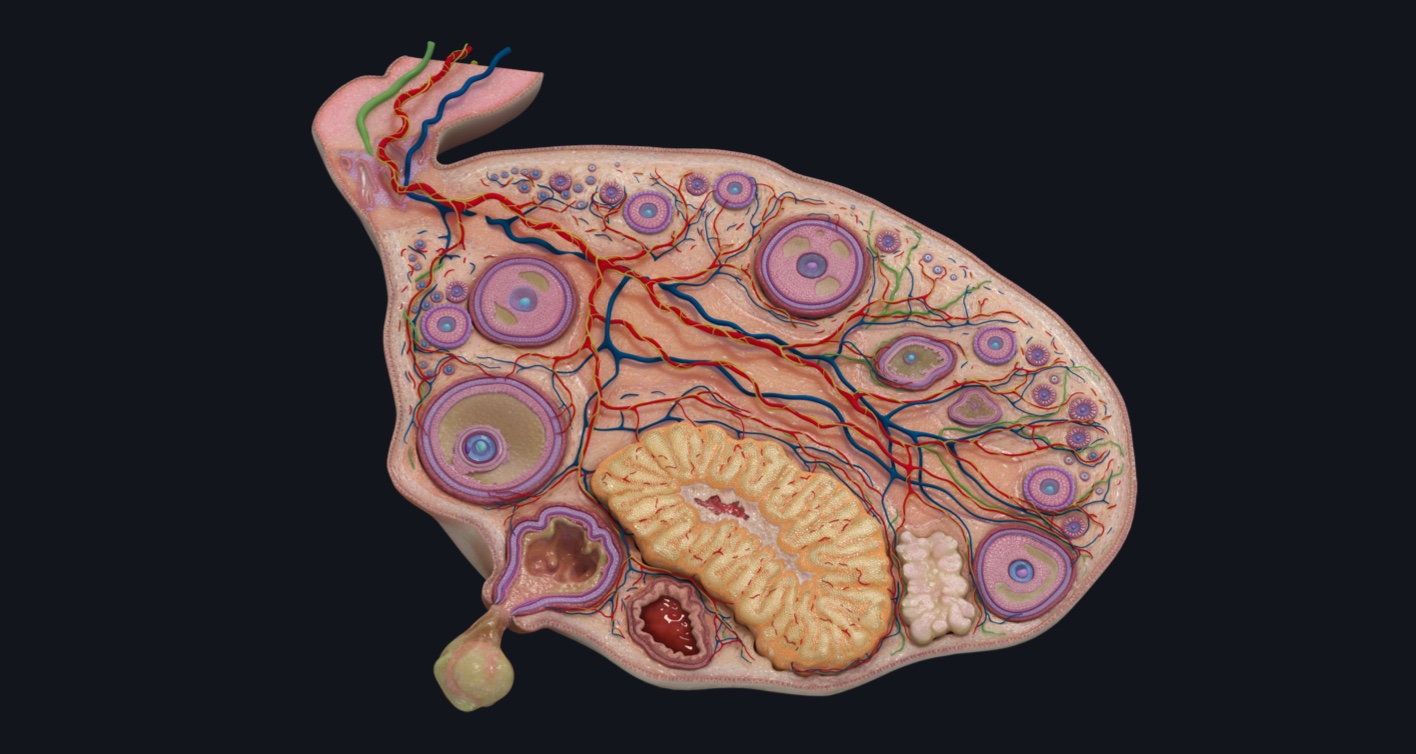
When it comes to the fascinating world of human anatomy, the ovarian follicles play a crucial role in the reproductive system of women. These small, but mighty structures are responsible for the maturation and release of eggs during the menstrual cycle. However, there is much more to ovarian follicles than meets the eye.
In this article, we will delve into 14 astounding facts about ovarian follicles that will leave you in awe of the intricacies of the female reproductive system. From their formation to their role in fertility, these facts will not only increase your knowledge but also deepen your appreciation for the wonders of the human body.
So, get ready to unravel the mysteries surrounding ovarian follicles as we dive into this informative and engaging journey.
Key Takeaways:
- Ovarian follicles are small sacs in the ovaries that nurture eggs and play a crucial role in female reproductive health. They are influenced by hormones and can be visualized using ultrasound technology.
- The number and quality of ovarian follicles impact a woman’s fertility, and their development can be affected by age and medical conditions. Ongoing research offers hope for fertility preservation and improved reproductive outcomes.
Ovarian follicles are small, fluid-filled sacs found within the ovaries.
Ovarian follicles are responsible for housing and nurturing immature eggs, known as ova or oocytes. These follicles are crucial for the reproductive process in females.
