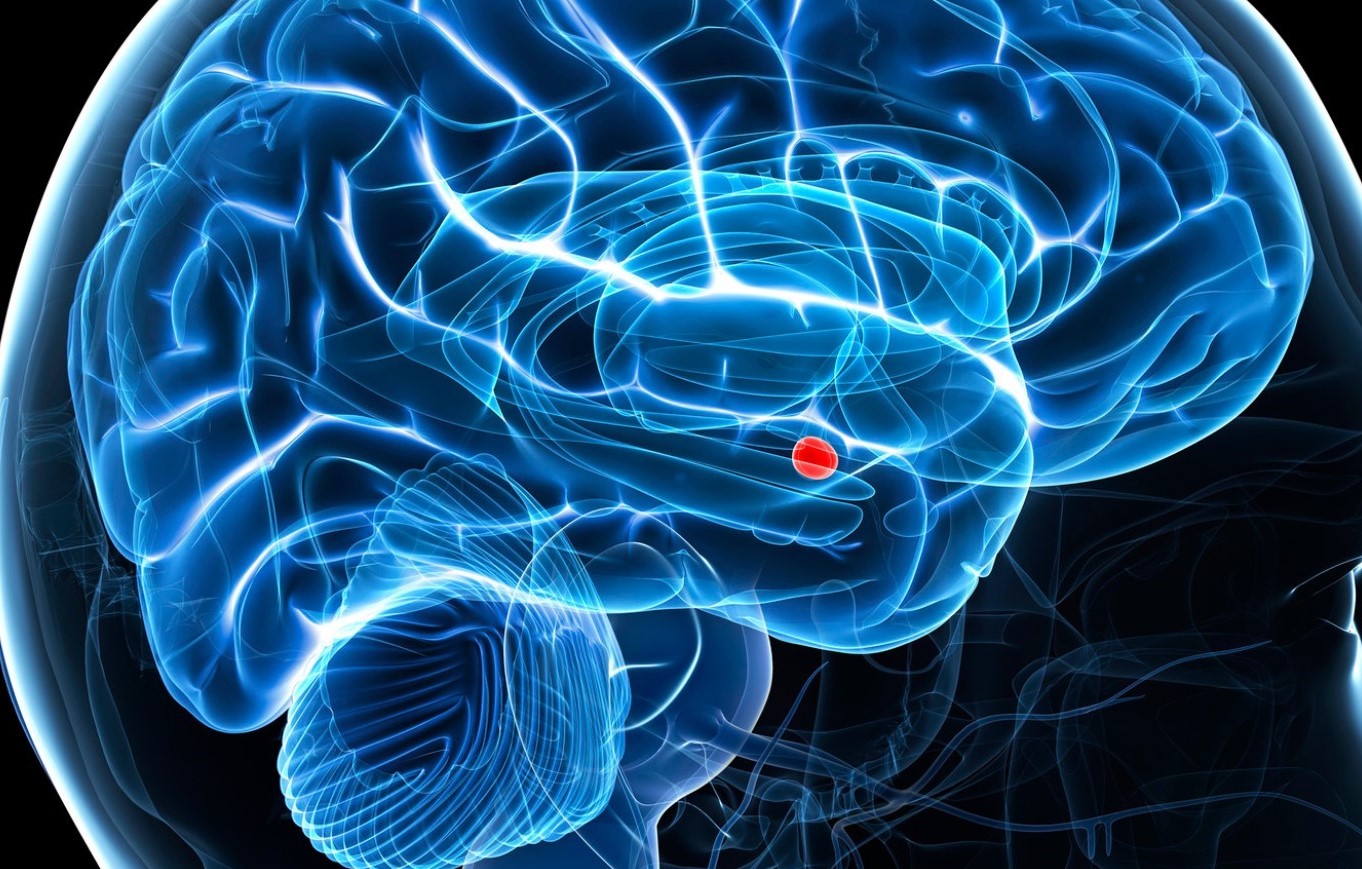
The amygdala, often referred to as the “emotional center” of the brain, is a small, almond-shaped structure nestled deep within the temporal lobes. Despite its small size, this remarkable little organ plays a crucial role in our emotions, behaviors, and even our memories. The amygdala is responsible for processing and responding to various stimuli in our environment, including fear, pleasure, and even social interactions.
