Cellular immunity, also known as cell-mediated immunity, is a critical defense mechanism of the immune system that plays a vital role in protecting our bodies against various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. While most people are familiar with the concept of immunity, there are several fascinating and surprising facts about cellular immunity that are often overlooked.
In this article, we will delve into 10 intriguing facts about cellular immunity that will enhance your understanding of how our immune system functions and its remarkable ability to combat infections. From the types of cells involved to the process of antigen presentation, these facts highlight the complexity and efficiency of cellular immunity. So, get ready to be astonished by the incredible world of cellular immunity!
Key Takeaways:
- Cellular immunity, led by T cells and NK cells, provides long-lasting protection against diseases and plays a crucial role in organ transplants and autoimmune diseases.
- Vaccines stimulate cellular immunity, and genetic factors and aging can impact its effectiveness. Excitingly, therapies targeting cellular immunity show promise in cancer treatment.
Cellular immunity is a vital component of the immune system.
Cellular immunity, also known as cell-mediated immunity, plays a critical role in protecting the body against various pathogens and diseases. It involves the action of specialized cells, such as T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, which are responsible for killing infected cells and coordinating the immune response.
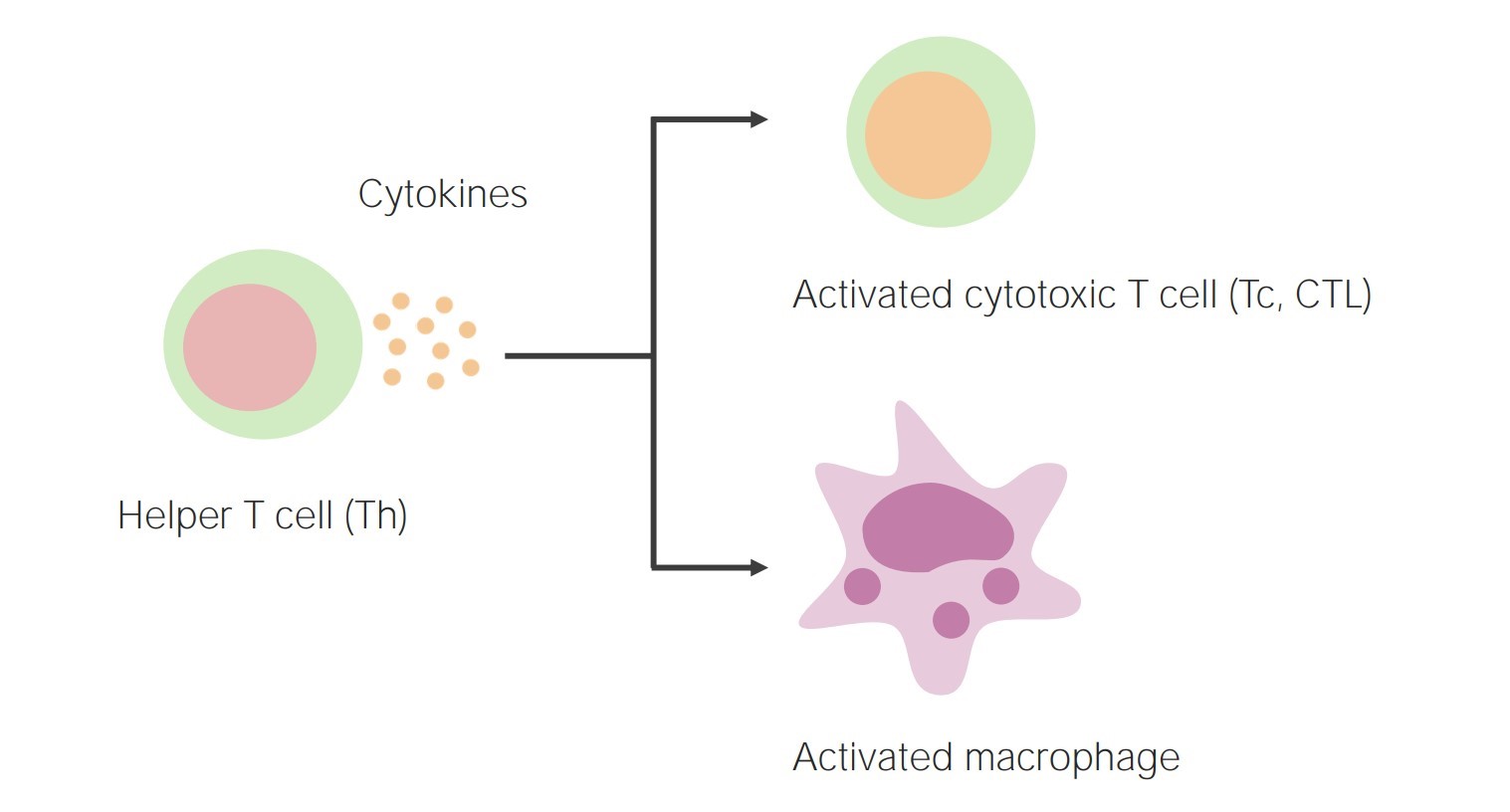
T cells are the key players in cellular immunity.
T cells are a type of white blood cell that are essential for the proper functioning of cellular immunity. These cells are diverse and can recognize a wide range of antigens, enabling them to identify and destroy infected or abnormal cells in the body.
Cellular immunity provides long-term immunity.
