Passivation is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the realm of chemistry. It involves the formation of a protective layer on the surface of a metal or alloy, effectively impeding corrosion and enhancing durability. This process is widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and many more.
In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of passivation and uncover 10 intriguing facts about this phenomenon. From its historical origins to its practical applications, we will explore the science behind passivation and its impact on various industries. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and unlock the mysteries of passivation.
Key Takeaways:
- Passivation forms a protective layer on metals, preventing corrosion and enhancing their appearance, making them last longer and look better in applications like aerospace, medical implants, and electronic devices.
- Passivation is a versatile process that extends the lifespan of materials, reduces environmental impact, and ensures the safety and quality of products in industries like pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and electronics.
Passivation is a process that forms a protective layer on the surface of metals.
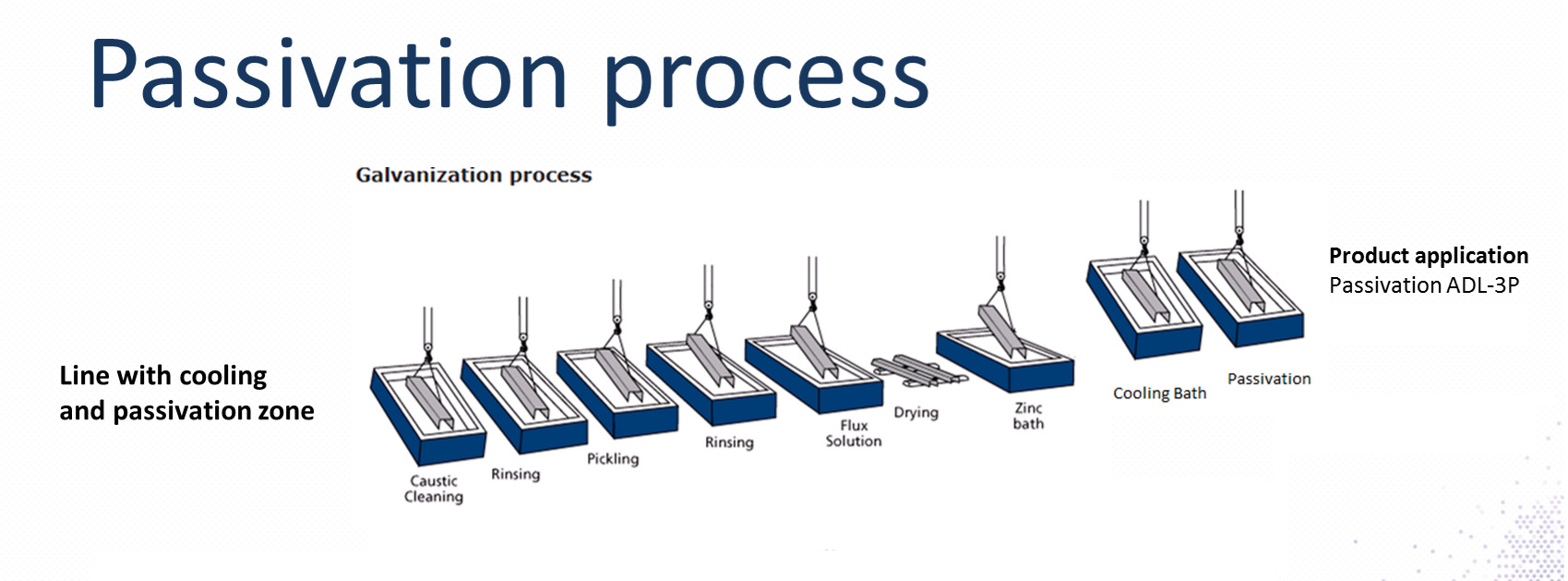
Passivation is the technique of treating a metal surface in order to make it more resistant to corrosion. It involves the formation of a thin, protective oxide layer on the metal’s surface, which serves as a barrier against environmental factors.
Passivation is commonly used in the aerospace industry.
The aerospace industry relies on passivation to enhance the corrosion resistance of components such as aircraft parts and engine components. This helps to prolong the lifespan of these critical parts and ensures the safety and efficiency of aircraft.
Passivation is an essential step in the stainless steel manufacturing process.
Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance, undergoes passivation to further enhance its ability to withstand harsh environments. This process removes any free iron particles from the surface and creates a passive layer that protects the steel from oxidation.
