The human body is a marvel of complexity, and its intricate design never ceases to amaze us. Among the numerous bones that make up our skeleton, one bone stands out for its unique shape and location – the vomer bone. The vomer bone, also known as the plowshare bone, is a thin, flat bone located in the nasal cavity. While it may seem like a small and insignificant bone, the vomer bone plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of our nasal passageways. In this article, we will explore 19 astounding facts about the vomer bone, shedding light on its importance and highlighting its fascinating attributes. So let’s dive into the world of anatomy and discover the wonders of the vomer bone!
Key Takeaways:
- The Vomer bone, also known as the “plowshare” bone, is a small but crucial part of the human skull, helping to regulate nasal airflow and support the sense of smell.
- Its unique shape and role in the nasal cavity make the Vomer bone an essential component of the human anatomy, contributing to our ability to breathe and produce sound.
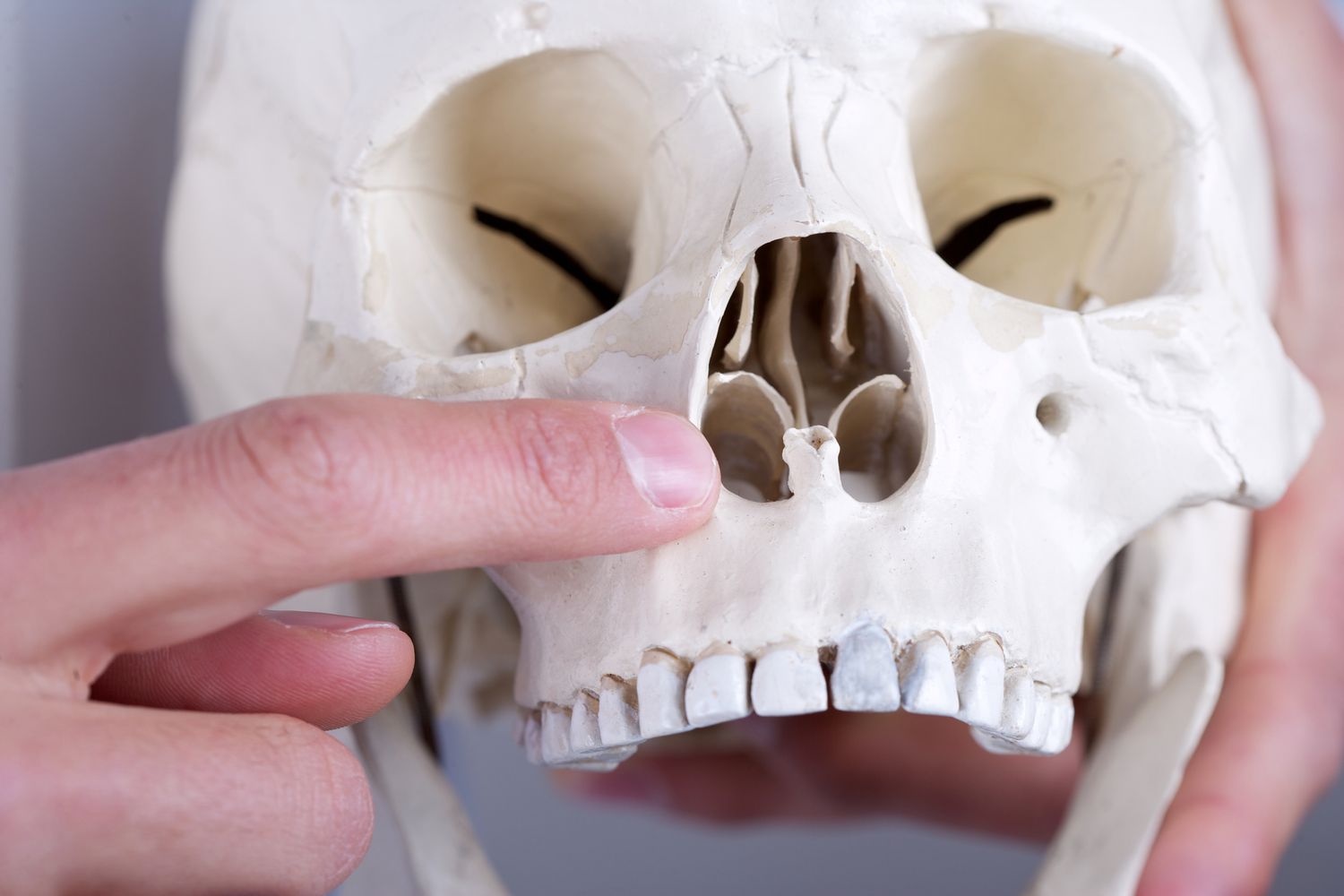
The Vomer bone is located in the human skull.
The Vomer bone is a small, flat bone that forms part of the nasal septum, which separates the left and right nasal cavities.
