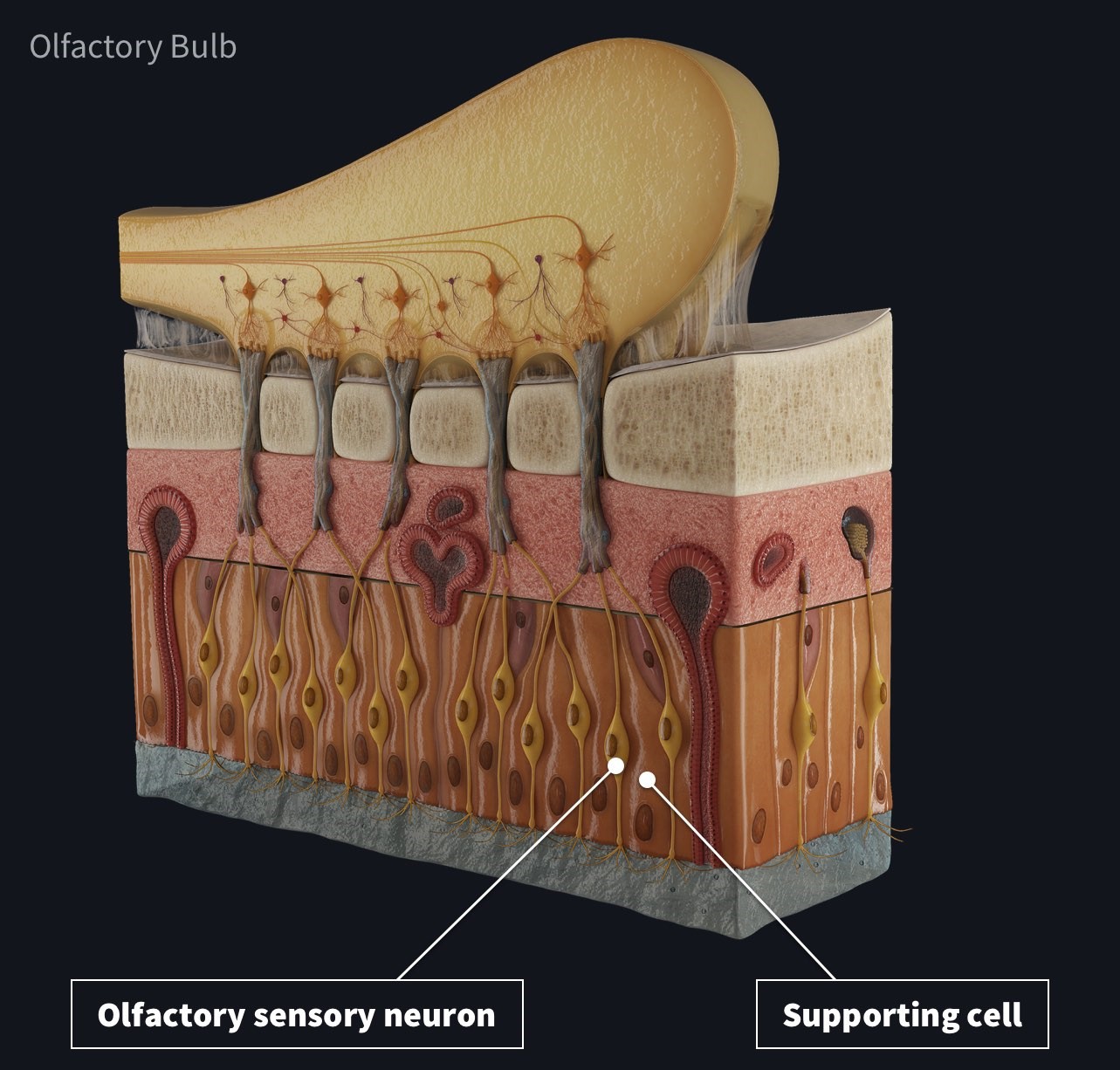
The olfactory epithelium is an intriguing and complex part of the human anatomy that is often overlooked and underappreciated. Located in the upper part of the nasal cavity, this specialized tissue is responsible for our sense of smell. But did you know that the olfactory epithelium has many more fascinating features that make it truly enigmatic? In this article, we will explore 18 intriguing facts about the olfactory epithelium that will not only expand your knowledge but also leave you in awe of the intricate workings of our sense of smell. From its unique cellular composition to its role in memory formation, the olfactory epithelium is a marvel of the human body that deserves our attention. So, let’s dive into the world of olfaction and unravel the mysteries of the olfactory epithelium.
Key Takeaways:
- The olfactory epithelium is a fascinating gateway to our sense of smell, allowing us to detect thousands of scents and even triggering memories and emotions associated with them.
- The olfactory epithelium is not only essential for our sense of smell but also plays a role in taste perception, social communication, and even potential disease detection.
The Olfactory Epithelium: A Gateway to Smell
The olfactory epithelium is a specialized tissue in the nasal cavity responsible for detecting and perceiving different odors. It acts as a gateway, allowing smell molecules to enter and interact with the receptors in our nose.
Unique Cell Types in the Olfactory Epithelium
The olfactory epithelium consists of several unique cell types, including olfactory receptor neurons, supporting cells, and basal cells. Each cell type plays a crucial role in the sense of smell, ensuring its proper functioning.
Regeneration of Olfactory Receptor Neurons
Unlike most neurons in the body, olfactory receptor neurons have the unique ability to regenerate throughout our lives. This constant renewal ensures the maintenance of our sense of smell, even after damage or loss.
The Power of Olfaction
Olfaction, or the sense of smell, is closely related to our memories and emotions. The olfactory epithelium plays a vital role in triggering these memories and eliciting emotional responses to various scents.