Passivation can be achieved through multiple methods.
There are several techniques used to achieve passivation, including chemical passivation, electrolytic passivation, and nitric acid passivation. The choice of method depends on the type of metal and the desired outcome.
Passivation helps to maintain the appearance of metal surfaces.
In addition to corrosion resistance, passivation also enhances the aesthetics of metal surfaces by preventing discoloration, staining, and pitting. This is particularly important in applications where the visual appeal of the metal is crucial, such as in jewelry or architectural components.
Passivation can improve the biocompatibility of medical implants.
Medical implants, such as pacemakers or orthopedic devices, often undergo passivation to make them more biocompatible and reduce the risk of adverse reactions within the body. The passivated surface minimizes the release of metal ions and promotes better integration with the surrounding tissues.
Passivation can be performed on other materials besides metals.
While passivation is commonly associated with metals, it can also be applied to other materials such as ceramics, polymers, and even semiconductors. This extends the benefits of passivation to a wider range of industries and applications.
Passivation can improve the efficiency of electronic devices.
Passivation plays a vital role in the semiconductor industry by reducing surface defects and increasing the stability and performance of electronic devices. It helps to minimize unwanted chemical reactions and ensures the longevity of the devices.
Passivation is a crucial step in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical equipment.
The pharmaceutical industry relies on passivation to ensure the cleanliness and corrosion resistance of equipment used in drug production. It prevents contaminants from adhering to the equipment surfaces and safeguards the quality and purity of the pharmaceutical products.
Passivation is a sustainable solution for corrosion prevention.
By extending the lifespan of metal components, passivation reduces the need for frequent replacement or repair, leading to cost savings and a reduced environmental impact. It is a sustainable approach to corrosion prevention that aligns with the principles of resource conservation and waste reduction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, passivation is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the world of chemistry. Understanding its principles and applications can greatly enhance our knowledge of corrosion prevention and surface protection. From the formation of a passive oxide layer to the various methods of passivation, there are numerous enigmatic facts to explore. Knowing how passivation works can enable us to make informed decisions regarding material selection, maintenance, and corrosion control in various industries. With the ongoing advancements in passivation techniques, it is an exciting field that continues to evolve and contribute to the development of durable and long-lasting materials.
FAQs
1. What is passivation?
Passivation is the process of treating a metal’s surface in order to make it more resistant to corrosion. It involves the formation of a protective oxide layer that acts as a barrier against corrosive agents.
2. Why is passivation important?
Passivation is important because it increases the corrosion resistance of metals, thereby extending their lifespan. It is particularly crucial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where materials are subjected to harsh environments or come into contact with corrosive substances.
3. How is passivation achieved?
Passivation can be achieved through various methods, including chemical treatment, electrochemical techniques, and exposure to natural environmental conditions. The specific method used depends on the type of metal and the desired level of corrosion resistance.
4. Are all metals capable of passivation?
No, not all metals are capable of passivation. Only metals that have a naturally occurring oxide layer (such as stainless steel) or can form an oxide layer through chemical reactions (such as aluminum) can undergo passivation.
5. What are some common applications of passivation?
Passivation is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and food processing. It is applied to components like surgical instruments, engine parts, food equipment, and pipelines to protect them from corrosion and ensure their long-term performance.
6. How long does passivation last?
The duration of passivation varies depending on factors such as the metal type, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. With proper care and periodic re-passivation if necessary, it is possible to maintain the passivation layer for extended periods.
7. Can passivation be reversed?
Passivation is not easily reversible. If the passivation layer is damaged or removed, it needs to be re-applied through additional passivation treatments to restore the corrosion resistance of the metal.
8. Is passivation a one-time process?
Passivation can be a one-time process, but in certain cases, especially for critical applications or when the metal is exposed to aggressive environments, periodic re-passivation may be required to maintain the desired level of corrosion resistance.
9. Can passivation be done on-site?
Yes, passivation can be done on-site or at specialized facilities. The method of passivation and the availability of equipment and expertise will determine whether on-site passivation is feasible.
10. Is passivation environmentally friendly?
Passivation processes can vary in terms of environmental impact. However, many passivation methods today strive to be environmentally friendly by using less hazardous chemicals, reducing waste generation, and implementing proper waste management practices.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.