The hyoid bone, despite its small size and often-overlooked presence in the human body, holds great significance in the field of anatomy. Positioned at the base of the tongue, the hyoid bone plays a crucial role in the support and movement of various structures in the neck and throat. In addition to its functional importance, the hyoid bone has also fascinated scientists and researchers due to its unique characteristics and evolutionary history. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the hyoid bone, exploring its structure, functions, and intriguing facts that make it a subject of scientific curiosity. So, buckle up and get ready to uncover 11 fascinating facts about the hyoid bone!
Key Takeaways:
- The hyoid bone is the only bone in the human body that doesn’t connect to any other bone, allowing for flexibility in speaking and swallowing.
- This horseshoe-shaped bone supports speech production, forensic identification, and varies in shape and size among individuals, influencing speech patterns and swallowing abilities.
The hyoid bone is the only bone in the human body that does not articulate with any other bone.
Unlike other bones in the skeletal system that connect and form joints, the hyoid bone floats freely, suspended by muscles and ligaments. This allows for greater flexibility and movement, especially in the tongue and larynx.
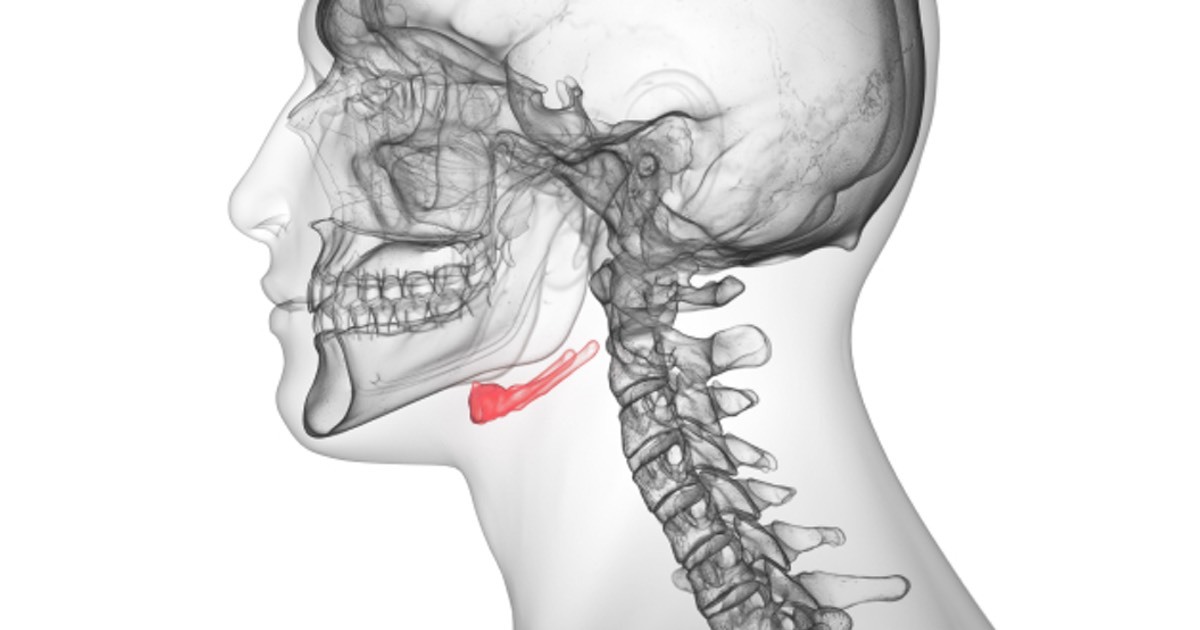
The hyoid bone is shaped like a horseshoe.
Resembling the shape of a horseshoe, the hyoid bone is curved with a body in the middle and two pairs of projections called horns. Its unique shape provides stability and support to the surrounding structures.
The hyoid bone is connected to multiple muscles.
The hyoid bone serves as an anchor point for various muscles in the neck and throat, including muscles involved in swallowing, speaking, and chewing. It acts as a platform for these muscles to move and coordinate their functions.
The hyoid bone is often used in forensic identification.
Due to its durability and uniqueness, the hyoid bone is often used in forensic investigations to establish the identity of a person. It can provide valuable information about a person’s age, sex, and even cause of death.
The hyoid bone develops during early childhood.
The hyoid bone starts as a pair of cartilaginous structures in infants and gradually fuses into a single bone during childhood. Its development is essential for the proper formation and functioning of the upper respiratory and digestive systems.
The hyoid bone is present in all mammals.
