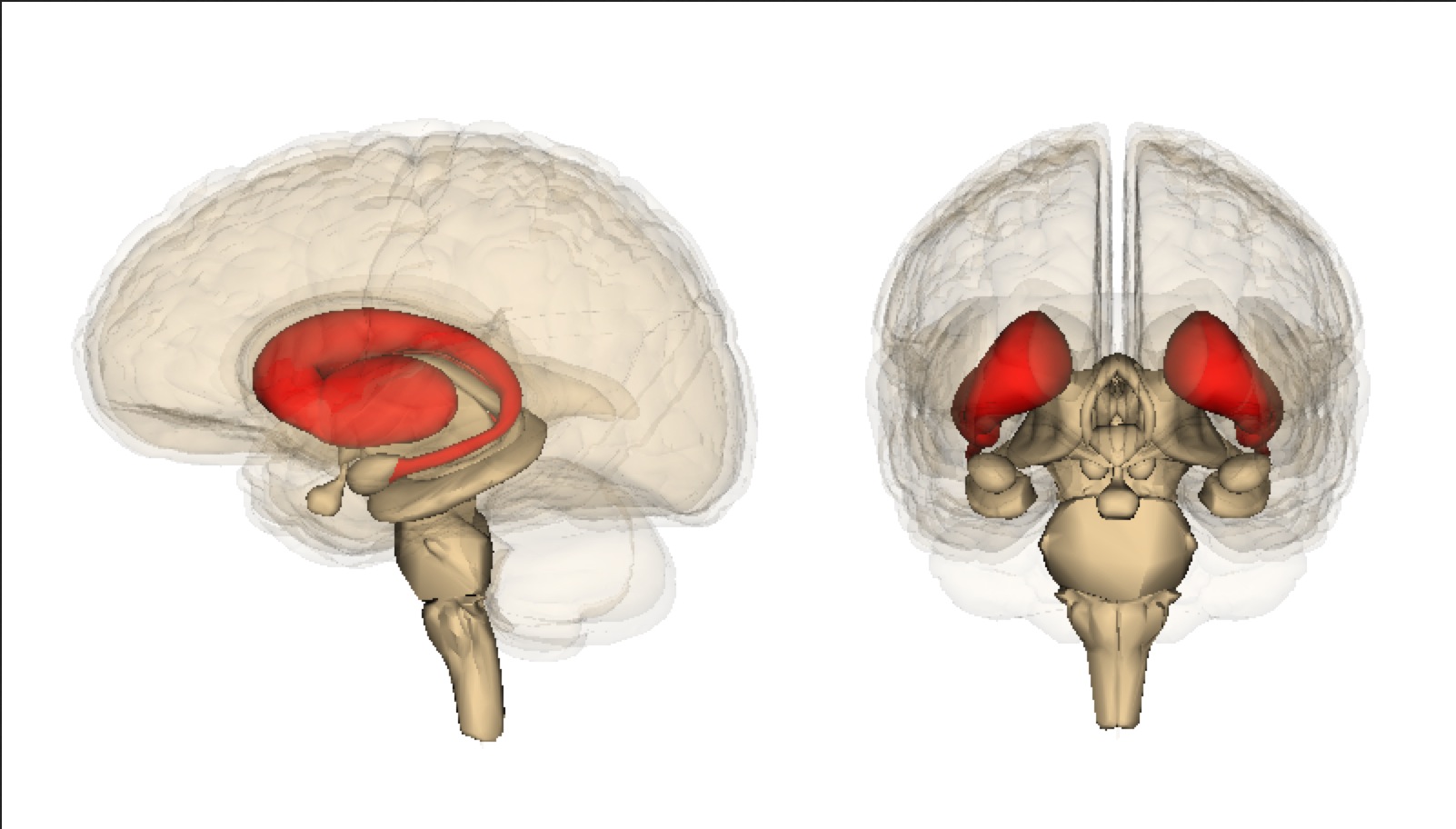
The Corpus striatum, also known as the striatum, is a fascinating part of the human brain that plays a critical role in movement and behavior. Comprised of several structures, including the caudate nucleus and the putamen, the Corpus striatum serves as a key connection point between the cerebral cortex and other parts of the brain. It is involved in the coordination and execution of voluntary movements, as well as in the regulation of emotions and motivation.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Corpus striatum and explore nine intriguing facts about this enigmatic brain structure. From its role in Parkinson’s disease to its influence on addiction and reward processing, the Corpus striatum holds many secrets waiting to be uncovered. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and gain a deeper understanding of the wonders of the Corpus striatum.
Key Takeaways:
- The Corpus striatum, deep in the brain, helps us move smoothly, feel pleasure, learn, and make decisions. It’s linked to disorders like Parkinson’s and depression, so understanding it is crucial for treatments.