Superhuman Sense of Smell
Some individuals possess an extraordinary sense of smell, a condition known as hyperosmia. This heightened olfactory perception allows them to detect and differentiate scents that may be indistinguishable to others.
Role in Taste Perception
The olfactory epithelium also contributes to our sense of taste. The combination of smell and taste enhances our ability to differentiate flavors and enjoy various culinary experiences.
Olfactory Nerve Pathway
The olfactory epithelium sends signals to the brain through the olfactory nerve pathway. This pathway is responsible for carrying smell information to the olfactory bulb and eventually to different regions of the brain that process and interpret smells.
Sensitivity to Odorants
The olfactory epithelium can detect and differentiate between thousands of different odorants. Its remarkable sensitivity allows us to discern even the most subtle scents in our environment.
Role in Social Communication
Our sense of smell, influenced by the olfactory epithelium, plays a significant role in social communication. It enables us to detect pheromones, chemical signals that convey information about an individual’s reproductive status, emotions, and more.
The Role of Olfactory Epithelium in Disease Detection
The olfactory epithelium’s ability to detect and discriminate smells makes it a potential tool for disease detection. Research suggests that changes in smell perception could serve as an early indicator of certain neurological disorders and other health conditions.
Gender Differences in Olfactory Sensitivity
Studies have shown that women tend to have a more sensitive sense of smell compared to men, partially due to hormonal differences. This variation in olfactory sensitivity is influenced by the olfactory epithelium’s intricate mechanism.
Development and Maturation of the Olfactory Epithelium
The olfactory epithelium undergoes continuous development and maturation from embryonic stages through adulthood. This dynamic process ensures the proper functioning of the olfactory system and our ability to perceive smells.
Olfactory Epithelium and Age-related Changes
As we age, the olfactory epithelium may undergo certain changes, leading to a decline in our sense of smell. This age-related decrease in olfactory function can affect our overall quality of life and well-being.
The Connection Between Olfactory Epithelium and Mental Health
Research has suggested a link between the olfactory epithelium and mental health. Olfactory dysfunction, resulting from changes in the olfactory epithelium, has been associated with conditions such as depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative disorders.
The Role of Olfactory Epithelium in Animal Behavior
The olfactory epithelium plays a crucial role in animal behavior, including mating, territory marking, and identification of prey or predators. It serves as a primary sensory organ to help animals navigate and survive in their environment.
Olfactory Epithelium and Genetic Variations
Genetic variations and mutations can impact the structure and function of the olfactory epithelium, leading to differences in smell perception among individuals. These genetic factors contribute to the unique olfactory experiences we all have.
Olfactory Epithelium and Allergies
Individuals with allergies may experience inflammation and irritation of the olfactory epithelium, causing temporary or long-term disruptions in their sense of smell. Understanding these effects can help in managing allergy-related symptoms.
Olfactory Epithelium and Olfactory Training
Olfactory training, a practice that involves exposing the olfactory epithelium to specific smells regularly, has been shown to improve smell perception in individuals with olfactory dysfunction. This technique harnesses the plasticity of the olfactory system and promotes its recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the olfactory epithelium is a fascinating component of the human anatomy that plays a crucial role in our sense of smell. Its unique structure and specialized nerve cells allow us to detect and distinguish various odors, leading to rich sensory experiences and even triggering memories and emotions.
Understanding the enigmatic facts about the olfactory epithelium helps us appreciate the complexities of our sense of smell and the intricate workings of the human body. From its ability to regenerate throughout our lifetime to its role in detecting pheromones, the olfactory epithelium continues to be an intriguing area of study for researchers.
By delving deeper into the workings of the olfactory epithelium, we can gain insights into the fascinating world of scent perception and its impact on our overall well-being. As we continue to unlock the mysteries of the olfactory epithelium, we open doors to potential advancements in diagnosing and treating conditions related to smell disorders.
FAQs
Q: What is the olfactory epithelium?
A: The olfactory epithelium is a specialized tissue located in the upper part of the nasal cavity, responsible for detecting and processing odors.
Q: How does the olfactory epithelium work?
A: The olfactory epithelium contains millions of olfactory receptor cells that detect specific odor molecules and transmit signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive different scents.
Q: Can the olfactory epithelium regenerate?
A: Yes, the olfactory epithelium has the remarkable ability to regenerate throughout our lifetime, ensuring the continuous function of our sense of smell.
Q: What is the role of the olfactory epithelium in our sense of taste?
A: The olfactory epithelium plays a significant role in our sense of taste by contributing to our ability to detect flavors. Smell and taste are closely linked, with the olfactory epithelium enhancing the overall taste experience.
Q: Do humans have different sensitivities to smells?
A: Yes, individuals can have varying sensitivities to smells due to differences in their olfactory epithelium’s structure and function. Some people may have a heightened sense of smell, while others may have a less acute sense of smell.
Q: What are pheromones, and how does the olfactory epithelium detect them?
A: Pheromones are chemical substances secreted by animals to communicate with others of the same species. The olfactory epithelium contains specialized receptors that can detect and respond to these pheromones, influencing behavior and social interactions.
Q: Can damage to the olfactory epithelium affect sense of smell?
A: Yes, damage to the olfactory epithelium can impair or even lead to a loss of the sense of smell, known as anosmia. It can result from various factors, including injuries, infections, and certain medical conditions.
Q: Can the olfactory epithelium be a target for therapies or treatments?
A: Yes, understanding the olfactory epithelium’s functions and regenerative abilities opens up possibilities for potential therapies or treatments for smell-related disorders. Research in this area continues to explore methods to restore or enhance the sense of smell.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
