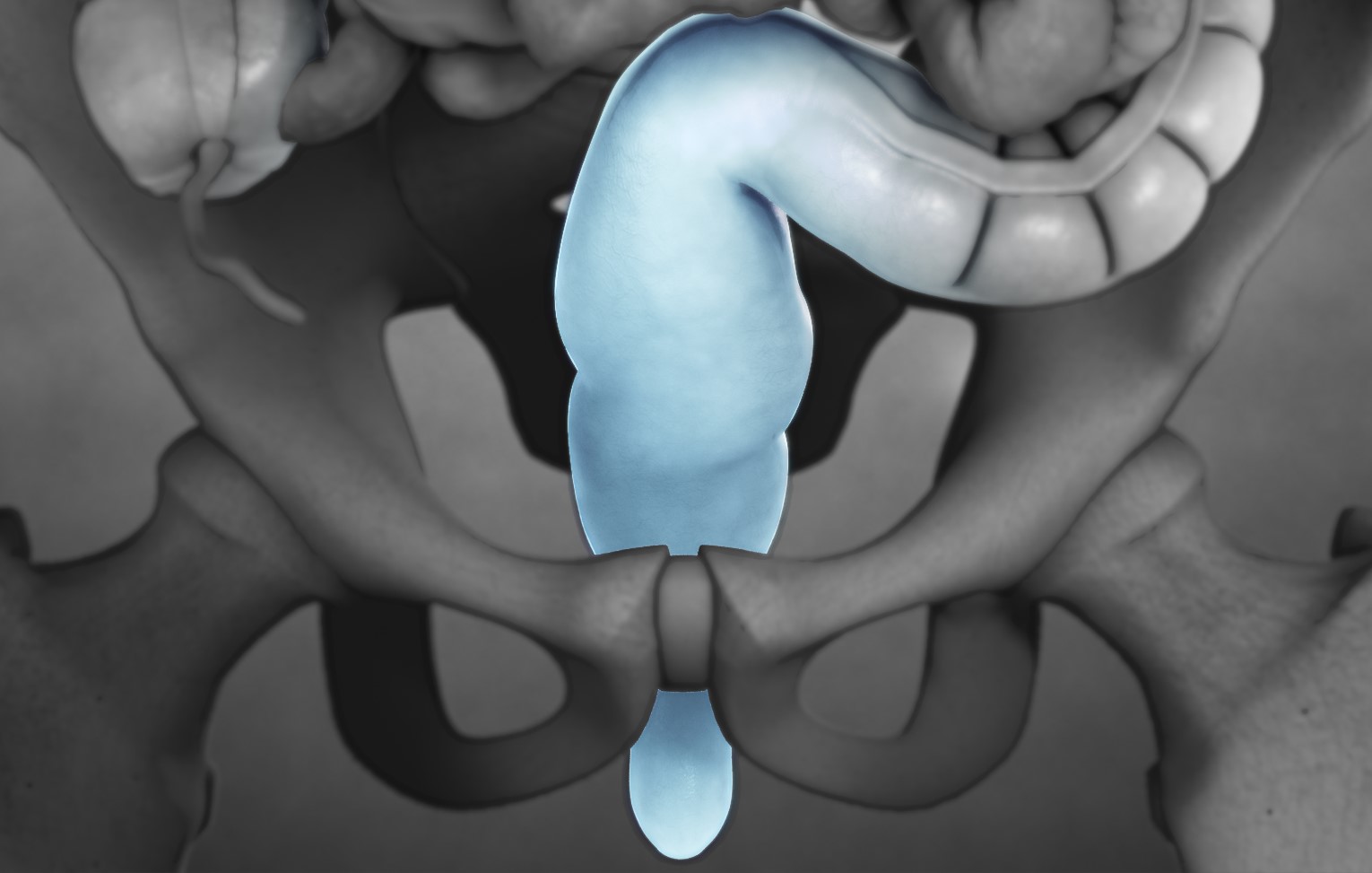
The rectal sphincter is a small but vital muscle located at the end of the digestive system. While it may not be a topic of casual conversation, understanding the rectal sphincter and its functions is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system. This small muscle plays a significant role in controlling the passage of stool and maintaining continence.
In this article, we will dive deep into the world of the rectal sphincter and explore 16 fascinating facts about this often overlooked part of the human anatomy. From its anatomy and functions to common disorders and tips for maintaining its health, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview that will leave you amazed by the complex workings of your body.