- Dopamine is crucial for the Corpus striatum’s functions. Imbalances can lead to movement and cognitive issues. Understanding this brain structure can provide insights into neurological and mental health conditions.
Location and Structure
The Corpus striatum is located deep within the brain, in the forebrain region. It consists of the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus, which work together to regulate motor function, reward system, and cognitive processes.
Control of Movement
One of the primary functions of the Corpus striatum is to control voluntary movement. It receives information from the cerebral cortex and relays it to the motor centers of the brain, allowing smooth and coordinated movement.
Reward and Pleasure
The Corpus striatum is involved in the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine when we experience pleasure or reward. This dopamine release reinforces behaviors and motivates us to repeat actions that lead to positive outcomes.
Role in Learning and Memory
The Corpus striatum plays an essential role in learning and memory processes. It is involved in the acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval of memories, contributing to both declarative and procedural memory formation.
Disorders Associated
Several neurological disorders are linked to dysfunction in the Corpus striatum. Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Tourette syndrome are examples of conditions that affect the proper functioning of this brain structure.
Connection to Mental Health
Studies have shown that abnormalities in the Corpus striatum can contribute to mental health disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, and addiction. Understanding its functions is crucial for improving treatments for these conditions.
Connection with Basal Ganglia
The Corpus striatum is a part of the basal ganglia, a group of interconnected structures responsible for motor control and movement coordination. It works in collaboration with other basal ganglia nuclei to ensure precise control over our actions.
Role in Decision Making
The Corpus striatum is involved in decision making and plays a role in evaluating risks and rewards. It aids in selecting appropriate actions based on the potential outcomes and helps us adapt our behavior accordingly.
Influenced by Dopamine
Dopamine plays a crucial role in modulating the activity of the Corpus striatum. Imbalances in dopamine levels can lead to disorders and impairments in motor control, reward processing, and cognitive functions.
In conclusion, the Corpus striatum is a fascinating brain structure with diverse functions. Understanding its role in controlling movement, cognition, reward, and memory can provide valuable insights into neurological and mental health conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Corpus striatum is a complex and fascinating structure within the human brain. Its involvement in various neural processes such as motor control, reward processing, and decision-making highlight its significance in our daily lives. Understanding the functions and characteristics of the Corpus striatum can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of the brain and potentially contribute to the development of treatments for neurological disorders. From its anatomy to its role in disease pathology, the Corpus striatum remains a subject of ongoing research and exploration in the field of neuroscience.
FAQs
Q: What is the Corpus striatum?
A: The Corpus striatum, also known as the basal ganglia, is a cluster of structures located deep within the brain. It includes the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus.
Q: What are the functions of the Corpus striatum?
A: The Corpus striatum is involved in various functions, including motor control, reward processing, habit formation, and decision-making. It plays a crucial role in coordinating movements and regulating emotions.
Q: What happens if the Corpus striatum is damaged?
A: Damage to the Corpus striatum can lead to movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease. It can also result in changes in behavior, mood, and cognitive abilities.
Q: How is the Corpus striatum connected to other parts of the brain?
A: The Corpus striatum has extensive connections with different areas of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem. These connections facilitate the integration of information from various brain regions.
Q: Can the Corpus striatum be affected by neurological disorders?
A: Yes, the Corpus striatum is vulnerable to various neurological disorders. Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and dystonia are a few examples of conditions that involve dysfunction or degeneration of this brain structure.
Q: Is the Corpus striatum the same as the limbic system?
A: No, the Corpus striatum is not the same as the limbic system. While both are involved in emotion and motivation, the limbic system primarily includes structures such as the amygdala and hippocampus.
Q: Can the Corpus striatum be studied through brain imaging techniques?
A: Yes, advancements in brain imaging techniques such as MRI and fMRI have allowed researchers to study the structure and function of the Corpus striatum non-invasively in living human subjects.
Q: Are there any therapeutic interventions targeted at the Corpus striatum?
A: Yes, treatments such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) have shown promise in managing movement disorders associated with the Corpus striatum. DBS involves implanting electrodes in the brain to modulate abnormal neural activity.
Q: Is there ongoing research about the Corpus striatum?
A: Yes, scientists continue to explore the detailed functioning of the Corpus striatum and its involvement in various neurological conditions. Ongoing research aims to enhance our understanding and develop novel therapeutic interventions.
Unraveling the mysteries of the brain's intricate structures, like the corpus striatum, is just the beginning. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of neuroanatomy and explore how other brain regions impact our lives. Discover the surprising role of the basal ganglia in movement, learning, and behavior. Gain insights into how motor control shapes our actions and interactions with the environment. Finally, uncover the astounding facts about the cerebral cortex, the brain's powerhouse responsible for higher-order thinking and cognition. Embark on a journey through the brain's labyrinth and unlock its secrets today!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
