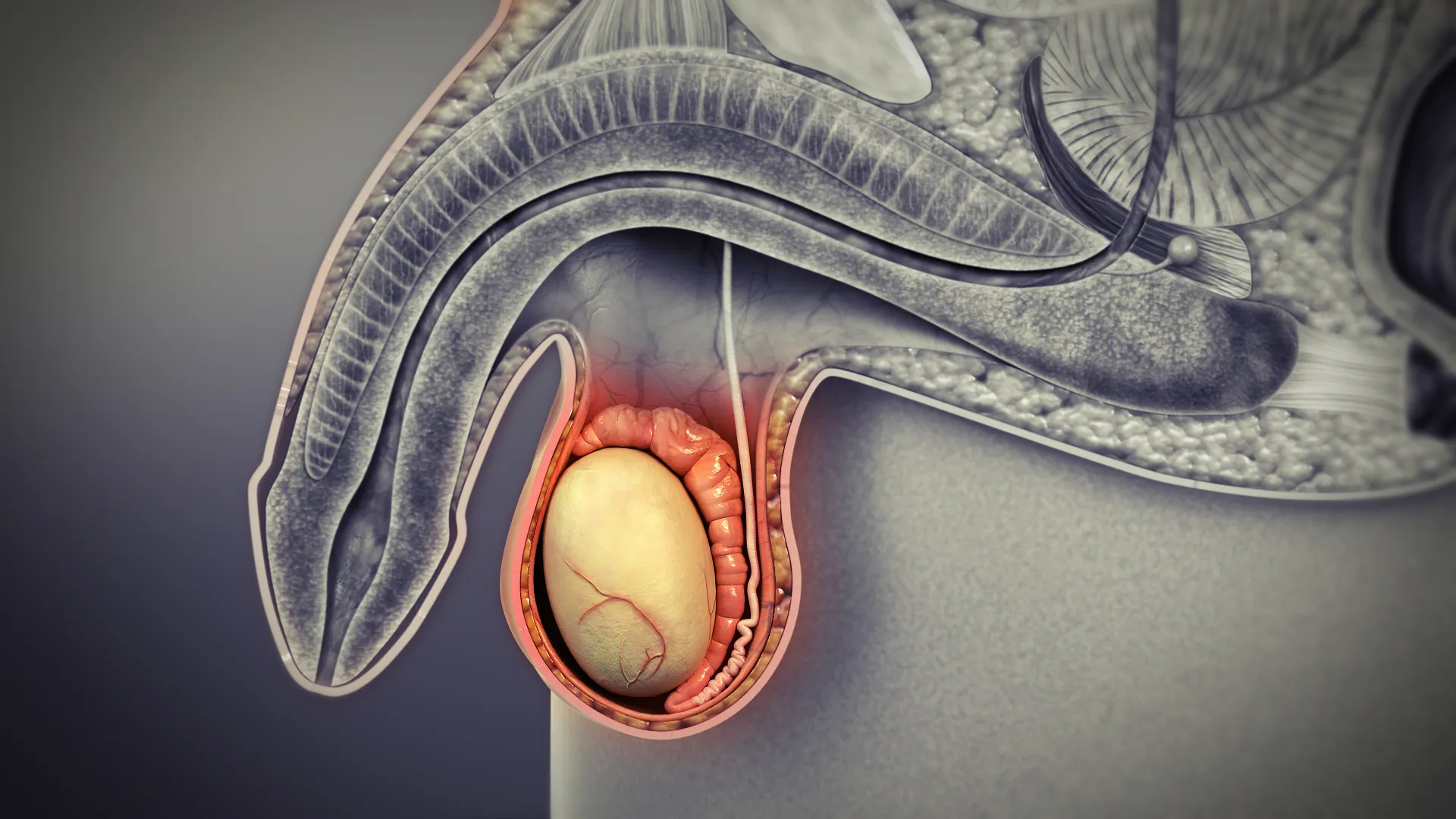
The testes, also known as the male gonads, are a fascinating part of the male reproductive system. These small egg-shaped organs are located in the scrotum, which hangs outside the body to maintain a cooler temperature necessary for sperm production. While the primary function of the testes is the production of sperm, they also play a vital role in hormone production, specifically testosterone.
In this article, we will delve into 16 intriguing facts about testes that you may not be aware of. From their development and structure to their role in fertility and overall health, we will explore the remarkable characteristics of this vital component of the male body. Whether you are curious about the intricacies of male reproductive anatomy or simply want to expand your knowledge on this topic, let’s dive into these fascinating facts about testes.
Key Takeaways:
- The testes are responsible for producing sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone, playing a crucial role in male reproduction and sexual development.
- Testicular health is essential for male fertility, and factors such as temperature, hormones, and medical conditions can impact the size and function of the testes.
The testes are the primary male reproductive organs.
The testes, also known as testicles, are two small, oval-shaped organs located in the scrotum. Their main function is to produce and store sperm, as well as secrete testosterone, the primary male sex hormone.
The average size of the testes is about 2-3 inches in length.
The testes vary in size among individuals, but the average length is typically around 2-3 inches. However, it’s important to note that size does not necessarily correlate with fertility or sexual function.
The testes are responsible for sperm production.
Inside the testes, there are numerous tiny structures called seminiferous tubules. These tubules are responsible for producing sperm through a process called spermatogenesis. Millions of sperm cells are produced in the testes every day.