One of the remarkable aspects of cellular immunity is its ability to provide long-lasting protection against pathogens. Once T cells encounter and eliminate a particular pathogen, they retain a memory of it. This memory allows them to mount a rapid and robust immune response upon subsequent encounters, offering long-term immunity.
Cellular immunity is involved in the rejection of transplanted organs.
When a person receives an organ transplant, the immune system recognizes the transplanted organ as foreign and triggers cellular immunity to reject it. This immune response is a major challenge in organ transplantation and requires careful management through immunosuppressive drugs.
Natural killer (NK) cells play a crucial role in cellular immunity.
Natural killer (NK) cells are a specialized subset of lymphocytes that are responsible for identifying and destroying virus-infected cells and tumor cells. They play a critical role in the early defense against viral infections and have the ability to directly kill target cells without prior sensitization.
Cellular immunity can contribute to autoimmune diseases.
In certain cases, cellular immunity can go awry and mistakenly target healthy cells in the body, leading to autoimmune diseases. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes are believed to involve dysregulation of cellular immune responses.
Vaccines stimulate cellular immunity.
Many vaccines are designed to activate and enhance cellular immunity. By introducing harmless fragments of pathogens or weakened forms of the pathogen into the body, vaccines prompt the immune system to mount a cellular immune response and develop immunity against the real pathogen.
Cellular immunity is influenced by genetic factors.
The effectiveness and efficiency of cellular immunity can vary among individuals due to genetic factors. Certain genetic variations can impact the functioning of T cells and other immune cells, affecting the strength of the cellular immune response.
Cellular immunity declines with age.
As people age, their cellular immune responses tend to weaken, making them more susceptible to infections and diseases. This decline in cellular immunity is believed to contribute to the increased prevalence of certain illnesses in the elderly population.
Therapies targeting cellular immunity show promise in cancer treatment.
Recent advancements in cancer treatment have focused on boosting the body’s cellular immune response against cancer cells. Immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, aim to unleash the power of cellular immunity to recognize and destroy cancer cells, offering new hope in the fight against cancer.
Conclusion
Cellular immunity is a fascinating and complex aspect of the immune system. Understanding its various facets and how it interacts with other components of immunity is crucial in developing effective treatments for a wide range of diseases and conditions. The 10 surprising facts about cellular immunity highlighted in this article shed light on its importance and the ongoing research aimed at harnessing its full potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cellular immunity is a fascinating aspect of our immune system that plays a crucial role in protecting our bodies against various diseases and infections. It involves the intricate interplay of different cells and molecules working together to identify and eliminate harmful pathogens. From the surprising ability of memory T cells to recognize previously encountered threats to the long-lasting protection offered by vaccines, cellular immunity continues to amaze scientists and researchers.Understanding the intricacies of cellular immunity not only provides insights into the body’s defense mechanisms but also opens doors to the development of novel therapeutic interventions. Harnessing the power of cellular immunity can lead to breakthroughs in the treatment of infectious diseases, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.As our knowledge of cellular immunity expands, so does the potential for medical advancements and targeted interventions. Delving deeper into this field will undoubtedly unveil more surprising facts in the future, leading to a better understanding of our immune system and ultimately, improved healthcare outcomes.
FAQs
1. What is cellular immunity?
Cellular immunity, also known as cell-mediated immunity, is a vital component of our immune system. It involves specialized cells, such as T cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages, working together to identify and eliminate pathogens and abnormal cells in the body.
2. What are the key players in cellular immunity?
The key players in cellular immunity are T cells, which come in several forms including helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, and memory T cells. These cells play essential roles in recognizing antigens, coordinating immune responses, and destroying infected or abnormal cells.
3. How does cellular immunity differ from humoral immunity?
Cellular immunity primarily deals with the direct action of immune cells against pathogens and abnormal cells. On the other hand, humoral immunity involves the production of antibodies by B cells to neutralize and eliminate pathogens in the body fluids.
4. Can cellular immunity be boosted?
Yes, cellular immunity can be boosted through various means. Vaccinations, for example, can stimulate the immune system to develop a strong cellular immune response against specific pathogens. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet, can help support optimal cellular immune function.
5. How does cellular immunity contribute to cancer treatments?
Cellular immunity plays a crucial role in cancer treatments, such as immunotherapies. By enhancing the body’s immune response against cancer cells, these therapies aim to stimulate the activity of immune cells like T cells, enabling them to recognize and target cancer cells more effectively.
6. Are there any disorders associated with cellular immunity?
Yes, there are several disorders associated with cellular immunity. Examples include primary immunodeficiencies, where there is a genetic defect in the cells responsible for cellular immunity, as well as autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells.
7. Can aging affect cellular immunity?
Yes, aging can affect cellular immunity. As we age, there is a gradual decline in the function of immune cells, including T cells. This can result in a reduced ability to mount an effective cellular immune response, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and other ailments.
8. Can stress impact cellular immunity?
Yes, chronic stress has been shown to affect cellular immunity negatively. Prolonged stress can suppress the activity of immune cells, impairing their ability to respond adequately to pathogens and potentially increasing the risk of infection and disease.
9. How can I support my cellular immune system?
To support your cellular immune system, focus on living a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, engaging in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, managing stress levels, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
10. Are there any ongoing research areas in cellular immunity?
Indeed, there are several ongoing research areas in cellular immunity. Scientists and researchers are continuously studying the complex mechanisms behind cellular immunity, exploring novel therapies, and investigating ways to enhance immune responses in various diseases, including infectious diseases, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
