The anal sphincter is a fascinating and enigmatic part of the human anatomy. This small, circular muscle at the end of the digestive tract serves a vital role in controlling the passage of stool and maintaining continence. Despite its relatively small size, the anal sphincter is a powerful muscle with a complex structure and function.
In this article, we will explore 14 intriguing facts about the anal sphincter. From its anatomical features to its role in digestion and the challenges it can face, we will delve into the depths of this fascinating part of the body. So, join us on this journey as we unravel the mysteries and shed light on the lesser-known aspects of the anal sphincter.
Key Takeaways:
- The anal sphincter is like a gatekeeper for poop, helping us hold it in and let it out. It’s made of special muscles and nerves that need care to stay healthy and strong.
- Just like doing exercises to build strong muscles, the anal sphincter can also be trained and strengthened. Eating fiber and staying hydrated can help keep it in good shape.
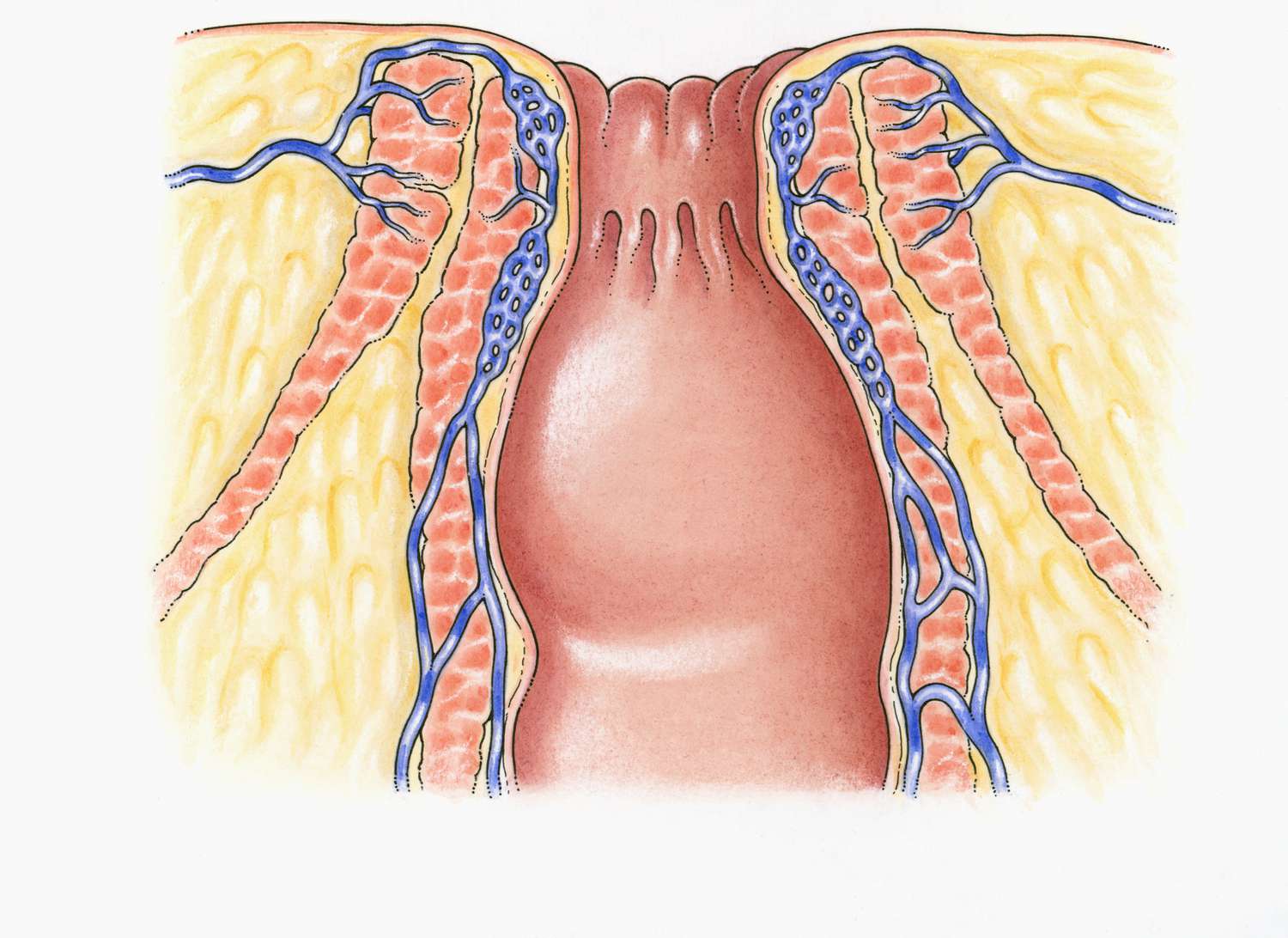
The anal sphincter has two main components.
