The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a fascinating organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage. The ER is a complex network of interconnected tubes and sacs that extends throughout the cytoplasm, acting as the cell’s manufacturing and transportation system.
While most people may not be familiar with the intricacies of the endoplasmic reticulum, it is truly a remarkable structure with several astonishing facts waiting to be discovered. In this article, we will delve into twelve astonishing facts about the endoplasmic reticulum that will not only expand your knowledge but also leave you in awe of the intricate workings of these tiny cellular compartments.
Key Takeaways:
- The endoplasmic reticulum is like a busy factory inside our cells, making proteins, storing calcium, and helping with drug metabolism. It’s like a multitasking superhero keeping our cells healthy and balanced.
- Just like a superhero, the endoplasmic reticulum can change and adapt to different situations in our body. It’s like a shape-shifter, always ready to help our cells stay strong and healthy.
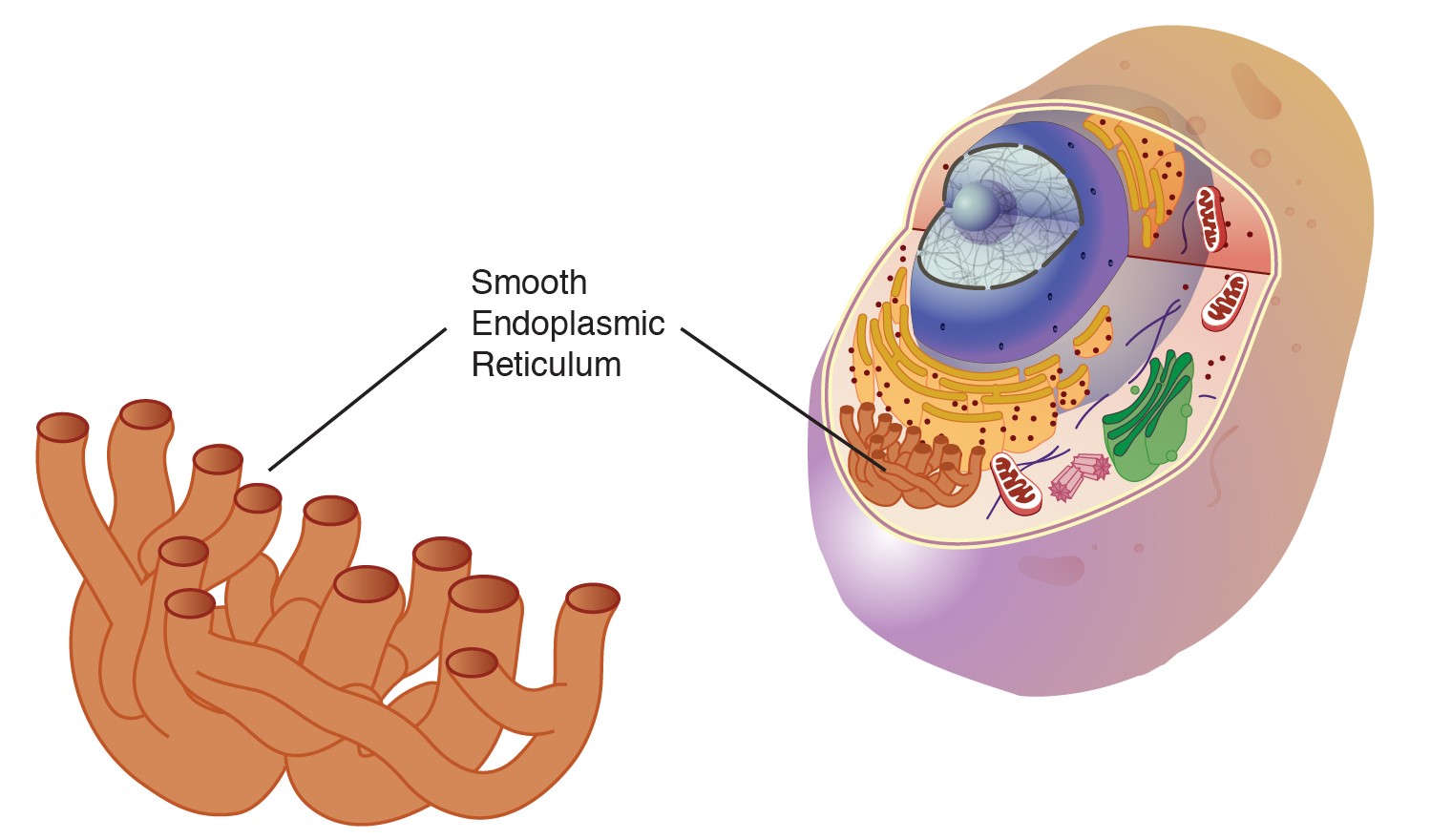
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is Extensively Branched
The ER consists of a complex network of tubules and flattened sacs, forming an intricate structure that extends throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. This extensive branching allows for greater surface area and facilitates various cellular processes.
