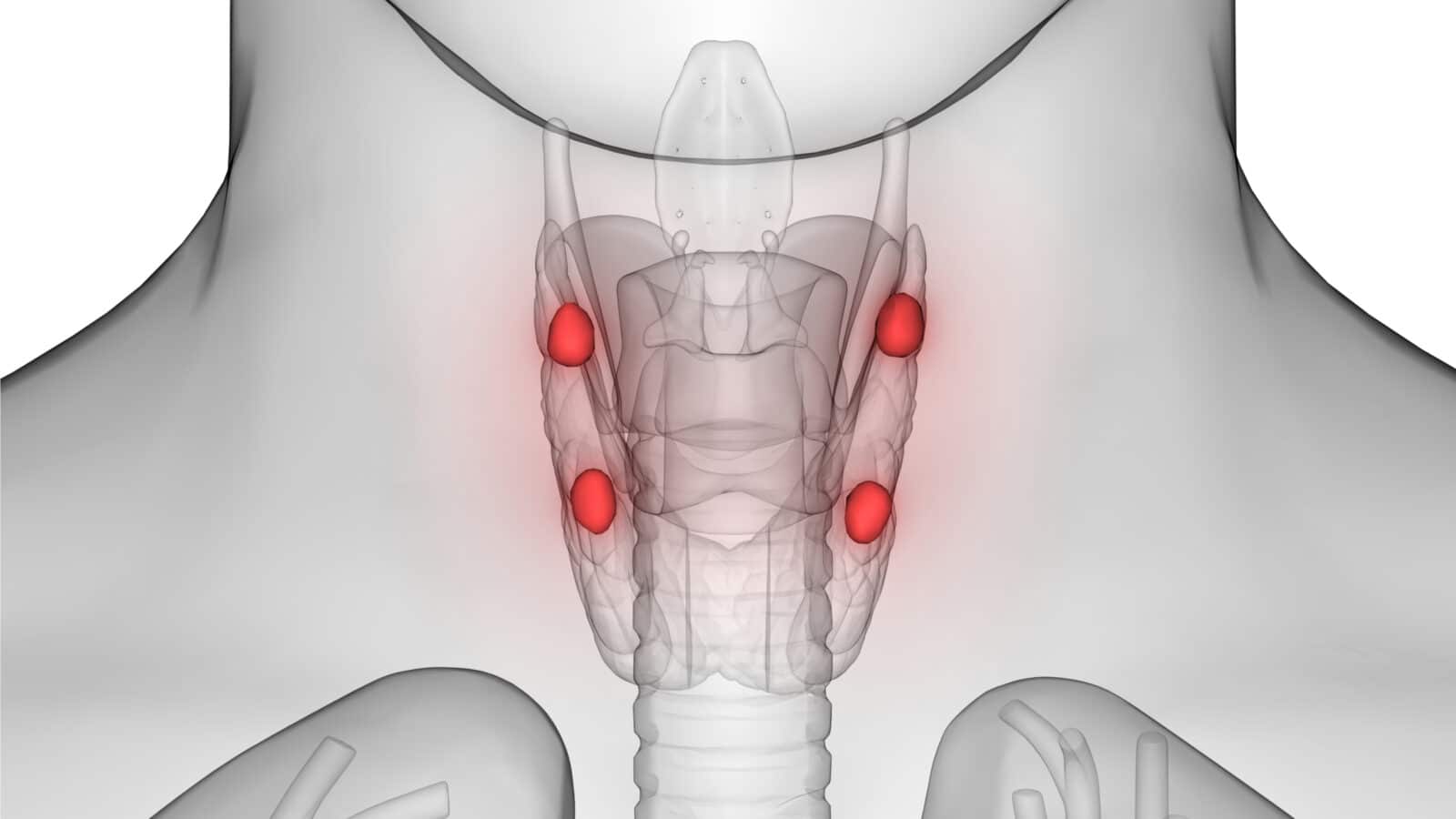
Parathyroid glands are tiny, yet incredibly vital, structures located in the neck, near the thyroid gland. Despite their small size, these four glands play a major role in regulating our body’s calcium levels, which is crucial for maintaining healthy bones and teeth, as well as proper nerve and muscle function.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of parathyroid glands and explore 18 astounding facts about them. From their discovery and location to their functions and disorders, we will uncover intriguing details that will give you a deeper understanding of these remarkable glands.
So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to embark on an educational journey that will leave you amazed by the complexity and significance of these often overlooked organs!
Key Takeaways:
- The parathyroid glands, located behind the thyroid, help keep our bones strong by controlling calcium levels in our bodies. They can develop tumors and affect our overall health.
- Understanding the parathyroid glands’ role in maintaining calcium balance and bone health is crucial for our overall well-being. They work closely with the thyroid and play a vital role in our body’s intricate workings.
