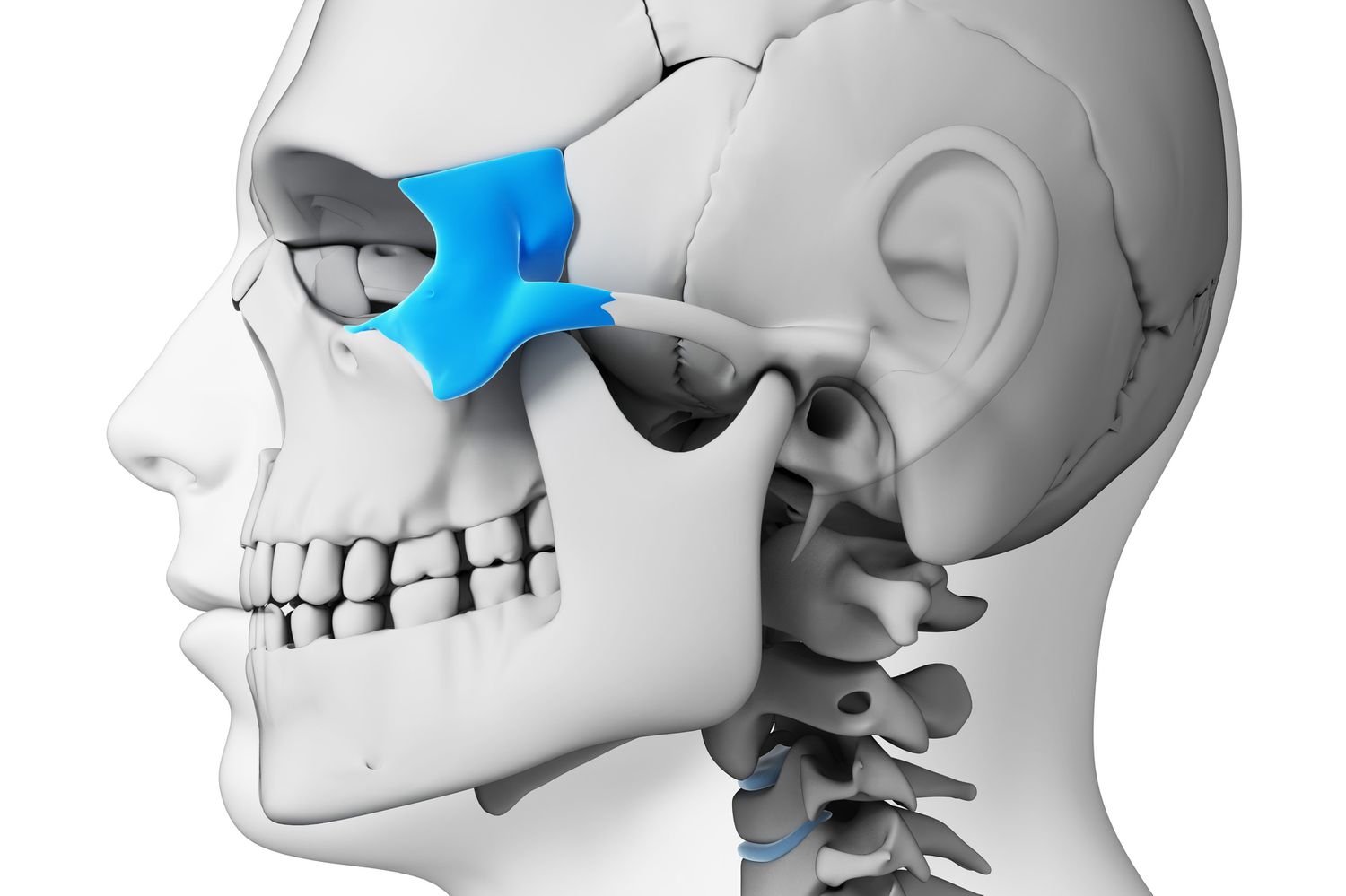
The zygomatic bone, also known as the cheekbone or malar bone, is a fascinating structure that plays a crucial role in our facial anatomy. Situated on each side of the face, the zygomatic bones contribute to the overall shape and structure of the face, while also protecting important underlying structures such as the eyes and the maxillary sinuses.
While it may seem like a small component of our anatomy, the zygomatic bone holds many intriguing secrets. In this article, we will uncover nine fascinating facts about the zygomatic bone, shedding light on its unique characteristics and functions. From its role in facial expressions to its connections with other facial bones, prepare to delve into the intricate world of the zygomatic bone.
Key Takeaways:
- The zygomatic bone protects the eyes and supports facial muscles, influencing facial structure and expressions. It’s crucial for facial stability and aesthetics.
- The zygomatic bone varies in shape and size, contributing to unique facial features across different ethnic groups. It plays a key role in facial development and expression.
