Seminiferous tubules are an essential part of the male reproductive system, playing a crucial role in the production of sperm. These tiny, coiled structures are found within the testes and are responsible for the process of spermatogenesis. Beyond their functional significance, seminiferous tubules hold some fascinating secrets waiting to be discovered. In this article, we will explore 20 captivating facts about seminiferous tubules that will give you a deeper understanding of this intricate part of the human body. From their intricate structure to the process of sperm production, get ready to dive into the world of seminiferous tubules and unravel their secrets!
Key Takeaways:
- Seminiferous tubules are tiny structures in the testes that produce millions of sperm daily, playing a vital role in male fertility and reproduction.
- These intricate tubules undergo constant remodeling and are sensitive to temperature changes, making them crucial for the production of healthy, functional sperm.
Seminiferous tubules are crucial for sperm production.
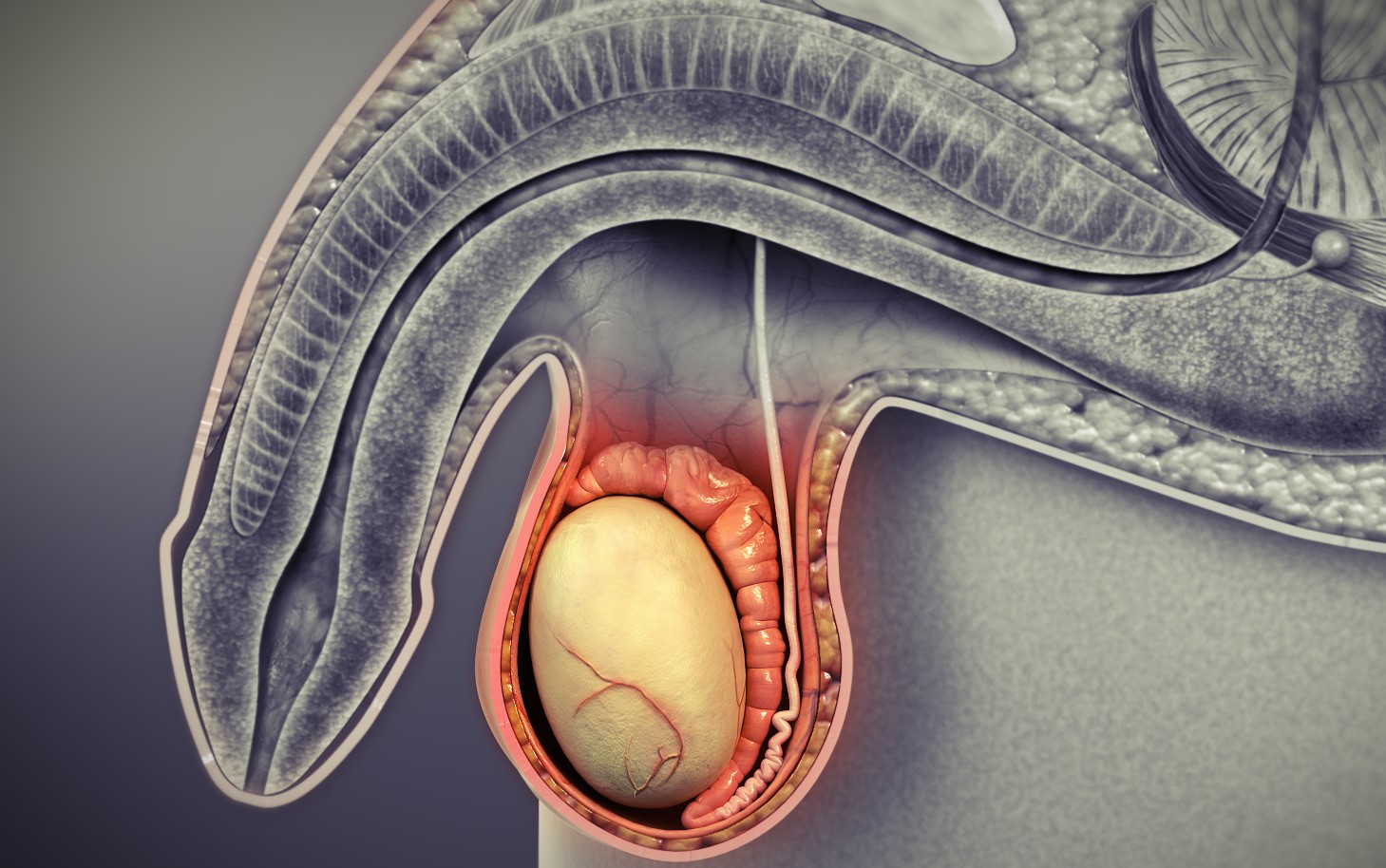
The seminiferous tubules are the key structures within the male reproductive system responsible for the production of sperm.
They are located within the testes.
The seminiferous tubules are found within the testes, the male reproductive organs situated in the scrotum.
Seminiferous tubules have a complex and intricate structure.
These tubules are coiled structures resembling tiny tubes, with an intricate network of cells and structures contained within them.
Sertoli cells provide support and nourishment.