The parathyroid glands are usually four in number.
In most individuals, there are four parathyroid glands, but the number can vary. They are typically located on the posterior side of the thyroid gland.
Parathyroid hormones help regulate calcium levels.
The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (PTH) which plays a vital role in controlling calcium levels in the blood and bones.
PTH stimulates the release of calcium from bones.
PTH signals the bones to release calcium into the bloodstream when levels are too low, ensuring proper calcium balance in the body.
PTH enhances calcium absorption in the intestines.
Parathyroid hormone increases the absorption of dietary calcium in the intestines, aiding in maintaining optimal calcium levels.
Parathyroid glands can develop tumors.
Parathyroid adenomas or benign tumors can form in the parathyroid glands, leading to excessive production of PTH and abnormal calcium levels.
Hyperparathyroidism is a common disorder.
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition characterized by overactive parathyroid glands, resulting in elevated levels of calcium in the blood.
Hypoparathyroidism is a rare condition.
Hypoparathyroidism occurs when the parathyroid glands don’t produce enough PTH, causing low calcium levels and impaired bone health.
Parathyroid glands develop early in the fetal stage.
The parathyroid glands start developing in the fetus around the sixth week of pregnancy and are functional by the tenth week.
Surgical removal of parathyroid glands can be necessary.
If a parathyroid adenoma causes severe symptoms or complications, surgical removal of the affected gland may be required.
Parathyroid glands work closely with the thyroid gland.
The parathyroid glands and thyroid gland are anatomically close but have distinct functions and do not directly influence each other.
Parathyroid hormone affects kidney function.
PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys, reducing calcium loss through urine and aiding in maintaining proper levels.
Parathyroid hormone production is regulated by calcium levels.
If calcium levels in the blood drop too low, the parathyroid glands release more PTH to restore the balance.
Parathyroid glands are essential for skeletal development.
During childhood and adolescence, the parathyroid glands play a crucial role in bone growth and mineralization.
The size of parathyroid glands can vary.
While parathyroid glands are typically small, their size can vary significantly between individuals.
Parathyroid glands can be affected by autoimmune disorders.
Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease can sometimes impact the function of the parathyroid glands.
Vitamin D deficiency can affect parathyroid function.
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to decreased calcium absorption, stimulating the parathyroid glands to increase PTH production.
Parathyroid hormone can regulate phosphate levels as well.
Besides calcium, PTH also helps maintain appropriate phosphate levels in the body, essential for bone health.
The parathyroid glands can undergo microscopic changes.
Microscopic examination of parathyroid tissue can reveal important insights about the health and function of the glands.
These 18 astounding facts about parathyroid glands highlight their importance in maintaining calcium balance, bone health, and overall well-being. Understanding the role and function of these small yet mighty glands can help us appreciate the intricate workings of our bodies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the parathyroid glands play a vital role in maintaining the balance of calcium in our bodies. These small, pea-sized glands are responsible for producing the parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium levels by interacting with the bones, kidneys, and intestines. Understanding the functions and importance of the parathyroid glands can provide valuable insight into various conditions and diseases related to calcium imbalance.By harnessing their incredible capabilities, healthcare professionals can diagnose and treat disorders such as hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism more effectively. The intricate connection between the parathyroid glands and our overall well-being highlights the significance of ongoing research and advancements in the field of endocrinology.As our understanding deepens, we continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding the parathyroid glands, further enhancing our knowledge of human anatomy and paving the way for innovative treatments and interventions in the future.
FAQs
Q: What are the parathyroid glands?
A: The parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands located in the neck, near the thyroid gland.
Q: How many parathyroid glands do we have?
A: Typically, humans have four parathyroid glands, two on each side of the thyroid gland.
Q: What is the function of the parathyroid glands?
A: The primary function of the parathyroid glands is to regulate calcium levels in the body by producing parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Q: What happens when the parathyroid glands produce too much PTH?
A: Overproduction of PTH can lead to a condition called hyperparathyroidism, which can cause high levels of calcium in the blood.
Q: What are the symptoms of parathyroid gland disorders?
A: Some common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, kidney stones, and mood changes.
Q: How are parathyroid disorders diagnosed?
A: Blood tests to measure calcium and PTH levels, along with imaging tests such as ultrasounds or nuclear medicine scans, are typically used for diagnosis.
Q: What are the treatment options for parathyroid disorders?
A: Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition but can include surgery, medication, and lifestyle modifications.
Parathyroid glands may be small, but their impact on our health is immense. Understanding how parathyroid hormone works and the role of oxyphil cells in these glands can help you better appreciate their significance. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of parathyroid physiology and uncover more mind-boggling facts that will leave you in awe of these tiny powerhouses. Join us on this journey of discovery as we explore the intricacies of parathyroid function and the incredible ways in which they contribute to our overall well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