There are Two Main Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum can be classified into two distinct types: the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The RER is studded with ribosomes, while the SER lacks ribosomes on its surface.
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Produces Proteins
As the name suggests, the RER is involved in protein synthesis. It synthesizes proteins that are destined for secretion or insertion into cellular membranes. The ribosomes attached to the RER play a crucial role in this process.
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum is Involved in Lipid Metabolism
Unlike the RER, the SER does not have ribosomes. It is primarily involved in lipid metabolism, including the synthesis of lipids, detoxification of drugs and toxins, and storage of calcium ions.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum Helps in Protein Folding
Proteins synthesized in the RER undergo a process called protein folding. This ensures that the proteins acquire their correct three-dimensional structure, which is essential for their proper functioning.
Misfolded Proteins are Recognized by the Endoplasmic Reticulum
If a protein fails to fold correctly, the ER has quality control mechanisms to identify and remove it. This helps maintain the overall integrity of the cellular protein pool and prevents the accumulation of misfolded proteins.
The ER Plays a Role in Calcium Homeostasis
The endoplasmic reticulum acts as a calcium storage site in the cell. It regulates calcium levels, releasing the ion into the cytoplasm when needed, and sequestering it back into the ER during calcium signaling events.
The ER is Connected to the Nuclear Envelope
The endoplasmic reticulum is in close proximity to the nucleus and is connected to the nuclear envelope. This allows for the seamless exchange of membranes and molecules between the ER and the nucleus.
The ER Participates in the Formation of Lipid Droplets
Lipid droplets are specialized organelles involved in lipid storage. The endoplasmic reticulum plays a crucial role in their formation, as it supplies lipids that are then encapsulated within these droplets.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is Important for Drug Metabolism
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum contains enzymes involved in drug metabolism and detoxification. It helps metabolize various drugs, making them more water-soluble and easier for the body to eliminate.
The ER is Essential for Cell Signaling
The endoplasmic reticulum plays a crucial role in cell signaling pathways. It houses receptors and channels that are involved in processes such as calcium release, lipid signaling, and regulation of cellular responses to external stimuli.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum Is Dynamic and Adaptable
The ER is a highly dynamic organelle that can respond to changes in cellular conditions. It can modify its structure and function depending on the needs of the cell, allowing for efficient adaptation to different physiological states.
These 12 astonishing facts about the endoplasmic reticulum highlight its importance in cellular processes and underscore its versatility as an organelle. From protein synthesis to drug metabolism, the ER plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and overall organismal health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a fascinating and essential organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, calcium homeostasis, and cellular communication. The ER consists of two distinct regions, the rough ER and the smooth ER, each with its own unique functions. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, involved in the synthesis and folding of proteins, while the smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification processes.
The ER’s intricate network of membranes allows for efficient transport and communication within the cell, ensuring proper functioning and homeostasis. Its importance in various cellular processes makes it a subject of great interest and research in the field of biology. The discoveries and ongoing studies related to the endoplasmic reticulum continue to unveil new insights into the complexity and functionality of cells and organisms.
FAQs
1. What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium homeostasis.
2. What are the two regions of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum consists of the rough ER and the smooth ER.
3. What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is responsible for the synthesis and folding of proteins, as it is studded with ribosomes.
4. What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification processes, and the regulation of calcium levels in the cell.
5. How does the endoplasmic reticulum contribute to cellular communication?
The endoplasmic reticulum plays a role in cellular communication by facilitating the transport of proteins and lipids between different organelles and the cell membrane.
6. Can the endoplasmic reticulum be found in prokaryotic cells?
No, the endoplasmic reticulum is a characteristic organelle of eukaryotic cells and is not present in prokaryotes.
7. What happens when the endoplasmic reticulum malfunctions?
Malfunctions in the endoplasmic reticulum can lead to various disorders and diseases, such as ER stress-related conditions and metabolic disorders.
8. Can the endoplasmic reticulum regenerate after damage?
Yes, the endoplasmic reticulum has the ability to regenerate and repair itself after damage or stress conditions.
9. Are there any drugs or treatments targeting the endoplasmic reticulum?
Yes, there are various drugs and treatments that target specific functions of the endoplasmic reticulum, such as protein folding, lipid metabolism, and calcium regulation.
10. How has the study of the endoplasmic reticulum contributed to scientific advancements?
The study of the endoplasmic reticulum has led to significant advancements in our understanding of cellular processes, protein folding, disease mechanisms, and drug development.
Endoplasmic reticulum's astonishing facts reveal its vital role in cellular processes. Delving deeper into cell biology, explore the intricacies of animal cells and their fascinating components. Protein trafficking, a complex process, ensures molecules reach their correct destinations within cells. ER targeting, an essential aspect of this process, guarantees proteins find their way to the endoplasmic reticulum. Unravel more captivating insights by exploring these related topics, expanding your knowledge of the microscopic world within our cells.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


