The bladder is an essential organ in the human body that plays a vital role in the urinary system. It serves as a reservoir for urine before it is excreted from the body. While it may seem like a simple organ, the bladder is fascinating in its structure and function. In this article, we will uncover some intriguing and lesser-known facts about the bladder. From its anatomy to its role in maintaining urinary health, we will dive into the world of the bladder and explore the wonders within.
The Anatomy of the Bladder
The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ located in the pelvic area, behind the pubic bone. It is shaped like a balloon and expands as it fills with urine. The bladder is made up of several layers, including the urothelium (inner lining), smooth muscle, and connective tissue.
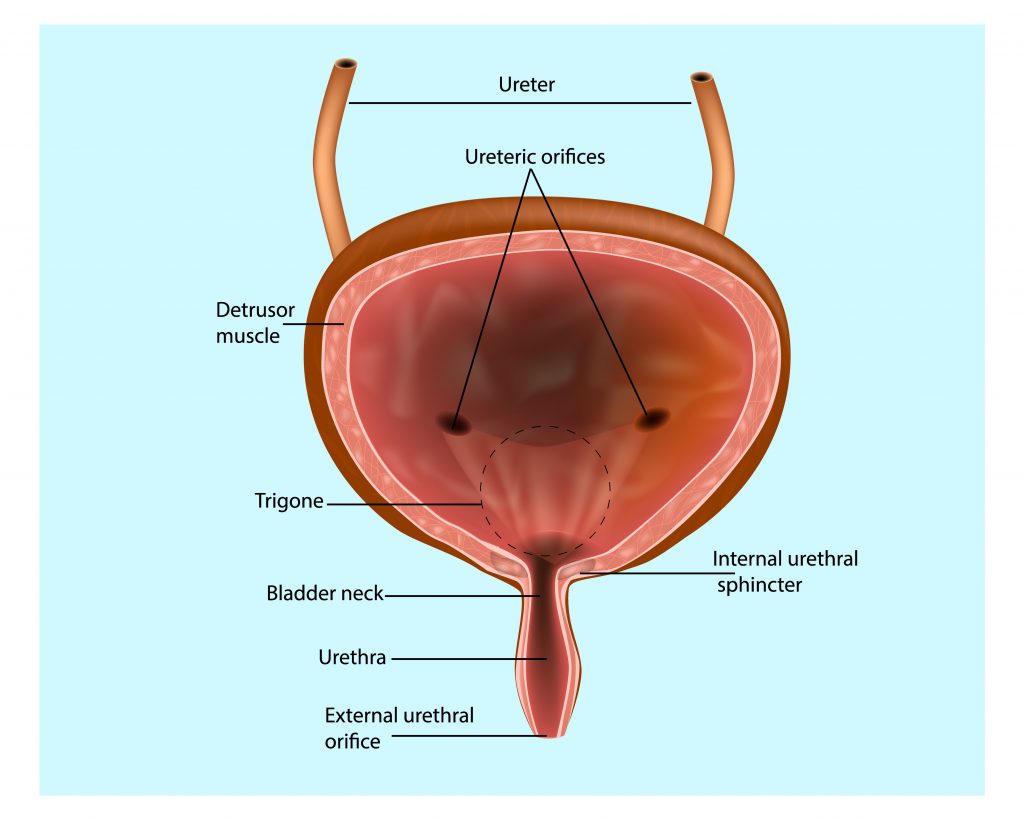
Structure of the Bladder
The bladder is composed of smooth muscle tissue called the detrusor muscle, which contracts to expel urine during urination. It has a stretchable lining called the urothelium, which allows the bladder to expand as it fills with urine.
Bladder Capacity and Urination
The capacity of the bladder can vary among individuals but is typically around 400-600 milliliters (13-20 fluid ounces). The sensation of needing to urinate is triggered when the bladder is about half full, which is approximately 200-300 milliliters (7-10 fluid ounces).
The Micturition Reflex
The process of urination is regulated by a complex neurological reflex called the micturition reflex. When the bladder reaches a certain level of distension, nerve signals are sent to the brain, which initiates the urge to urinate. The brain can override the urge to urinate temporarily by contracting the external urethral sphincter muscles, allowing for voluntary control over urination.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary system and multiply, leading to infection. Symptoms may include frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, and cloudy urine.
Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder is a condition characterized by a sudden and frequent urge to urinate, often accompanied by involuntary bladder contractions.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence refers to the involuntary leakage of urine. It can result from weakened pelvic floor muscles, nerve damage, or other underlying medical conditions.

Bladder Stones
Bladder stones are hard mineral deposits that can form in the bladder. They may cause symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urination, and blood in the urine.
Conclusion
The bladder is an incredible organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining urinary health. From its anatomy to its intricate function, the bladder’s significance cannot be underestimated. Understanding the bladder and practicing healthy habits can contribute to overall well-being and urinary system function. By staying hydrated, practicing good bathroom habits, and seeking appropriate medical attention when necessary, you can support your bladder health and enjoy a comfortable and functioning urinary system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can bladder health be improved through diet?
While there is no specific diet to guarantee bladder health, maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated can contribute to overall urinary system health. Avoiding bladder irritants, such as caffeine and alcohol, may also help in managing bladder-related symptoms.
Can bladder problems occur at any age?
Bladder problems can occur at any age, from childhood to adulthood. However, certain conditions, such as urinary incontinence and overactive bladder, become more common with age.
Can holding urine for too long damage the bladder?
Holding urine for extended periods can put a strain on the bladder and potentially affect its function. It may increase the risk of urinary tract infections and contribute to bladder-related discomfort. It is best to empty the bladder regularly and avoid prolonged periods without urination.
Can stress affect bladder function?
Yes, stress can impact bladder function. Stress and anxiety can contribute to overactive bladder symptoms or exacerbate existing bladder conditions. Managing stress through relaxation techniques or seeking professional support may help alleviate associated bladder symptoms.
Are bladder problems more common in women or men?
Certain bladder conditions, such as urinary incontinence, are more prevalent in women. However, bladder problems can occur in both men and women. The frequency and type of bladder issues may vary between genders due to anatomical and physiological differences.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