In this article, we will explore 16 extraordinary facts about the amygdala that will not only fascinate you but also deepen your understanding of its remarkable functions. From its evolutionary significance to its role in anxiety and decision-making, the amygdala holds secrets that continue to captivate and intrigue scientists and researchers around the world.
Key Takeaways:
- The amygdala, shaped like an almond, controls emotions, memories, and decision-making. It can be affected by stress and psychological disorders, impacting our behavior and responses.
- The amygdala’s role in fear, pleasure, and social behavior makes it a crucial part of our brain. It can even change and adapt over time through learning and experience.
The amygdala is an almond-shaped structure.
The word “amygdala” actually comes from the Greek word for almond, due to its distinctive shape.
It is located deep within the brain.
The amygdala is situated in the medial temporal lobe, underneath the cerebral cortex.
The amygdala is involved in the processing of emotions.
This tiny structure plays a significant role in the experience and recognition of emotions such as fear, anger, and pleasure.
It also plays a crucial role in the formation of memories.
The amygdala helps to consolidate memories with emotional significance, making them more enduring.
The amygdala is connected to other brain regions.
Through neural pathways, the amygdala communicates with various brain areas such as the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and hypothalamus.
It has a role in the “fight or flight” response.
The amygdala activates the body’s stress response system, preparing it for potential threats.
The amygdala plays a role in social and emotional behavior.
It helps in interpreting facial expressions, body language, and vocal tones, contributing to our social interactions.
It can influence decision-making.
The amygdala can impact our choices by assessing the emotional significance of different options.
The amygdala can be affected by psychological disorders.
Conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder can alter the activity of the amygdala.
The amygdala is involved in fear conditioning.
Through associative learning, the amygdala can link a neutral stimulus to a fear response.
It has a role in maternal behavior.
The amygdala is instrumental in promoting nurturing behaviors and attachment between mothers and their offspring.
The amygdala can modulate pain perception.
Research suggests that the amygdala can influence how we experience and interpret pain signals.
It has been linked to the development of phobias.
An overactive amygdala may contribute to the irrational and intense fear associated with specific phobias.
The amygdala can be affected by stress.
Prolonged stress can lead to structural and functional changes in the amygdala, affecting emotional regulation.
It interacts with the reward pathway in the brain.
The amygdala’s connections with the reward system play a role in the experience of pleasure and motivation.
The amygdala can undergo neuroplasticity.
Through learning and experience, the connections and functions of the amygdala can adapt and change over time.
As we delve deeper into the intricate workings of the brain, the amygdala continues to captivate scientists and researchers alike. Its influence on our emotions, behaviors, and memories remains a subject of ongoing exploration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the amygdala is truly an extraordinary part of the human brain. Its crucial role in processing emotions, forming memories, and detecting threats makes it essential for our survival and overall well-being. From its almond-shaped structure to its intricate connections with other brain regions, the amygdala continues to fascinate researchers and scientists.Understanding the amygdala’s functions and how it influences our behaviors and responses can provide valuable insights into various mental and emotional disorders. Further research may uncover new findings about this enigmatic structure, leading to the development of innovative therapies and interventions.Overall, the amygdala reminds us of the incredible complexity and beauty of the human brain. Its intricate workings not only shape our emotions and memories but also contribute to our individual experiences and identities.
FAQs
1. What is the amygdala?
The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure located deep within the brain. It is part of the limbic system, responsible for processing emotions and forming memories.
2. What are the functions of the amygdala?
The amygdala plays a crucial role in emotional processing, fear response, memory consolidation, and social behaviors.
3. How does the amygdala influence our behavior?
The amygdala helps regulate and interpret emotional responses, including fear, aggression, and pleasure. It also plays a role in social behaviors, such as recognizing facial expressions and interpreting social cues.
4. Can damage or dysfunction in the amygdala lead to mental health issues?
Yes, damage or dysfunction in the amygdala can contribute to various mental health disorders, including anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and certain mood disorders.
5. Are there any known factors that can influence the development of the amygdala?
Both genetic and environmental factors can influence the development of the amygdala. Early life experiences, such as trauma or stress, can impact its structure and function.
6. Can the amygdala be targeted for therapeutic purposes?
Yes, researchers explore various therapeutic techniques, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medications, to modulate the amygdala’s hyperactivity or dysfunction in individuals with certain mental health conditions.
7. Is the amygdala unique to humans?
No, the amygdala is not unique to humans. It is present in other mammalian species and plays similar roles in emotional processing and behavior regulation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