Sertoli cells, which are specialized cells lining the seminiferous tubules, provide support and nourishment to the developing sperm cells.
Germ cells undergo spermatogenesis within the seminiferous tubules.
The germ cells within the seminiferous tubules undergo a process called spermatogenesis, which involves the transformation of immature sperm cells into mature, functional sperm.
The seminiferous tubules produce millions of sperm cells daily.
These tubules have a remarkable ability to produce a large number of sperm cells every day, ensuring the continuous supply of sperm for reproduction.
Seminiferous tubules have a high turnover rate.
The cells lining the seminiferous tubules have a rapid turnover rate, constantly renewing themselves to support the continuous production of sperm.
Leydig cells produce testosterone within the testes.
Leydig cells, located in the spaces between the seminiferous tubules, are responsible for the production of testosterone, the male sex hormone.
Seminiferous tubules undergo different stages of development.
During puberty, the seminiferous tubules undergo further development and maturation, leading to increased sperm production and fertility.
The health of seminiferous tubules is essential for male fertility.
Any disruption or damage to the seminiferous tubules can result in decreased sperm production and fertility issues in males.
Sperm cells are transported out of the seminiferous tubules.
Once sperm cells are fully developed within the seminiferous tubules, they are transported out of the tubules through a series of ducts for further maturation and storage.
Seminiferous tubules play a crucial role in sperm quality control.
The seminiferous tubules have mechanisms in place to ensure the quality and viability of sperm cells, discarding defective or abnormal sperm through a process called spermiation.
Genetic mutations can affect seminiferous tubule function.
In some cases, genetic mutations or abnormalities can disrupt the normal functioning of the seminiferous tubules, leading to infertility or reproductive disorders.
Seminiferous tubules are influenced by hormonal regulation.
The production and development of sperm within the seminiferous tubules are regulated by various hormones, including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
Seminiferous tubules undergo constant remodeling.
The structure and composition of the seminiferous tubules undergo continuous remodeling to accommodate the changing reproductive needs and hormonal regulation.
Seminiferous tubules are highly vascularized.
The seminiferous tubules have an extensive network of blood vessels, ensuring the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to support the processes of spermatogenesis.
Seminiferous tubules are sensitive to temperature changes.
Any significant changes in testicular temperature can affect the function and health of the seminiferous tubules, potentially leading to decreased sperm production.
Seminiferous tubules exhibit cellular interactions.
The cells within the seminiferous tubules interact with each other through complex signaling pathways to ensure the proper coordination of sperm production and development.
Seminiferous tubules can be affected by certain medical conditions.
Conditions such as testicular infections, hormonal imbalances, and testicular tumors can impact the function and health of the seminiferous tubules.
The integrity of seminiferous tubules can be assessed through medical tests.
Doctors can assess the health and function of the seminiferous tubules through tests such as semen analysis, hormone level measurements, and imaging studies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the seminiferous tubules play a crucial role in the male reproductive system. These tiny, coiled structures are responsible for the production of sperm through the process of spermatogenesis. They are found within the testes and contain various types of cells that support and nourish developing sperm.
Throughout this article, we explored 20 captivating facts about seminiferous tubules. From their structure and function to the hormonal regulation and disorders associated with them, seminiferous tubules are a fascinating topic of study.
Understanding the importance of seminiferous tubules can help us appreciate the complexity and intricacy of the male reproductive system. By delving into the workings of these tubules, we gain insight into the incredible process of sperm production and the role it plays in human reproduction.
Overall, the study of seminiferous tubules is a testament to the wonders of the human body and the fascinating world of anatomy and physiology.
FAQs
1. What are seminiferous tubules?
Seminiferous tubules are small, coiled structures located within the testes, responsible for the production of sperm.
2. How does spermatogenesis occur in seminiferous tubules?
Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules. It involves the replication and maturation of germ cells into sperm cells.
3. What cells are found in the seminiferous tubules?
The seminiferous tubules contain various types of cells, including Sertoli cells, Leydig cells, and spermatogenic cells, which all contribute to the process of sperm production.
4. Can seminiferous tubules be damaged?
Yes, various factors such as infections, trauma, hormonal imbalances, or genetic disorders can cause damage to the seminiferous tubules, resulting in impaired sperm production.
5. Are seminiferous tubules involved in fertility?
Absolutely! The healthy functioning of seminiferous tubules is crucial for male fertility as they are responsible for the production of mature and viable sperm.
6. Can disorders of seminiferous tubules be treated?
In some cases, yes. Treatment options depend on the specific disorder but can include hormone replacement therapy, surgical interventions, or assisted reproductive technologies.
Seminiferous tubules are truly remarkable structures that play a vital role in male reproductive health. Their intricate design and precise function enable the production of millions of sperm cells every day. From the supportive Sertoli cells to the hormone-producing Leydig cells, each component of the seminiferous tubules works in harmony to ensure optimal sperm development. Exploring the captivating world of seminiferous tubules has undoubtedly piqued your curiosity about other fascinating aspects of male reproductive biology. Why not continue your journey of discovery by learning more about the incredible Sertoli cells and their crucial role in supporting spermatogenesis?
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.