomach and covers the intestines.
2. What is the function of the Greater omentum?
The Greater omentum performs several functions, including insulation, protection, and immune response regulation.
3. Can the Greater omentum help in fighting inflammation?
Yes, the Greater omentum contains immune cells that help patrol for inflammation and can contribute to its resolution.
4. Does the Greater omentum have any role in cancer prevention?
Yes, the Greater omentum can help minimize the spread of cancer cells by trapping them and preventing their further dissemination.
5. Is the Greater omentum present in all individuals?
Yes, the Greater omentum is a normal anatomical structure present in all humans.
Fascinated by your body's hidden wonders? Colon health is crucial for overall well-being, so learning about digestive health can be eye-opening. Greater omentum is part of the peritoneum, a complex structure worth exploring further. For more surprising facts about your body, dive into the captivating world of anatomy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