The number of ovarian follicles is determined at birth.
Women are born with a fixed number of ovarian follicles, which gradually decrease over time. This reserve of follicles is often referred to as the ovarian reserve.
Ovarian follicles undergo a maturation process.
Throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle, multiple ovarian follicles begin to mature. However, typically only one follicle reaches full maturity and releases an egg during ovulation.
Ovarian follicles produce hormones.
The granulosa cells within the ovarian follicles produce estrogen, a vital hormone for regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting reproductive health.
Ovarian follicles are influenced by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
FSH, produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates the growth and development of ovarian follicles. It plays a crucial role in follicle recruitment and selection.
Ovarian follicles can be visualized using ultrasound imaging.
Ultrasound technology allows medical professionals to visualize the ovaries and the presence of ovarian follicles. This imaging is commonly used to monitor fertility treatments and assess ovarian health.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can affect ovarian follicles.
PCOS, a common hormonal disorder in women, can disrupt the normal development and release of ovarian follicles. This condition is characterized by the formation of multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
Ovarian follicles play a crucial role in fertility.
The quality and quantity of ovarian follicles directly impact a woman’s fertility. A healthy ovarian reserve and proper follicle development are essential for successful conception.
Ovarian follicles can be stimulated for assisted reproductive techniques.
In some cases, medications can be administered to stimulate the growth and development of multiple ovarian follicles. This is often done in assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Ovarian follicles have a lifespan.
Not all ovarian follicles reach full maturity and release an egg. Many follicles undergo atresia, a process of natural degeneration and resorption within the ovary.
Ovarian follicles can produce progesterone.
In addition to estrogen, mature ovarian follicles also produce progesterone, another essential hormone for maintaining a healthy reproductive system.
Ovarian follicles are regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH).
Luteinizing hormone plays a vital role in the final stage of follicle development, triggering ovulation and the release of the mature egg from the ovary.
Ovarian follicle development can be affected by age and certain medical conditions.
As a woman ages, the quality and quantity of ovarian follicles decline. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as endometriosis or hormonal imbalances, can disrupt normal follicle development.
Ovarian follicles are a subject of ongoing research in fertility preservation.
Researchers are exploring various techniques to preserve and protect ovarian follicles, offering hope for fertility preservation in women facing medical treatments or premature ovarian failure.
Conclusion
Ovarian follicles are remarkable structures within the ovaries that play a crucial role in female reproductive health. These tiny sacs contain immature eggs and are responsible for their development and release. Understanding the fascinating facts about ovarian follicles can deepen our appreciation for the intricate workings of the female reproductive system.
From the astonishing number of follicles present at birth to the remarkable journey each egg takes, these facts shed light on the incredible complexity of human anatomy. Ovarian follicles are at the core of female fertility and understanding their function can provide valuable insights into reproductive health and potential issues.
Exploring the astonishing facts about ovarian follicles not only increases our knowledge of the human body but also highlights the incredible capabilities of the female reproductive system.
FAQs
Q: What are ovarian follicles?
A: Ovarian follicles are small fluid-filled sacs found within the ovaries that contain immature eggs.
Q: How many ovarian follicles are present at birth?
A: At birth, a female typically has around 1-2 million ovarian follicles.
Q: How many ovarian follicles mature and release eggs during a woman’s lifetime?
A: Out of the millions of ovarian follicles present at birth, only around 400-500 will mature and release eggs during a woman’s lifetime.
Q: What is the role of ovarian follicles in the menstrual cycle?
A: Ovarian follicles play a crucial role in the menstrual cycle by growing and maturing under the influence of hormones. One dominant follicle eventually releases a mature egg during ovulation.
Q: Can ovarian follicles be affected by medical conditions?
A: Yes, certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can disrupt the normal development and release of ovarian follicles.
Q: Are the size and number of ovarian follicles constant?
A: No, the size and number of ovarian follicles can fluctuate during different stages of a woman’s life. They decrease over time due to a natural aging process.
Q: Can ovarian follicles be measured or monitored?
A: Yes, healthcare professionals can measure ovarian follicles through ultrasound and monitor their growth and development.
Q: Are ovarian follicles important for fertility?
A: Yes, ovarian follicles are crucial for fertility as they house and release mature eggs necessary for conception.
Q: Can ovarian follicles be stimulated to enhance fertility?
A: Yes, in certain fertility treatments, medications can be used to stimulate the growth and development of ovarian follicles to increase the chances of pregnancy.
Q: Can the health of ovarian follicles impact reproductive health?
A: Yes, the health and quality of ovarian follicles can affect reproductive health and may impact the ability to conceive.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
