Passive immunity is a fascinating aspect of our immune system that provides immediate protection against various pathogens without the body having to mount its own immune response. This form of immunity, which is acquired from external sources, plays a crucial role in defending our bodies against infections during the early stages of life. From maternal antibodies passed on to the developing fetus to the administration of preformed antibodies for immediate protection against specific diseases, passive immunity serves as a powerful defense mechanism.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of passive immunity, exploring its definition, mechanisms, and various ways in which it is acquired. Get ready to uncover some intriguing facts about passive immunity and appreciate the complexity of our immune system’s ability to ward off infections.
Key Takeaways:
- Passive immunity provides immediate protection through transferred antibodies, benefiting newborns and immunocompromised individuals. It’s like borrowing a shield to fend off specific germs, but it’s temporary.
- Whether from a mother’s milk or medical intervention, passive immunity offers rapid defense against targeted diseases. It’s like a quick-fix bodyguard, but it doesn’t stick around for the long haul.
What is Passive Immunity?
Passive immunity is a type of immunity that is acquired through the transfer of pre-formed antibodies to an individual. Unlike active immunity, which is developed by the body’s own immune system, passive immunity provides immediate protection against specific pathogens.
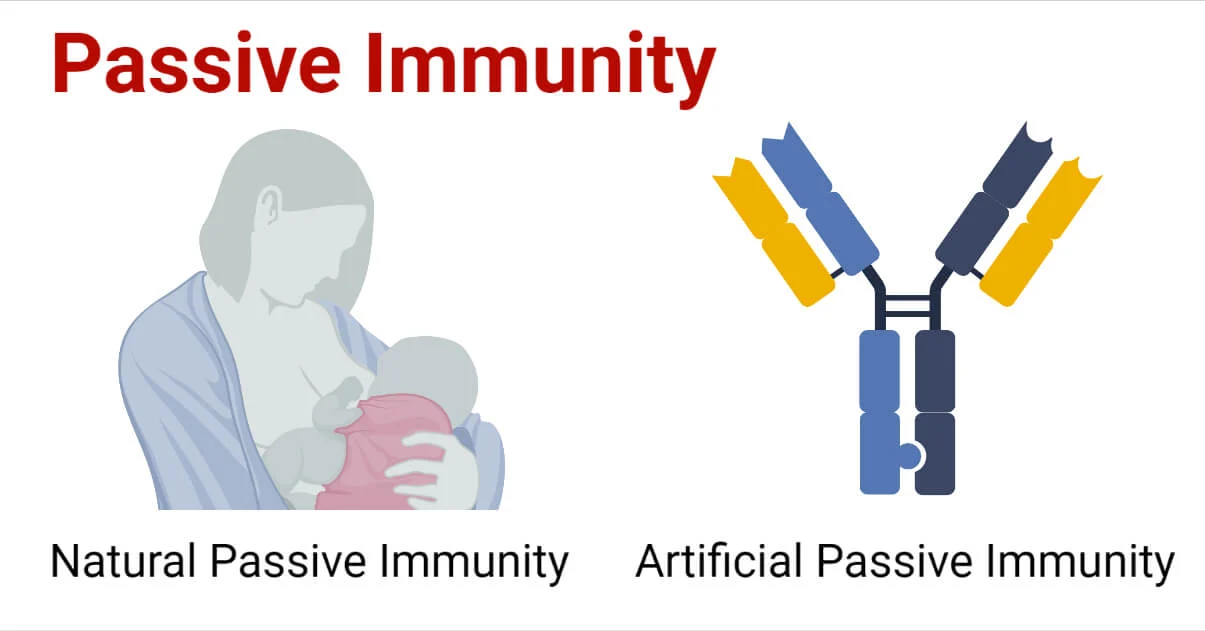
Natural Passive Immunity
Natural passive immunity occurs naturally when a mother passes antibodies to her baby through breastfeeding or placental transfer during pregnancy. This helps protect the newborn from various infections in the early stages of life.
Artificial Passive Immunity
Artificial passive immunity is achieved by giving an individual pre-formed antibodies obtained from another source, such as through the administration of immune globulins or antitoxins. This method is commonly used for the prevention or treatment of certain infectious diseases.
Temporary Protection
Passive immunity provides temporary protection as the transferred antibodies gradually decrease over time. Eventually, the individual’s own immune system needs to develop active immunity for long-term protection.
Rapid Onset of Action
One of the advantages of passive immunity is its rapid onset of action. Since the antibodies are already present, they can immediately bind to and neutralize antigens, providing instant defense against pathogens.
Protection against Specific Pathogens
Passive immunity offers protection against specific pathogens for which antibodies have been transferred. This targeted defense can be particularly helpful in cases of known exposure to a particular infection.
Passive Immunization for Immunocompromised Individuals
Passive immunization is often used for individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplant recipients. It provides an additional layer of protection against infections that their compromised immune systems may not be able to handle effectively.