It is commonly referred to as the “plowshare” bone.
The Vomer bone gets its nickname from its shape, which resembles a plowshare used in agricultural farming.
The Vomer bone plays a crucial role in nasal airflow.
As part of the nasal septum, the Vomer bone helps to direct and regulate the flow of air as we breathe through our nose.
It is one of the smallest bones in the skull.
Measuring only about two inches in length, the Vomer bone is relatively small compared to other bones in the skull.
The Vomer bone is singular and symmetrical.
Unlike many other bones in the body, the Vomer bone is singular, meaning there is only one of it in the skull, and it is symmetrical in shape.
The Vomer bone is made up of spongy bone tissue.
Inside the dense outer layer of the Vomer bone, there is a honeycomb-like structure made up of spongy bone tissue.
It is connected to other bones of the skull through sutures.
The Vomer bone articulates with several other bones in the skull through sutures, including the ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary bones.
The Vomer bone is involved in the sense of smell.
It helps to support and protect the olfactory epithelium, which contains the specialized cells responsible for the sense of smell.
The Vomer bone can vary in shape and size among individuals.
While it generally has a plowshare shape, the size and exact contours of the Vomer bone can vary slightly among different individuals.
It is derived from embryonic mesenchymal tissue.
The Vomer bone, like other bones in the skull, develops from mesenchymal tissue during embryonic development.
The Vomer bone is part of the facial skeleton.
Along with other bones like the maxilla and mandible, the Vomer bone contributes to the structure and support of the facial skeleton.
It can be affected by certain medical conditions.
Medical conditions such as nasal septal deviations or fractures can impact the position and function of the Vomer bone.
The Vomer bone aids in the production of sound.
By helping to shape the nasal cavity, the Vomer bone contributes to the resonance and quality of our voice when speaking or singing.
It is named after its resemblance to a plowshare.
The term “Vomer” is derived from the Latin word for plowshare, further emphasizing the bone’s characteristic shape.
The Vomer bone is present in both humans and some animals.
While the shape and size may differ, the Vomer bone exists in other mammals as well, serving a similar function in the nasal cavity.
It is often used in forensic anthropology.
Due to its unique shape and position, the Vomer bone can be utilized in identifying human remains in forensic investigations.
The Vomer bone can be affected by age-related changes.
As we age, the Vomer bone may undergo changes in its density and structure, similar to other bones in the body.
It provides stability to the nasal septum.
Together with other structures, the Vomer bone helps to maintain the stability and integrity of the nasal septum, preventing it from collapsing or shifting.
The Vomer bone is an essential component of the human anatomy.
Without the Vomer bone, our nasal passages would not be properly separated, affecting our breathing and the overall function of the respiratory system.
These 19 astounding facts about the Vomer bone shed light on its vital role in the human anatomy. From its unique shape and connection to other bones in the skull, to its involvement in nasal airflow and the sense of smell, the Vomer bone is truly a remarkable structure. Understanding its anatomy and functions helps us appreciate the complexity and intricacy of the human body.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the vomer bone is a remarkable and often overlooked component of the human anatomy. It plays a critical role in the structure and function of the nasal cavity, aiding in breathing and speech production. Its unique shape and location make it an interesting bone to study and understand. From its formation during fetal development to its role in facial symmetry and its function in the resonance of sound, the vomer bone holds many intriguing secrets. Exploring and appreciating the wonders of the vomer bone helps us gain a deeper understanding of the complexity and marvels of the human body.
FAQs
1. What is the vomer bone?
The vomer bone is a thin, flat bone located in the midline of the nasal cavity, separating the left and right sides.
2. What is the function of the vomer bone?
The primary function of the vomer bone is to provide structural support to the nasal septum and aid in the passage of air through the nasal cavity.
3. How is the vomer bone formed?
The vomer bone is formed through a process called intramembranous ossification, where mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts, which then deposit bone tissue.
4. Does the vomer bone have any other roles besides supporting the nasal cavity?
Yes, the vomer bone also plays a role in maintaining facial symmetry and is involved in the resonance of sound during speech.
5. Can the vomer bone be damaged or fractured?
Yes, the vomer bone can be fractured due to trauma or injury. However, it is one of the less commonly fractured bones in the body.
6. Can the vomer bone be affected by certain medical conditions?
Yes, certain conditions such as deviated nasal septum or cleft palate can affect the positioning and function of the vomer bone.
7. Can the vomer bone be surgically altered or corrected?
Yes, in cases where the vomer bone is causing breathing difficulties or other issues, surgical procedures such as septoplasty or rhinoplasty may be performed to correct and realign the bone.
8. Are there any notable variations or anomalies associated with the vomer bone?
Yes, variations in the shape, size, and position of the vomer bone can occur, but they are relatively rare and may not necessarily cause any functional problems.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
