The Dorsalis pedis artery, also known as the anterior tibial artery, is a vital component of the circulatory system located in the foot. It plays a crucial role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to the lower extremities, enabling proper function and movement. This artery is an essential part of the intricate network of blood vessels in the human body, ensuring adequate blood flow to the foot and toes.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Dorsalis pedis artery and uncover 13 captivating facts about its structure, function, and clinical significance. From its anatomical features to its role in diagnosing medical conditions, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable artery. So, let’s dive in and explore the incredible complexities of the Dorsalis pedis artery!
Key Takeaways:
- The Dorsalis Pedis Artery is crucial for foot health, supplying oxygen and nutrients. It’s used to diagnose vascular diseases and assess bypass surgery success, making it a vital part of overall cardiovascular health.
- Healthcare providers use the Dorsalis Pedis pulse to assess circulation and foot temperature regulation. It’s also important for individuals with diabetes, helping reduce the risk of foot complications.
The Dorsalis pedis artery is vital for foot function.
The Dorsalis pedis artery is a critical blood vessel responsible for supplying blood to the foot. Without this artery, the foot would not receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients essential for proper function.
It is a branch of the anterior tibial artery.
The Dorsalis pedis artery arises from the anterior tibial artery, which is located in the lower leg. It branches off and travels down towards the foot, playing a significant role in supplying blood to the lower limb.
The Dorsalis pedis artery has an important role in diagnosing vascular diseases.
Doctors often examine the pulses of the Dorsalis pedis artery to assess the blood flow and evaluate the condition of the arterial system. A weak or absent pulse in this artery may indicate underlying vascular diseases such as peripheral artery disease (PAD).
It is crucial for assessing the success of a lower limb bypass surgery.
After a lower limb bypass surgery, doctors check the presence and strength of the Dorsalis pedis pulse to determine if the procedure was successful in restoring proper blood flow to the foot.
The Dorsalis pedis artery is susceptible to compression and injury.
As the artery passes through the foot, it can be compressed by tight footwear or injured by trauma. Conditions like nerve impingement or fractures can lead to compromised blood flow in this critical artery.
It supplies blood to important structures in the foot.
The Dorsalis pedis artery provides oxygenated blood to essential structures in the foot, including the bones, muscles, tendons, and skin. This ensures their proper functioning and promotes overall foot health.
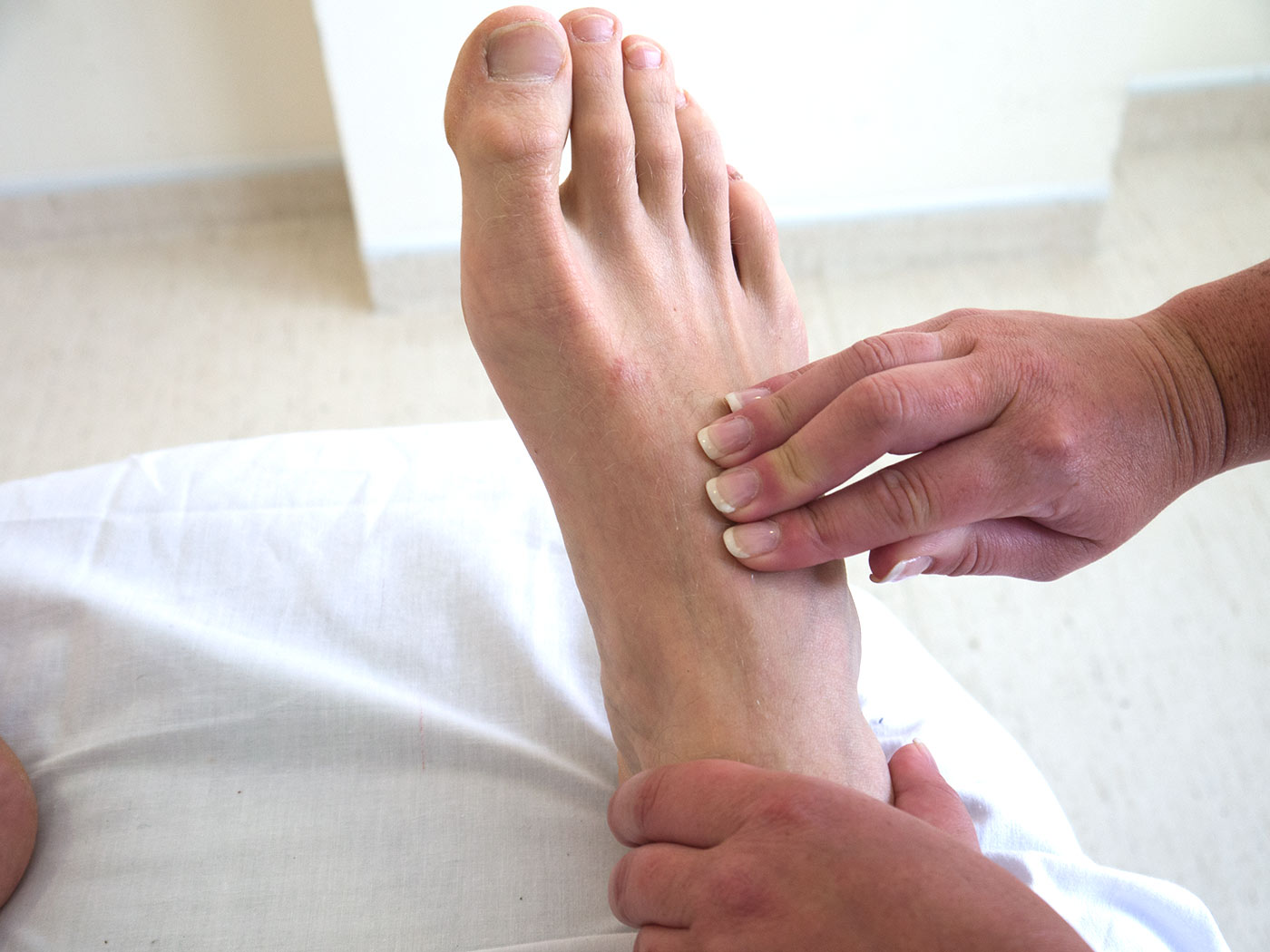
The Dorsalis pedis pulse is used as a key marker in medical examinations.