The anal sphincter is made up of an internal and external component. The internal sphincter is involuntary and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, while the external sphincter is voluntary and can be consciously controlled.
It plays a crucial role in maintaining continence.
The anal sphincter plays a vital role in controlling the release of feces from the rectum. It contracts to prevent involuntary leakage and relaxes during bowel movements.
The anal sphincter is comprised of specialized muscles.
The muscles that make up the anal sphincter are unique in structure and function. They are designed to provide both strength and flexibility to facilitate proper bowel control.
It is essential for sexual function.
The anal sphincter also plays a role in sexual function, particularly during anal intercourse. It contributes to pleasurable sensations and helps with the expulsion of semen in males.
The anal sphincter receives nerve supply from different sources.
The nerves supplying the anal sphincter come from various sources, including the pudendal nerve, pelvic nerves, and sympathetic nerves. This intricate network ensures proper coordination and control of the sphincter.
It can be affected by certain medical conditions.
Medical conditions such as anal fissures, hemorrhoids, and inflammatory bowel disease can affect the function of the anal sphincter, leading to discomfort and dysfunction.
Childbirth can temporarily weaken the anal sphincter.
The strain and pressure exerted on the anal sphincter during childbirth can cause temporary weakness. This can result in postpartum anal incontinence, which usually resolves with time and pelvic floor exercises.
The anal sphincter can be trained and strengthened.
Like any other muscle, the anal sphincter can be strengthened through exercises such as Kegels or pelvic floor exercises. This can improve muscle tone and enhance control over bowel movements.
There are two types of anal sphincter tears.
Anal sphincter tears can occur during childbirth or as a result of trauma. There are two types: a first-degree tear involves the superficial layer of the sphincter, while a third-degree tear extends into the muscle.
The anal sphincter can be repaired surgically.
If severe tears or injuries occur, surgical repair of the anal sphincter may be necessary. This procedure aims to restore proper muscle function and improve continence.
Relaxation techniques can help alleviate anal sphincter spasms.
Some individuals may experience anal sphincter spasms or anal fissures, causing pain and discomfort. Relaxation techniques, such as warm baths and deep breathing exercises, can help relieve these symptoms.
The anal sphincter can be affected by nerve damage.
Nerve damage due to conditions like diabetes or trauma can disrupt the function of the anal sphincter, leading to fecal incontinence. In such cases, targeted treatments may be necessary.
Proper hydration and a fiber-rich diet aid in anal sphincter health.
Ensuring adequate hydration and consuming a diet rich in fiber can promote regular bowel movements and maintain the health of the anal sphincter.
The anal sphincter undergoes aging-related changes.
As we age, the anal sphincter may experience reduced muscle tone and elasticity, making it more susceptible to issues such as fecal incontinence. Regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate these changes.
In conclusion, the anal sphincter is a fascinating and vital component of the human body. Understanding its functions and taking care of its health is crucial for maintaining bowel control and overall well-being.
Conclusion
The anal sphincter is a fascinating and enigmatic part of the human anatomy. It plays a crucial role in maintaining continence and allowing for the controlled release of feces. Understanding its structure and function can help us appreciate the complexity of our bodies and the intricate mechanisms that keep us healthy.
From its powerful muscles to its unique nerve supply, the anal sphincter is a marvel of biological engineering. Its ability to relax and contract allows us to control bowel movements, while its sensitive nerve endings help us detect the presence of stool.
While the anal sphincter may not be a topic of everyday conversation, it deserves our attention and appreciation. So take a moment to marvel at the amazing capabilities of this small but mighty muscle.
FAQs
1. What is the anal sphincter?
The anal sphincter is a group of muscles in the anus that controls the release of feces.
2. How many types of anal sphincter are there?
There are two types of anal sphincter: the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter.
3. What is the function of the anal sphincter?
The anal sphincter’s main function is to maintain continence and control the passage of stool.
4. Can the anal sphincter be weakened?
Yes, the anal sphincter can be weakened due to various factors, such as childbirth, aging, or certain medical conditions.
5. How can I strengthen my anal sphincter?
Exercises, such as Kegels and pelvic floor exercises, can help strengthen the anal sphincter.
6. Are there any disorders associated with the anal sphincter?
Yes, some disorders include anal fissures, anal incontinence, and anal sphincter dysfunction.
7. Does the anal sphincter have any nerve supply?
Yes, the anal sphincter is innervated by the pudendal nerve.
8. Can the anal sphincter be damaged?
Yes, trauma, surgery, or certain medical conditions can cause damage to the anal sphincter.
9. Can the anal sphincter be voluntarily controlled?
Yes, with practice and awareness, most people can gain some level of voluntary control over their anal sphincter.
10. Is it common for the anal sphincter to relax involuntarily?
Yes, the anal sphincter can relax involuntarily in response to certain stimuli or conditions, such as the urge to defecate.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