Prevention of Diseases
Passive immunity has been instrumental in the prevention of various diseases. For example, the administration of immune globulins has proven effective in providing temporary protection against hepatitis A, measles, and tetanus.
Treating Rabies
Passive immunity plays a crucial role in the treatment of rabies. Rabies immune globulin, along with a series of rabies vaccinations, is administered to individuals who may have been exposed to the rabies virus to prevent the onset of the disease.
Protecting Healthcare Workers
Passive immunity has been utilized to protect healthcare workers against certain infections. For instance, the administration of immune globulins can provide immediate protection to those who have been exposed to diseases like hepatitis B and varicella-zoster virus.
Short-Lived Immunity
Unlike active immunity, which can provide long-lasting protection, the immunity provided by passive immunity is temporary. The transferred antibodies naturally degrade over time, resulting in the waning of this form of immunity.
No Memory Cells Involved
In passive immunity, the recipient does not generate memory cells, as the antibodies are not produced by their own immune system. This means that there is no long-term immune response or memory of the specific antigen.
Safe during Pregnancy
Passive immunization is generally considered safe during pregnancy as it does not introduce live pathogens to the mother or the developing fetus. However, it is always important to consult with a healthcare professional before any medical intervention.
Protection for Travelers
Passive immunity has been recommended for travelers visiting regions with a high risk of specific diseases. By receiving appropriate immunoglobulins, travelers can gain temporary protection against diseases like hepatitis A or typhoid fever.
Immunotherapy
Passive immunity is used in the field of immunotherapy for various conditions, including certain cancers and autoimmune diseases. Monoclonal antibodies or antibody-based therapies can be administered to target specific molecules or cells associated with the disease.
The Role of Passive Immunity in Newborn Health
Passive immunity plays a vital role in maintaining the health of newborns. The transfer of maternal antibodies through breast milk helps protect infants from various infections during the early months of life, when their own immune systems are still developing.
Passive immunity is an intriguing aspect of our immune system, offering immediate protection against specific pathogens. Whether it’s through natural transfer from a mother to her child or artificial administration to prevent or treat diseases, passive immunity has shown its significance in various medical contexts. Understanding the mechanisms and limitations of passive immunity can help researchers and healthcare professionals harness its potential for the betterment of human health.
Conclusion
Passive immunity is a fascinating aspect of our immune system that plays a crucial role in protecting our bodies from diseases. Through the transfer of pre-formed antibodies, either naturally or artificially, passive immunity provides immediate protection against pathogens without the need for the body to produce its own antibodies.Understanding passive immunity helps us comprehend the importance of vaccination, maternal antibodies, and antibody-based therapies. It also sheds light on the concept of herd immunity and its significance in preventing outbreaks of infectious diseases.As we continue to unravel the complexities of the immune system, passive immunity remains a captivating area of study. Its applications in medicine and its ability to confer temporary protection against various diseases make it an invaluable tool in the fight against infections.By harnessing the power of passive immunity, we can enhance our immune responses and work towards a healthier and more resilient future for all.
FAQs
Q: What is passive immunity?
A: Passive immunity refers to the transfer of pre-formed antibodies from one individual to another, providing immediate protection against pathogens.
Q: How is passive immunity acquired naturally?
A: Passive immunity can be acquired naturally through the transfer of maternal antibodies from a mother to her baby during pregnancy or through breast milk.
Q: What is the primary advantage of passive immunity?
A: The primary advantage of passive immunity is that it provides immediate protection, as the body does not have to produce its own antibodies.
Q: How is passive immunity obtained artificially?
A: Passive immunity can be obtained artificially through the administration of antibodies derived from humans or animals, such as through antibody-based therapies or immunization with serum containing antibodies.
Q: How long does passive immunity last?
A: Passive immunity is temporary and typically lasts for a few weeks to a few months, as the transferred antibodies gradually degrade in the recipient’s body.
Q: Can passive immunity replace active immunity?
A: Passive immunity provides immediate but temporary protection. It does not stimulate the body’s immune response, and therefore, cannot replace active immunity, which provides long-term protection by stimulating the production of antibodies.
Q: What is the role of passive immunity in vaccination?
A: Passive immunity plays a role in vaccination when individuals receive pre-formed antibodies, either as part of the vaccine or through antibody-based therapies, to provide immediate protection while their bodies develop active immunity.
Q: Does passive immunity contribute to herd immunity?
A: Yes, passive immunity contributes to herd immunity as it helps protect individuals who are unable to mount an immune response, such as infants or immunocompromised individuals, indirectly reducing the spread of infectious diseases within a population.
Q: Are there any risks associated with passive immunity?
A: While passive immunity is generally safe, there can be risks of allergic reactions, transmission of infectious agents, or a temporary dampening of the recipient’s immune response in some cases.
Q: Can passive immunity be used for the treatment of diseases?
A: Yes, passive immunity can be used for the treatment of diseases. For example, antibody-based therapies have been developed to treat conditions like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and viral infections.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