Key Takeaways:
- The rectal sphincter is a powerful muscle that controls bowel movements and continence. It can be strengthened through exercise and trained to improve control, but can be affected by aging and certain medical conditions.
- The rectal sphincter plays a crucial role in our daily lives, from regulating bowel movements to contributing to sexual function. It’s a remarkable feat of evolution that has helped humans thrive throughout history.
The rectal sphincter is composed of two main muscles.
The internal sphincter is an involuntary muscle that is always contracted to prevent any leakage. The external sphincter is a voluntary muscle that allows us to control the timing of bowel movements.
It works in coordination with the nervous system.
The rectal sphincter muscle receives signals from the brain via the autonomic and somatic nervous systems, allowing for precise control over bowel movements.
The rectal sphincter is highly elastic.
It can stretch and relax to accommodate the passage of stool without causing any damage or discomfort.
Damage to the rectal sphincter can result in fecal incontinence.
Conditions such as childbirth trauma, injury, or surgery can weaken the sphincter muscles, leading to the inability to control bowel movements.
Certain medical conditions can affect the rectal sphincter.
Disorders such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, inflammatory bowel disease, and rectal prolapse can impact the functioning of the sphincter.
Regular exercise can help strengthen the rectal sphincter.
Engaging in exercises that target the pelvic floor muscles, such as Kegels, can enhance the strength and tone of the sphincter.
The rectal sphincter can be voluntarily relaxed.
This relaxation is necessary during defecation, and it can be achieved by consciously relaxing the external sphincter muscle.
An overactive rectal sphincter can lead to constipation.
If the sphincter muscles are constantly contracted, it can hinder the passage of stool and result in difficulty in bowel movements.
The rectal sphincter has sensory receptors.
These receptors can detect the presence of stool in the rectum and send signals to the brain, indicating the need for a bowel movement.
The rectal sphincter can be affected by aging.
As we age, the muscles and nerves that control the sphincter may weaken, making it more challenging to maintain continence.
The rectal sphincter can be trained.
Through biofeedback techniques and pelvic floor exercises, individuals experiencing incontinence can improve their control over the sphincter muscle.
The rectal sphincter has a resting pressure.
Even when not actively engaged, the sphincter maintains a baseline level of tension to prevent accidental leakage.
Spasms of the rectal sphincter can cause pain.
In some cases, the sphincter muscles can contract excessively, leading to discomfort, pain, and even difficulty in passing gas.
The rectal sphincter is essential for sexual function.
During sexual activity, the sphincter muscles help regulate the flow of blood to the pelvic region, contributing to sexual pleasure and orgasm.
The rectal sphincter can be affected by certain medications.
Medications used to treat conditions like diarrhea or constipation may impact the functioning of the sphincter, causing temporary changes in bowel habits.
The rectal sphincter is a remarkable feat of evolutionary adaptation.
Throughout human history, the development of the rectal sphincter has allowed for efficient waste elimination, contributing to our survival and well-being.
Conclusion
The rectal sphincter is a remarkable muscle that plays a crucial role in maintaining continence and regulating bowel movements. Understanding its function and anatomy is important for maintaining overall health and well-being. From its intricate network of nerves to its ability to relax and contract, the rectal sphincter is a complex structure that deserves our attention and appreciation.
By learning about the fascinating facts about the rectal sphincter, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexity of the human body. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions about our health and seek appropriate medical care when needed.
So next time you think about the rectal sphincter, remember its importance and the incredible feats it performs. Take care of this vital muscle and cherish the intricate workings of your body.
FAQs
1. What is the rectal sphincter?
The rectal sphincter is a muscular ring that surrounds the rectum and controls the flow of feces from the body.
2. How many types of rectal sphincter are there?
There are two types of rectal sphincter – the internal sphincter, which is involuntary, and the external sphincter, which is under voluntary control.
3. Can the rectal sphincter be strengthened?
Yes, through targeted exercises such as Kegels, the pelvic floor muscles, including the rectal sphincter, can be strengthened.
4. Can problems with the rectal sphincter cause incontinence?
Yes, damage or dysfunction of the rectal sphincter can result in fecal incontinence, making it difficult to control bowel movements.
5. Are there any medical conditions associated with the rectal sphincter?
Medical conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and rectal prolapse can affect the rectal sphincter and disrupt its normal function.
6. Can the rectal sphincter be affected by age?
Yes, the rectal sphincter can weaken with age, leading to an increased risk of bowel control issues.
7. Can stress affect the function of the rectal sphincter?
Yes, stress can contribute to the development or worsening of conditions affecting the rectal sphincter, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