The Zygomatic Bone Consists of Two Parts
The zygomatic bone is composed of two parts: the temporal process and the zygomatic arch. The temporal process connects with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch, while the body of the zygomatic bone contributes to the prominence of the cheek.
It Plays a Protective Role
The zygomatic bone not only defines the shape of the face but also provides protection for delicate structures such as the eyes. Its position, along with the surrounding bones, acts as a barrier against potential injuries to the eyes and other facial structures.
It Articulates with Multiple Bones
The zygomatic bone articulates with several other bones in the skull, including the frontal bone, maxillary bone, sphenoid bone, and temporal bone. These connections contribute to the overall stability and mobility of the facial skeleton.
It Supports Facial Muscles
The zygomatic bone provides attachment sites for important facial muscles, such as the masseter muscle, which is responsible for chewing. These muscles rely on the zygomatic bone for stability and efficient movement.
It influences Facial Structure
The prominent position of the zygomatic bone significantly affects the overall appearance of the face. Individuals with well-defined cheekbones often possess a more aesthetically pleasing and symmetrical facial structure.
It Can Be Affected by Trauma
Due to its location on the face, the zygomatic bone is susceptible to fractures resulting from facial trauma. These fractures can affect both the functional and aesthetic aspects of the face and may require medical intervention for proper healing.
It Contributes to Facial Expressions
The zygomatic bone plays a role in expressing emotions through facial expressions. When the zygomatic muscles contract, they elevate the corners of the mouth, creating a smile or happy expression.
It Develops from Multiple Embryonic Origins
The zygomatic bone has a complex embryological development. It arises from multiple embryonic origins, including neural crest cells and mesodermal cells, which migrate and contribute to its formation during early fetal development.
It Varies in Shape and Size
The size and shape of the zygomatic bone can vary among individuals and populations. These variations contribute to the unique facial features and characteristics seen across different ethnic groups.
These 9 intriguing facts about the zygomatic bone highlight its essential role in facial structure, protection, and expression. Understanding the importance of this bone enhances our knowledge of the intricate workings of human anatomy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the zygomatic bone is a fascinating and important component of the human anatomy. It plays a crucial role in our facial structure and provides protection for vital structures, such as the eye socket and the temporal bone. Understanding the anatomy and function of the zygomatic bone can provide valuable insight into various facial injuries and conditions.Through these 9 intriguing facts about the zygomatic bone, we have learned about its location, shape, and unique features. We have explored its role in facial symmetry, its anatomical variations, and its significance in forensics and anthropology.Whether you are a healthcare professional, a student, or simply curious about the human body, delving into the world of the zygomatic bone can deepen your understanding of facial anatomy and its remarkable intricacies.Remember, the zygomatic bone is just one piece of the complex puzzle that makes up the human body. Every bone, every muscle, and every organ works together to keep us functioning and alive. So, let’s continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the human anatomy.
FAQs
Q: What is the zygomatic bone?
A: The zygomatic bone, commonly known as the cheekbone, is a facial bone that forms part of the orbit (eye socket) and the prominence of the cheek.
Q: How many zygomatic bones are there in the human skull?
A: There are two zygomatic bones in the human skull, one on each side of the face, forming the cheekbones.
Q: Why is the zygomatic bone important?
A: The zygomatic bone is important as it provides structural support to the midface, contributes to facial symmetry, and protects vital structures, including the eye socket.
Q: Can the zygomatic bone be fractured?
A: Yes, the zygomatic bone can be fractured due to trauma, such as facial injuries or accidents. These fractures may require medical intervention depending on their severity.
Q: Are there any variations in the shape of the zygomatic bone?
A: Yes, there can be variations in the size and shape of the zygomatic bone among individuals. These anatomical variations are normal and contribute to the unique characteristics of each person’s face.
Q: Can the zygomatic bone affect facial appearance?
A: Yes, the zygomatic bone plays a significant role in facial appearance. Its prominence and position contribute to the overall structure and symmetry of the face.
Q: How does the zygomatic bone play a role in forensic anthropology?
A: The zygomatic bone, along with other craniofacial features, is studied in forensic anthropology to determine the age, sex, and ancestry of skeletal remains in criminal investigations or archaeological discoveries.
Q: Is there any specific care needed for the zygomatic bone?
A: The zygomatic bone does not require specific care unless it is fractured or injured. In such cases, medical attention may be necessary to ensure proper healing.
Q: Can the zygomatic bone be affected by diseases?
A: Yes, like any other bone in the body, the zygomatic bone can be affected by diseases such as tumors or infections. These conditions may require specialized treatment.
The zygomatic bone, a crucial component of the facial skeleton, plays a significant role in protecting vital structures and shaping our unique appearances. Delving deeper into the intricacies of the human skull reveals even more fascinating facts about this complex structure. Beyond the skull lies the skeletal system, a remarkable framework that supports and protects our bodies. Aspiring medical professionals and curious learners alike can benefit from exploring anatomy and physiology, gaining valuable insights into the intricate workings of the human body.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.