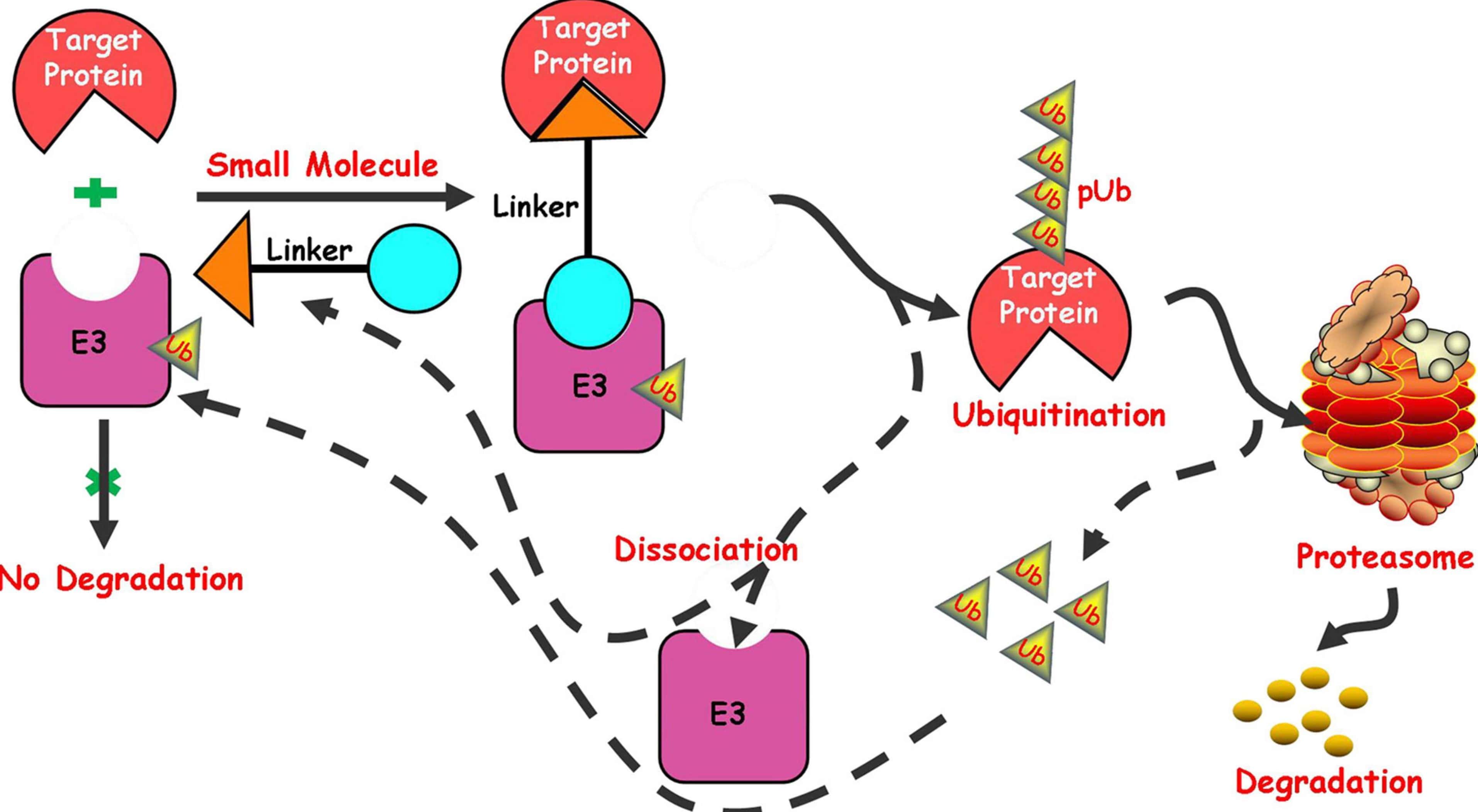
The process of proteasome degradation might sound complex and intimidating, but it plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating key biological processes. The proteasome is a large protein complex found in all eukaryotic cells that acts as a molecular machine responsible for degrading damaged or unwanted proteins. While many people might not be familiar with proteasome degradation, it is essential for various cellular functions, including cell cycle regulation, immune response, protein quality control, and even programmed cell death. In this article, we will explore 17 surprising facts about proteasome degradation that will not only expand your knowledge of this essential biological process but also leave you amazed at the intricate mechanisms involved. So let’s dive right into these fascinating facts about proteasome degradation!
