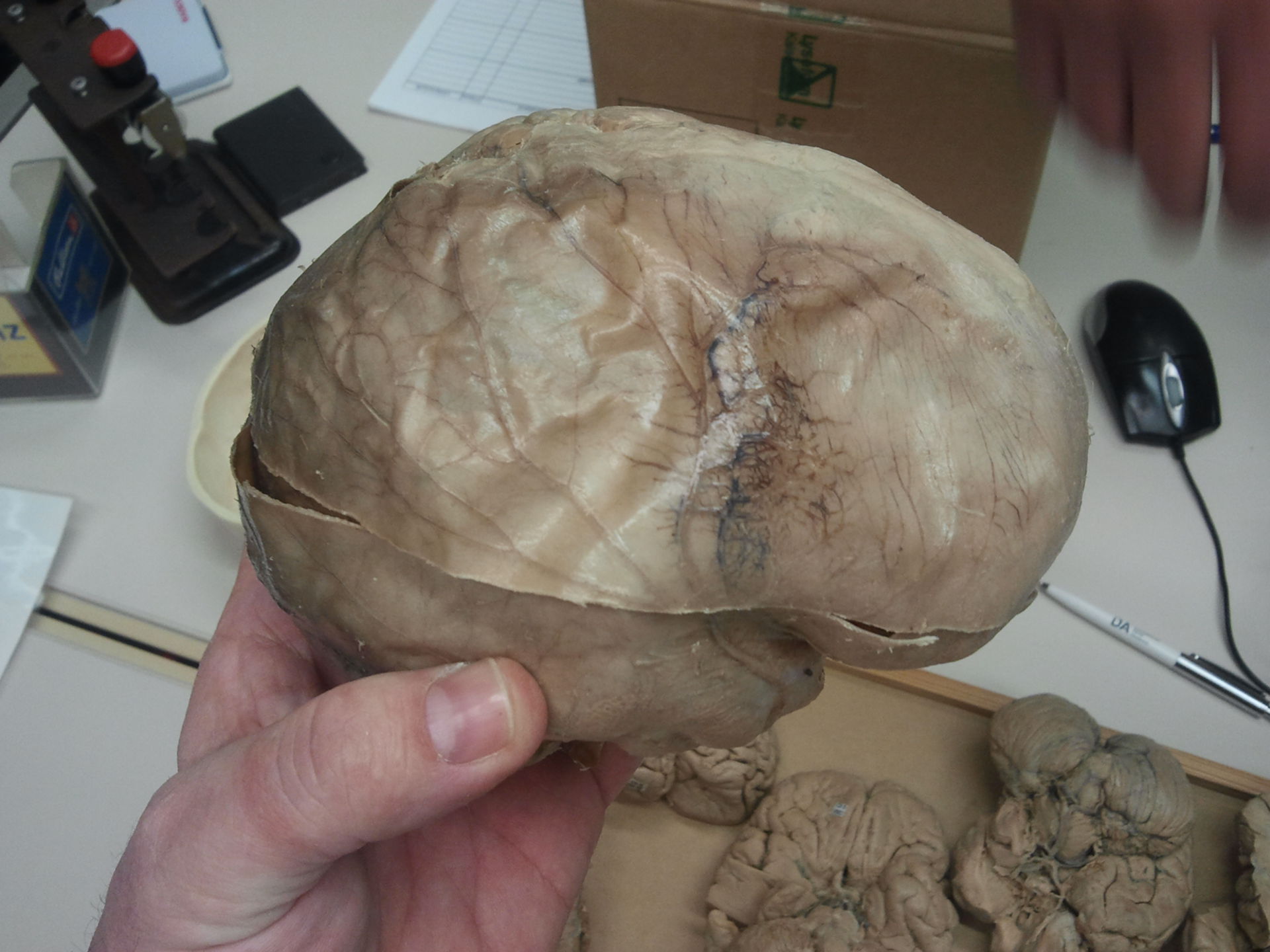
The human body is a marvelous and intricate masterpiece of nature. From the skin to the bones, every part plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. One of the essential components of the human anatomy is the Dura mater.
The Dura mater, which translates to “tough mother” in Latin, is a strong and thick membrane that envelops and protects the brain and spinal cord. It acts as a protective barrier, shielding these vital organs from any possible damage or injury.
But did you know that the Dura mater has some fascinating facts and features that might surprise you? In this article, we will explore 15 unbelievable facts about the Dura mater, shedding light on its structure, function, and significant roles in our body. So, let’s dive into this incredible journey to unravel the mysteries of this extraordinary membrane!
Key Takeaways:
- The dura mater is like a tough mother, protecting the brain and spinal cord with its impenetrable strength and essential support, while also playing a role in headaches and infections.
- Surgeons rely on the dura mater as a protective cover and entry point during brain and spinal cord surgeries, showcasing its vital role in medical procedures and potential for regeneration.
The Dura Mater: What is it?
The dura mater is the toughest and outermost layer of the three meninges that enclose and protect the brain and spinal cord. Derived from Latin, dura mater translates to “tough mother.” And indeed, it lives up to its name, providing a robust shield against external forces.
A Multilayered Shield
The dura mater consists of two layers: the outer endosteal layer and the inner meningeal layer. The endosteal layer is attached to the skull, while the meningeal layer lies closer to the brain and spinal cord.
Impenetrable Strength
The dura mater is highly resistant to tearing or puncturing due to its dense fibrous structure. This feature ensures that the delicate neural tissues remain safeguarded from potential damage.