Testes have a temperature regulation mechanism.
The testes have a temperature-sensitive mechanism that helps regulate their temperature. They are located outside of the body within the scrotum, which allows them to remain slightly cooler than body temperature. This lower temperature is essential for proper sperm production and function.
Testes can shrivel up in cold temperatures.
In cold environments, the muscles in the scrotum contract, causing the testes to move closer to the body for warmth. This involuntary response, known as the cremasteric reflex, helps protect the testes from cold temperatures but can also cause them to shrink temporarily.
The average lifespan of sperm is about 2-3 days.
Once sperm is ejaculated, it can survive inside the female reproductive system for an average of 2-3 days. However, under ideal conditions, such as in fertile cervical mucus, sperm can survive for up to 5 days, increasing the chances of fertilization.
Testicular size can vary throughout the day.
The size of the testes can vary slightly throughout the day due to factors such as temperature, physical activity, and arousal level. They are typically larger in the morning and may shrink slightly in the evening.
The testes produce approximately 300 million sperm per day.
The testes are highly efficient in sperm production. On average, they produce around 300 million sperm cells per day, contributing to the vast number of sperm available for fertilization.
Testosterone is vital for male sexual development and function.
Testosterone, produced by the testes, is the primary male sex hormone. It plays a crucial role in male sexual development, including the growth of the penis and testes during puberty, as well as the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as facial hair and deepening of the voice.
Testicular size can be affected by various factors.
Testicular size can be influenced by factors such as age, genetics, hormonal imbalances, and certain medical conditions. It’s important to note that variations in testicular size are generally normal and not necessarily indicative of any underlying health issues.
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in young men.
Testicular cancer primarily affects young men between the ages of 15 and Fortunately, with early detection and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for testicular cancer is generally positive.
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency.
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord, which provides blood supply to the testes, becomes twisted, cutting off the blood flow. It is a painful condition that requires immediate medical intervention to prevent testicular damage or loss.
The testes produce inhibin, which regulates testosterone levels.
In addition to testosterone, the testes also produce a hormone called inhibin. Inhibin helps regulate the production of testosterone, ensuring a balance in hormone levels for optimal reproductive function.
Testes can be affected by sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
STIs, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, can cause inflammation and damage to the testes if left untreated. It’s essential to practice safe sex and seek medical attention if any symptoms of STIs arise.
Testosterone levels decline with age.
As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline. This gradual reduction in testosterone can lead to various symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, and mood changes.
Testes play a crucial role in fertility.
The testes play a vital role in male fertility by producing sperm cells that are essential for fertilization. Any abnormalities or issues with the testes can impact male fertility and reproductive health.
Conclusion
The testes, also known as the male gonads, are fascinating organs that play a crucial role in reproduction and hormone production. Hopefully, these 16 intriguing facts have shed some light on the complexity and importance of the testes.
From their dual function of producing sperm and testosterone to their connection with male fertility and sexual development, the testes are truly remarkable. Understanding how they work and the factors that can affect their health is essential for overall well-being.
Whether you are curious about the size and shape of the testes or interested in learning about common testes-related health issues, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of male anatomy. Remember to seek professional medical advice if you have any concerns or questions about your testes.
FAQs
Q: What are the testes?
A: The testes, commonly referred to as testicles, are the male reproductive organs responsible for producing sperm and testosterone.
Q: Where are the testes located?
A: The testes are located in the scrotum, a sac-like structure located outside the body, below the penis.
Q: How many testes does a male have?
A: Typically, males have two testes, one on each side of the scrotum.
Q: What is the function of the testes?
A: The primary function of the testes is to produce sperm, the male reproductive cells, and testosterone, the primary male sex hormone.
Q: Are testes involved in hormone production?
A: Yes, the testes are responsible for producing testosterone, which plays a crucial role in male sexual development, muscle mass maintenance, and bone strength.
Q: Can the size of the testes vary?
A: Yes, the size of the testes can vary from person to person. However, significant changes in size should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Q: What is testicular torsion?
A: Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle twists, cutting off the blood supply to the organ. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Q: Can testes be affected by injuries?
A: Yes, the testes can be susceptible to injuries, including trauma or direct blows. If you experience severe pain or swelling, seek medical attention.
Q: Can testes be affected by medical conditions?
A: Yes, certain medical conditions, such as testicular cancer, infection, or hormonal imbalances, can impact the health and function of the testes.
Q: Can lifestyle choices affect testicular health?
A: Yes, certain lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug abuse, can negatively impact testicular health and fertility.
Q: Are there any preventive measures to maintain testes health?
A: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing safe sex, performing regular testicular self-exams, and seeking medical attention for any concerns can help maintain testes health.
Q: Can testicular cancer be detected early?
A: Yes, testicular cancer can often be detected early through self-examination or regular check-ups with a healthcare professional.
Q: Are testes involved in fertility?
A: Yes, the testes are crucial for male fertility as they produce sperm, which is necessary for fertilization.
Q: Can the testes shrink with age?
A: Yes, it is common for the testes to shrink slightly with age, and this is typically a natural part of the aging process.
Q: Can hormonal imbalances affect the testes?
A: Yes, hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone levels, can affect testicular function and overall health.
Q: Can testes be affected by infections?
A: Yes, infections, such as epididymitis or orchitis, can affect the testes and may cause pain, swelling, or discomfort.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