Key Takeaways:
- The proteasome is like a cell’s garbage disposal, breaking down unwanted proteins to keep the cell healthy and functioning properly. It’s crucial for preventing diseases and maintaining cellular balance.
- Proteasome degradation is like a superhero fighting off bad proteins in the cell. It helps with DNA repair, cell division, and even gets rid of misfolded proteins that can cause diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
The Proteasome is the Cellular Waste Disposal System
The proteasome is a complex protein structure found in all eukaryotic cells that acts as the cell’s waste disposal system. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by degrading unwanted or damaged proteins.
It Plays a Key Role in Protein Quality Control
The proteasome ensures the quality control of proteins by selectively targeting misfolded or damaged proteins for degradation. This helps prevent the accumulation of abnormal proteins that can lead to cellular dysfunction and diseases such as neurodegenerative disorders.
The Proteasome Degrades Regulatory Proteins
In addition to misfolded proteins, the proteasome also targets regulatory proteins involved in cell cycle control, DNA repair, apoptosis, and immune response. By degrading these proteins, the proteasome influences a wide range of cellular processes.
It Plays a Role in Antigen Presentation
The proteasome is involved in the antigen presentation pathway, where it degrades intracellular proteins into peptide fragments that are presented on the cell surface to the immune system. This process is essential for the recognition and elimination of infected or cancerous cells by immune cells.
Ubiquitin Marks Proteins for Degradation
Proteins destined for degradation by the proteasome are labeled with a small protein called ubiquitin. Ubiquitin serves as a molecular tag that signals the proteasome to recognize and degrade the labeled protein.
The Proteasome Has Multiple Catalytic Sites
The proteasome consists of multiple subunits, each with its specific function. Within the proteasome, there are catalytic sites known as proteolytic cores, where the actual degradation of proteins occurs. These cores have different enzymatic activities, allowing for the efficient breakdown of a wide range of protein substrates.
It Plays a Role in DNA Repair
The proteasome is involved in the repair of damaged DNA by degrading proteins that inhibit DNA repair processes. This ensures the integrity of the genome and prevents the accumulation of DNA damage that can lead to mutations and cancer.
Dysregulation of Proteasome Degradation Implicated in Diseases
Aberrant proteasome function has been associated with various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding the mechanisms of proteasome degradation may lead to the development of targeted therapies for these conditions.
It Can Influence Gene Expression
The proteasome can regulate gene expression by degrading transcription factors or proteins involved in the modulation of gene expression. By removing these proteins, the proteasome can either activate or suppress certain genes, shaping the cellular response to different stimuli.
The Proteasome is Regulated by Ubiquitin Ligases
Ubiquitin ligases are enzymes that attach ubiquitin molecules to proteins, marking them for degradation by the proteasome. These ligases play a crucial role in controlling proteasome activity and ensuring the timely degradation of specific proteins.
The Proteasome Can Degrade Long-Lived Proteins
While the proteasome primarily degrades short-lived proteins, it can also target and degrade long-lived proteins that have undergone post-translational modifications or have become damaged beyond repair. This helps maintain protein homeostasis and turnover in the cell.
It Can Degrade Polyubiquitin Chains
Polyubiquitin chains are formed when multiple ubiquitin molecules are attached to a protein. The proteasome can recognize and efficiently degrade these polyubiquitin chains, ensuring the recycling of ubiquitin and preventing their accumulation in the cell.
The Proteasome Can Respond to Cellular Stress
Under conditions of cellular stress, such as oxidative stress or heat shock, the proteasome can be upregulated to meet the increased demand for protein degradation. This adaptive response helps maintain cellular proteostasis and survival.
It Is Essential for Cell Division
The proteasome plays a crucial role in cell division by degrading proteins involved in cell cycle regulation and mitotic spindle formation. Proper proteasome function is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes and the maintenance of genomic stability.
It Can Recognize and Degrade Mislocalized Proteins
Proteins that are mislocalized within the cell, such as those that end up in the wrong organelle or compartment, can be recognized and degraded by the proteasome. This helps maintain the proper localization and function of proteins within the cell.
It Can Degrade Aggregated Proteins
In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, misfolded proteins can form aggregates, leading to cellular toxicity. The proteasome plays a critical role in degrading these aggregated proteins and preventing their accumulation in the cell.