Essentials of Support
Along with its protective role, the dura mater also provides structural support to the brain and spinal cord. It keeps these vital organs in position, preventing excessive movement and potential injuries.
The Dural Sinuses
Lying within the dura mater are specialized structures called dural sinuses, which serve as venous channels for draining deoxygenated blood from the brain. These sinuses play a crucial role in maintaining optimal blood flow and pressure within the central nervous system.
Aiding in Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation
The dura mater contributes to the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord. It forms the outermost layer of the meninges, which contain and support the CSF.
Pain Receptors Abound
Unlike the inner layers of the meninges that lack pain receptors, the dura mater is richly supplied with sensory nerves. This abundance of pain receptors makes the dura mater highly sensitive to touch, pressure, and inflammation.
Dura Mater and Migraines
Studies have shown that the dura mater plays a significant role in migraines, a debilitating neurological condition. The activation of pain receptors in the dura mater can trigger migraine headaches, leading to the characteristic throbbing pain.
Protective Barrier against Infections
The dura mater acts as a robust barrier against bacterial and viral infections that attempt to invade the central nervous system. It prevents pathogens from reaching the brain and spinal cord, thereby safeguarding their essential functions.
Dura Mater Pathologies
Though resilient, the dura mater is not impervious to diseases. Various conditions, such as dural tears, meningiomas, and meningitis, can affect the dura mater, necessitating medical intervention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Surgical Importance
During certain surgical procedures, surgeons may need to access the brain or spinal cord. The dura mater provides an entry point while also acting as a protective cover that can be carefully opened and closed to ensure a successful operation.
Connection with Spinal Taps
When performing a lumbar puncture or spinal tap, medical practitioners insert a needle into the dura mater of the spinal cord to safely collect cerebrospinal fluid for diagnostic purposes.
The Dura Mater and Brain Trauma
In cases of severe head injuries or trauma, the dura mater can tear or become damaged. This type of injury can have serious consequences and may require immediate medical attention to mitigate potential complications.
Dura Mater Regeneration Potential
Research in regenerative medicine has shown promising possibilities for the regeneration of damaged dura mater. The discovery of new techniques and materials may contribute to the development of advanced therapies for patients with dural pathologies.
The Dura Mater: A Fascinating Enigma
The dura mater is undoubtedly a captivating element of our central nervous system. Its strength, protective qualities, and essential roles make it a remarkable creation of nature, deserving our awe and appreciation.
There you have it – 15 unbelievable facts about the dura mater. This incredible protective shield challenges us to marvel at the intricacies of the human body and reminds us of its phenomenal capacity for adaptability and survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Dura mater is a remarkable and complex layer of the meninges that plays a crucial role in protecting and supporting the brain and spinal cord. Its strong and durable nature ensures that these vital organs are safeguarded from external forces and potential damage. The Dura mater also houses numerous blood vessels, which provide essential nutrients and oxygen to the brain and spinal cord.Throughout this article, we have explored fifteen unbelievable facts about the Dura mater, shedding light on its fascinating characteristics and functions. From its distinctive histological structure to its ability to form protective barriers, the Dura mater continues to captivate researchers and medical professionals alike.By understanding the intricacies of the Dura mater, we recognize the intricate beauty of the human body and the incredible mechanisms that allow it to function. It serves as a constant reminder of the wonders and complexities that lie within us, encouraging further exploration and research into the world of human anatomy.
FAQs
1. What is the primary function of the Dura mater?
The Dura mater functions as a protective barrier for the brain and spinal cord, shielding them from external forces and potential damage.
2. Is the Dura mater a single layer?
No, the Dura mater is composed of two layers: the periosteal layer, which is attached to the skull, and the meningeal layer, which is closely adhered to the brain and spinal cord.
3. Can the Dura mater repair itself?
In certain cases, the Dura mater can repair itself after injury or surgery. However, severe damage may require surgical intervention for repair.
4. What is the role of the blood vessels within the Dura mater?
The blood vessels within the Dura mater supply essential nutrients and oxygen to the brain and spinal cord, ensuring their proper function.
5. Does the Dura mater have any connection to headaches?
Yes, certain types of headaches, such as migraines or tension headaches, can be associated with the Dura mater’s sensitization and inflammation.
6. Can diseases affect the Dura mater?
Yes, certain diseases, such as meningitis or intracranial hypotension, can directly impact the health and function of the Dura mater.
7. How thick is the Dura mater?
The thickness of the Dura mater can vary, ranging from 0.3 to 3 millimeters, depending on the location in the body.
8. Is the Dura mater present only in humans?
No, the Dura mater is present in all vertebrates, serving as a protective layer for the brain and spinal cord.
9. Can the Dura mater be affected by trauma?
Yes, trauma to the head or spine can lead to injuries or tears in the Dura mater, which may require medical attention.
10. Are there any medical conditions specifically related to the Dura mater?
Yes, conditions such as Dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) and Dural ectasia are specific to the Dura mater and require specialized treatment.
Unraveling the mysteries of the dura mater is just the beginning. Dive into the captivating world of neuroscience with Dr. May-Britt Moser's enigmatic discoveries. Explore the critical role of the meninges in protecting the brain and spinal cord, and learn about the potential risks posed by meningitis. Embark on a fascinating journey through the intricacies of brain anatomy, uncovering the secrets that lie within its complex structures. Each topic offers a unique perspective on the incredible workings of the human brain, inviting you to expand your knowledge and appreciation for this remarkable organ.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