Medical professionals often palpate the Dorsalis pedis pulse to assess the overall cardiovascular health of an individual. A weak or absent pulse may indicate arterial blockages or other underlying circulatory issues.
Dorsalis pedis artery palpation is a skill taught to healthcare providers.
Healthcare providers are taught how to locate and palpate the Dorsalis pedis artery to accurately assess the pulse. This skill is crucial for diagnosing vascular conditions and determining the effectiveness of treatment.
An absent Dorsalis pedis pulse can indicate vascular insufficiency.
If the Dorsalis pedis pulse is absent, it can be an indication of inadequate blood supply to the foot. This may be caused by conditions like arterial occlusion or peripheral artery disease.
The Dorsalis pedis artery plays a role in foot temperature regulation.
Ensuring proper blood flow to the foot helps regulate its temperature. The Dorsalis pedis artery contributes to this by delivering warm blood to the foot to maintain its optimal temperature.
It can be used for arterial blood gas sampling.
In some situations, the Dorsalis pedis artery may be selected as a site for arterial blood gas sampling. This allows healthcare providers to assess blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels without the need for invasive procedures.
The Dorsalis pedis artery can be visualized using Doppler ultrasound.
Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that can be used to visualize and assess the blood flow within the Dorsalis pedis artery. This helps in diagnosing blockages or other vascular abnormalities.
For individuals with diabetes, the Dorsalis pedis artery is crucial for foot health.
Individuals with diabetes often have compromised circulation to their feet. The Dorsalis pedis artery plays a vital role in maintaining proper blood flow to the foot, reducing the risk of complications such as ulcers or infections.
Conclusion
The Dorsalis pedis artery is a vital component of the circulatory system and plays a crucial role in supplying blood to the foot and toes. Understanding its anatomy and function is essential for medical professionals and individuals seeking to improve their knowledge of human anatomy. From its origin to its branching patterns, the Dorsalis pedis artery exhibits fascinating characteristics that contribute to its significance in the field of medicine. Its clinical importance is evident in procedures like foot pulse assessment and invasive interventions, making it a subject of interest for healthcare professionals. By exploring the captivating facts about the Dorsalis pedis artery, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the human body and the incredible mechanisms that allow us to function and thrive.
FAQs
1. What is the Dorsalis pedis artery?
The Dorsalis pedis artery is a major blood vessel located on the top of the foot. It is responsible for supplying blood to the toes and foot region.2. How does the Dorsalis pedis artery differ from other arteries?
Unlike other arteries, the Dorsalis pedis artery is located closer to the surface of the skin, which allows for easier assessment of foot pulses.3. Why is the Dorsalis pedis artery important in medical examinations?
The Dorsalis pedis artery is palpated during medical examinations to assess the presence and quality of foot pulses. It can provide valuable information about circulation and certain medical conditions.4. Can the Dorsalis pedis artery be blocked?
Yes, like any other artery, the Dorsalis pedis artery can become blocked or narrowed due to various factors such as atherosclerosis or blood clots. This can lead to decreased blood flow to the foot and may require medical intervention.5. Are there any specific conditions associated with the Dorsalis pedis artery?
In certain medical conditions, such as peripheral artery disease (PAD), the Dorsalis pedis artery can be affected, leading to reduced blood flow to the foot. It is important to monitor the health of this artery in individuals with diabetes or circulation issues.6. Can the Dorsalis pedis artery be used for medical interventions?
In some cases, the Dorsalis pedis artery can be used for invasive procedures, such as arterial catheterization or angiography. However, its use for such interventions is less common compared to other arteries.
Exploring the intricacies of the Dorsalis pedis artery is just the beginning of your journey into the fascinating world of vascular health. Dive deeper into this captivating field by discovering surprising facts about the skilled professionals who keep our blood flowing smoothly – vascular surgeons. Their expertise and dedication play a crucial role in maintaining the well-being of our circulatory system, ensuring that every part of our body receives the vital nutrients and oxygen it needs to thrive.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