The hyoid bone is not unique to humans; it is found in all mammals. However, its structure and size may vary across different species. In some animals, such as dogs and horses, the hyoid bone is longer and more rigid.
The hyoid bone plays a significant role in speech production.
As a crucial component of the vocal apparatus, the hyoid bone helps in shaping and controlling the movements of the tongue, larynx, and other vocal structures. It contributes to the production of a wide range of sounds and speech patterns.
Injuries to the hyoid bone can occur in cases of strangulation.
Due to its position in the neck, the hyoid bone is vulnerable to injuries in cases of strangulation or severe trauma. Detecting fractures or damage to the hyoid bone can be crucial in forensic investigations and determining the cause of death.
The hyoid bone is used by some animals to produce sounds.
In certain animals, such as birds and frogs, the hyoid bone is used to produce unique sounds for communication and mating purposes. Its flexibility and ability to move independently allow for a diverse range of vocalizations.
The hyoid bone is located between the chin and the thyroid cartilage.
Positioned in the front of the neck, the hyoid bone sits between the mandible (lower jaw bone) and the thyroid cartilage (Adam’s apple). It acts as a central anchor point for several muscles and structures in this region.
The hyoid bone can vary in shape and size among individuals.
While the basic structure of the hyoid bone remains consistent, there can be variations in its shape and size among individuals. These differences can be influenced by genetic factors and can contribute to variations in speech patterns and swallowing abilities.
The hyoid bone may be small and often overlooked, but its functions and features are truly remarkable. From supporting speech production to aiding in forensic investigations, this fascinating bone plays a significant role in human anatomy. Understanding its unique characteristics deepens our appreciation for the intricate design of our bodies.
Conclusion
The hyoid bone is a small but fascinating part of the human anatomy. Despite its size, it plays a crucial role in supporting various functions within the body, including swallowing and speech. Its unique structure and position in the neck make it an intriguing subject of study for anatomists and medical professionals.Throughout this article, we have explored 11 fascinating facts about the hyoid bone. From its only bone that does not articulate with another bone in the body to its connections to the larynx and tongue, the hyoid bone’s significance cannot be understated. Understanding its anatomy and function can help us appreciate the complexity and marvel of the human body.Next time you swallow or speak, take a moment to appreciate the hyoid bone’s contribution to these everyday actions. It may be small, but it plays a big role in our lives.
FAQs
Q: What is the hyoid bone?
A: The hyoid bone is a U-shaped bone located in the neck, above the larynx and below the tongue. It is the only bone in the human body that does not directly articulate with another bone.
Q: What is the function of the hyoid bone?
A: The hyoid bone serves as a point of attachment for various muscles involved in swallowing and speech. It helps support the structure of the tongue and aids in the movement of the larynx.
Q: Can the hyoid bone be fractured?
A: Yes, the hyoid bone can be fractured, usually as a result of severe trauma or strangulation. However, hyoid bone fractures are relatively rare.
Q: Can the hyoid bone be used for forensic purposes?
A: Yes, the hyoid bone can be helpful in forensic investigations. Its fractures or abnormalities can provide valuable information about the cause and manner of death.
Q: Can you feel the hyoid bone in your neck?
A: The hyoid bone is not easily palpable, so most individuals cannot feel it from the outside. It is located deeper within the neck, nestled in the soft tissues.
Q: Can the hyoid bone change shape or position?
A: The hyoid bone is relatively stable and does not change shape or position under normal circumstances. However, certain medical conditions or injuries can lead to hyoid bone abnormalities.
Q: Are there any common medical conditions associated with the hyoid bone?
A: Certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea or dysphagia, can be related to the hyoid bone. A better understanding of the hyoid bone’s role in these conditions can aid in diagnosis and treatment.
Q: Does everyone have the same number of hyoid bones?
A: Yes, every individual typically has one hyoid bone. Unlike other bones that can vary in number (e.g., ribs), the hyoid bone remains consistent in all human beings.
Q: Can the hyoid bone change with age?
A: The hyoid bone does not undergo significant changes with age. However, it may become more prominent due to changes in surrounding structures, such as muscle atrophy or fat redistribution.
Q: Can you live without a hyoid bone?
A: Technically, it is possible to live without a hyoid bone. However, its absence would significantly impact functions such as swallowing and speech, making them difficult or impossible to perform properly.
Q: Can the hyoid bone provide insight into our ancestors?
A: Yes, examination of the hyoid bone can provide valuable information about the vocal capabilities and anatomical differences between modern humans and our early ancestors.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