The Proteasome Has Different Types and Variants
There are different types of proteasomes found in different cellular compartments, including the cytosol, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum. These distinct proteasome variants have specialized functions and substrate preferences, allowing for precise control of protein degradation in specific cellular compartments.
In conclusion, the proteasome degradation pathway is a fascinating and essential process in cellular biology. It plays a vital role in maintaining protein quality control, cellular homeostasis, and regulating various cellular processes. Understanding the intricacies of proteasome degradation can have significant implications for the development of therapies targeting diseases associated with aberrant protein degradation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, proteasome degradation is a fascinating and intricate process that plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating various cellular processes. It involves the targeted degradation of proteins that are damaged, misfolded, or no longer needed by the cell. The proteasome, a large and complex molecular machinery, acts as the primary site of protein degradation within the cell.
Throughout this article, we have explored 17 surprising facts about proteasome degradation, ranging from its discovery and structure to its regulation and involvement in diseases. Understanding the intricacies of proteasome degradation not only expands our knowledge of cellular biology but also opens up new possibilities for therapeutic interventions.
From the sheer versatility of the proteasome to the complex mechanisms that govern its activity, proteasome degradation continues to be an area of intense research and discovery. By delving deeper into the mysterious world of proteasome degradation, scientists strive to unravel its mysteries and apply this knowledge to various fields, ranging from medicine and drug development to biotechnology and environmental sciences.
As we continue to uncover more about proteasome degradation, it becomes increasingly clear that this process is not only essential for cellular health but also holds the key to unlocking numerous biological puzzles.
FAQs
1. What is proteasome degradation?
Proteasome degradation is the process by which damaged, misfolded, or unneeded proteins are selectively destroyed by a cellular machinery called the proteasome.
2. How does the proteasome function?
The proteasome is a complex molecular machine that consists of multiple subunits working together to recognize, unfold, and degrade proteins. It utilizes specialized enzymes to break down proteins into smaller peptides.
3. What is the significance of proteasome degradation?
Proteasome degradation is vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating protein levels, and eliminating abnormal or unwanted proteins. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including cell cycle control, DNA repair, and immune response.
4. Can proteasome degradation be regulated?
Yes, proteasome degradation is tightly regulated by various cellular mechanisms, including the addition of specific tags to target proteins for degradation and the activation of specific pathways in response to cellular stress or signaling.
5. Is proteasome degradation involved in diseases?
Yes, dysfunction in proteasome degradation has been associated with several diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, as well as certain types of cancer. Understanding proteasome dysfunction can open up new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
6. Are there drugs that target the proteasome?
Yes, there are drugs known as proteasome inhibitors that target the activity of the proteasome. These inhibitors have shown promise in treating certain types of cancer by blocking the degradation of proteins involved in cancer cell growth and survival.
7. Can proteasome degradation be harnessed for biotechnology applications?
Yes, proteasome degradation can be utilized in biotechnology applications such as protein engineering and the production of recombinant proteins. Researchers can manipulate proteasome activity to fine-tune protein levels and improve protein quality in industrial processes.
8. How is proteasome degradation related to protein turnover?
Proteasome degradation is a key mechanism in protein turnover, which refers to the balance between the synthesis and degradation of proteins in cells. By degrading unwanted or damaged proteins, the proteasome helps maintain the proper protein balance in cellular environments.
9. What are some recent discoveries in the field of proteasome degradation?
Recent studies have uncovered novel regulatory mechanisms and specific protein targets involved in proteasome degradation. Additionally, researchers have developed new techniques to visualize and study the proteasome’s activity in live cells, providing valuable insights into its function and regulation.
10. How does proteasome degradation contribute to cellular quality control?
Proteasome degradation functions as a crucial aspect of cellular quality control by eliminating proteins that are misfolded, damaged, or no longer needed. This process ensures that only properly folded and functional proteins are present in the cell, minimizing the risk of cellular dysfunction and disease.
Proteasome degradation is a fascinating process, but there's more to explore in the world of cellular biology. Dive into the wonders of cell biology with our article on 20 Extraordinary Facts About Embryonic Stem Cells and their incredible potential. Don't forget about the importance of ubiquitin tagging, the small protein that plays a big role in marking proteins for degradation. Finally, expand your knowledge of the microscopic world with our collection of 20 Astonishing Facts About Molecular Biology that will leave you in awe of the complex processes occurring within our cells. Keep reading to uncover more surprises hidden in the realm of cellular biology.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
